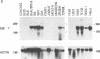Abstract
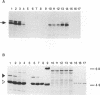
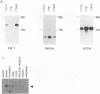
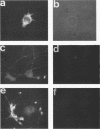
