Abstract
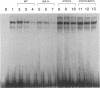
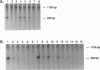
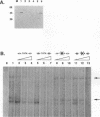
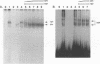
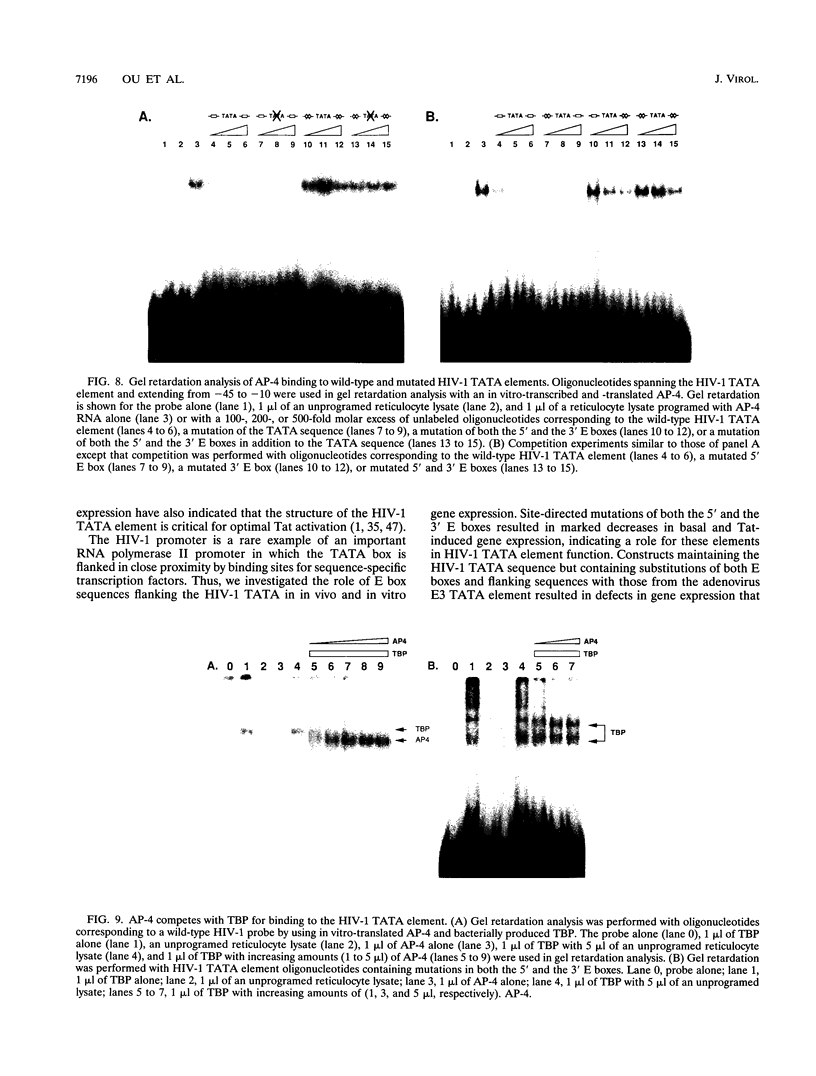
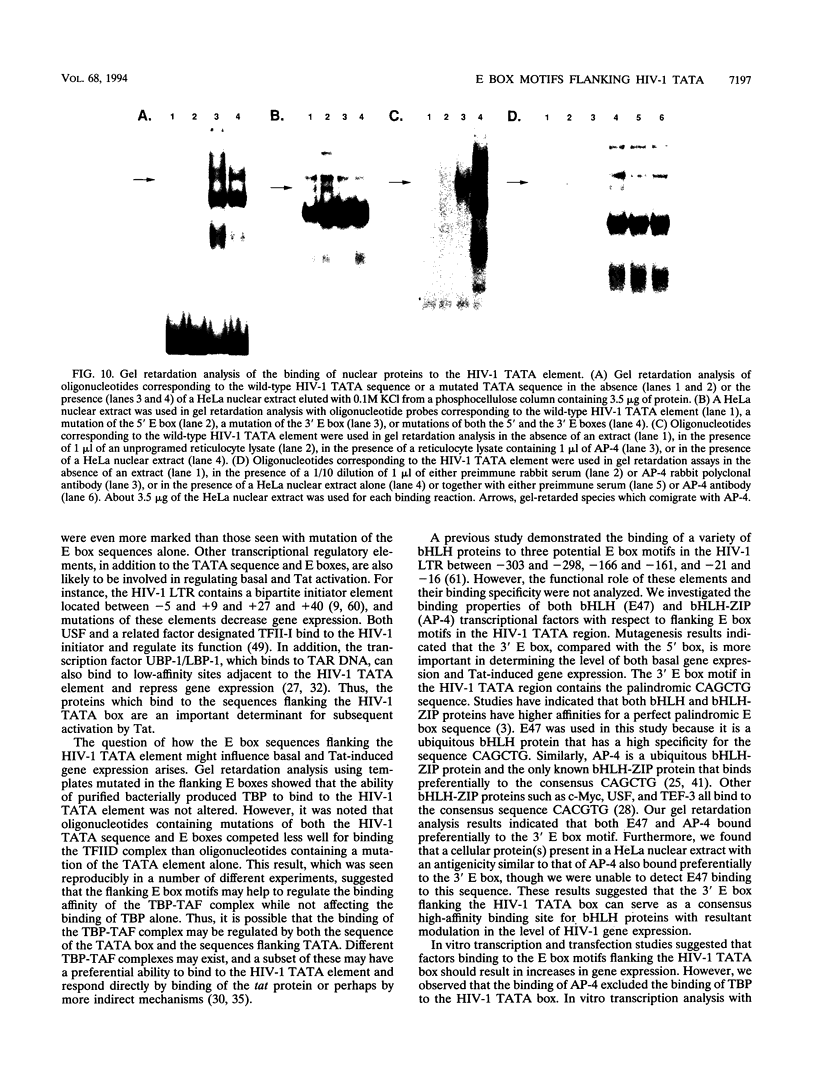
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gene expression is dependent on a number of cis-acting DNA elements present in the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. Previous studies have demonstrated that the TATA element is critical for basal and Tat-induced HIV-1 gene expression. The HIV-1 TATA region has an unusual structure in that the TATA sequence is flanked by two palindromic sequence motifs (CANNTG) known as E boxes which can serve as binding sites for the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) class of DNA-binding proteins. In this study, we performed site-directed mutagenesis of both the TATA and the flanking E box sequences of HIV-1. We also substituted the sequences flanking the adenovirus E3 promoter TATA sequence for those flanking the HIV-1 TATA sequence. Constructs were assayed for their levels of basal and Tat-induced gene expression by both in vitro transcription and transient expression assays. Both the TATA box and flanking sequences including the E box motifs were found to be important in modulating both basal gene expression and Tat-induced HIV-1 gene expression. Gel retardation analysis demonstrated that binding of both the recombinant TATA-binding protein (TBP) and the TFIID fraction which contains both TBP and TBP-associated factors was dependent primarily on the TATA element. However, competition analysis suggested that the E boxes may play a role in stabilizing the binding of TFIID but not recombinant TBP. Two proteins representing different classes of bHLH proteins, E47 and AP-4, were assayed for their ability to bind to the flanking E box motifs. We isolated a cDNA clone encoding the complete AP-4 protein and demonstrated that both AP-4 and E47 bound specifically to the 3' E box motif, which contains sequences that correspond to the consensus binding site (CAGCTG). Gel retardation analysis indicated that the binding of AP-4 to the E boxes excluded the binding of TBP to the TATA box. These studies are consistent with a model in which different classes of cellular bHLH proteins may be involved in regulating HIV-1 TATA element function by either inhibiting or promoting the assembly of different preinitiation transcriptional complexes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. Functional roles for the TATA promoter and enhancers in basal and Tat-induced expression of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):139–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.139-149.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Chakraborty T., Olson E. N. Mutagenesis of the myogenin basic region identifies an ancient protein motif critical for activation of myogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5675–5679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C. M., Ge H., Wang Z., Hoffmann A., Roeder R. G. Unique TATA-binding protein-containing complexes and cofactors involved in transcription by RNA polymerases II and III. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2749–2762. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05936.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostatni N., Lambert P. F., Sousa R., Ham J., Howley P. M., Yaniv M. The functional BPV-1 E2 trans-activating protein can act as a repressor by preventing formation of the initiation complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1657–1671. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du H., Roy A. L., Roeder R. G. Human transcription factor USF stimulates transcription through the initiator elements of the HIV-1 and the Ad-ML promoters. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):501–511. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05682.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elroy-Stein O., Fuerst T. R., Moss B. Cap-independent translation of mRNA conferred by encephalomyocarditis virus 5' sequence improves the performance of the vaccinia virus/bacteriophage T7 hybrid expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6126–6130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D., Frankel A. D. The role of Tat in the human immunodeficiency virus life cycle indicates a primary effect on transcriptional elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré-D'Amaré A. R., Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B., Burley S. K. Recognition by Max of its cognate DNA through a dimeric b/HLH/Z domain. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):38–45. doi: 10.1038/363038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Harrich D., Pearson L., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Functional domains required for tat-induced transcriptional activation of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3143–3147. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Harrich D., Soultanakis E., Wu F., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 LTR TATA and TAR region sequences required for transcriptional regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):765–778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. Cellular transcription factors involved in the regulation of HIV-1 gene expression. AIDS. 1992 Apr;6(4):347–363. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199204000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeble M. A., Churcher M. J., Lowe A. D., Gait M. J., Karn J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transactivator protein, tat, stimulates transcriptional read-through of distal terminator sequences in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6184–6188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. Roles of TFIID in transcriptional initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90027-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Garcia J., Wu F., Mitsuyasu R., Gonazalez J., Gaynor R. Role of SP1-binding domains in in vivo transcriptional regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2585–2591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2585-2591.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Weinzierl R. O., Gill G., Chen J. L., Dynlacht B. D., Tjian R. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of Drosophila TAF110 reveal properties expected of coactivators. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90664-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H. L., Wadman I., Baer R. Formation of in vivo complexes between the TAL1 and E2A polypeptides of leukemic T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3181–3185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. F., Lüscher B., Admon A., Mermod N., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-4 contains multiple dimerization domains that regulate dimer specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1741–1752. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Luciw P. A., Duchange N. Structural arrangements of transcription control domains within the 5'-untranslated leader regions of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 promoters. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1101–1114. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. Consequences of heteromeric interactions among helix-loop-helix proteins. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Jan;4(1):49–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Murre C., Sun X. H., Baltimore D. A new homeobox gene contributes the DNA binding domain of the t(1;19) translocation protein in pre-B ALL. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. Y., Calman A. F., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Anti-termination of transcription within the long terminal repeat of HIV-1 by tat gene product. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):489–493. doi: 10.1038/330489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Repression of HIV-1 transcription by a cellular protein. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1476–1479. doi: 10.1126/science.2006421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornuc M., Kliewer S., Garcia J., Harrich D., Li C., Gaynor R. Adenovirus early region 3 promoter regulation by E1A/E1B is independent of alterations in DNA binding and gene activation of CREB/ATF and AP1. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2004–2013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2004-2013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. HIV-1 Tat protein increases transcriptional initiation and stabilizes elongation. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Welsh T. M., Peterlin B. M. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat specifies two different transcription complexes, only one of which is regulated by Tat. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1752–1760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1752-1760.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y., Stenzel M., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Effects of long terminal repeat mutations on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4115–4119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4115-4119.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Calnan B. J., Frankel A. D., Sharp P. A. HIV-1 Tat protein trans-activates transcription in vitro. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):791–802. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Sharp P. A. HIV-1 Tat protein promotes formation of more-processive elongation complexes. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4189–4196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Roeder R. G. Family of proteins that interact with TFIID and regulate promoter activity. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90530-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Williams T. J., Tjian R. Enhancer binding factors AP-4 and AP-1 act in concert to activate SV40 late transcription in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):557–561. doi: 10.1038/332557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen H. S., Rosen C. A. Contribution of the TATA motif to Tat-mediated transcriptional activation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5594–5597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5594-5597.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA binding protein. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.2363050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W. Three in one and one in three: it all depends on TBP. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90042-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Fisch T. M., Benecke B. J., Nevins J. R., Heintz N. Definition of multiple, functionally distinct TATA elements, one of which is a target in the hsp70 promoter for E1A regulation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):723–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. An inhibitory domain of E12 transcription factor prevents DNA binding in E12 homodimers but not in E12 heterodimers. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90653-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Baltimore D. Id proteins Id1 and Id2 selectively inhibit DNA binding by one class of helix-loop-helix proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5603–5611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wefald F. C., Devlin B. H., Williams R. S. Functional heterogeneity of mammalian TATA-box sequences revealed by interaction with a cell-specific enhancer. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):260–262. doi: 10.1038/344260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinzierl R. O., Dynlacht B. D., Tjian R. Largest subunit of Drosophila transcription factor IID directs assembly of a complex containing TBP and a coactivator. Nature. 1993 Apr 8;362(6420):511–517. doi: 10.1038/362511a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley S. R., Kraus R. J., Mertz J. E. Functional binding of the "TATA" box binding component of transcription factor TFIID to the -30 region of TATA-less promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5814–5818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F., Garcia J., Sigman D., Gaynor R. tat regulates binding of the human immunodeficiency virus trans-activating region RNA loop-binding protein TRP-185. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2128–2140. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Advances in RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):488–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenzie-Gregory B., Sheridan P., Jones K. A., Smale S. T. HIV-1 core promoter lacks a simple initiator element but contains a bipartite activator at the transcription start site. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15823–15832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Doyle K., Bina M. Interactions of HTF4 with E-box motifs in the long terminal repeat of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5631–5634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5631-5634.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Lieberman P. M., Boyer T. G., Berk A. J. Holo-TFIID supports transcriptional stimulation by diverse activators and from a TATA-less promoter. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1964–1974. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]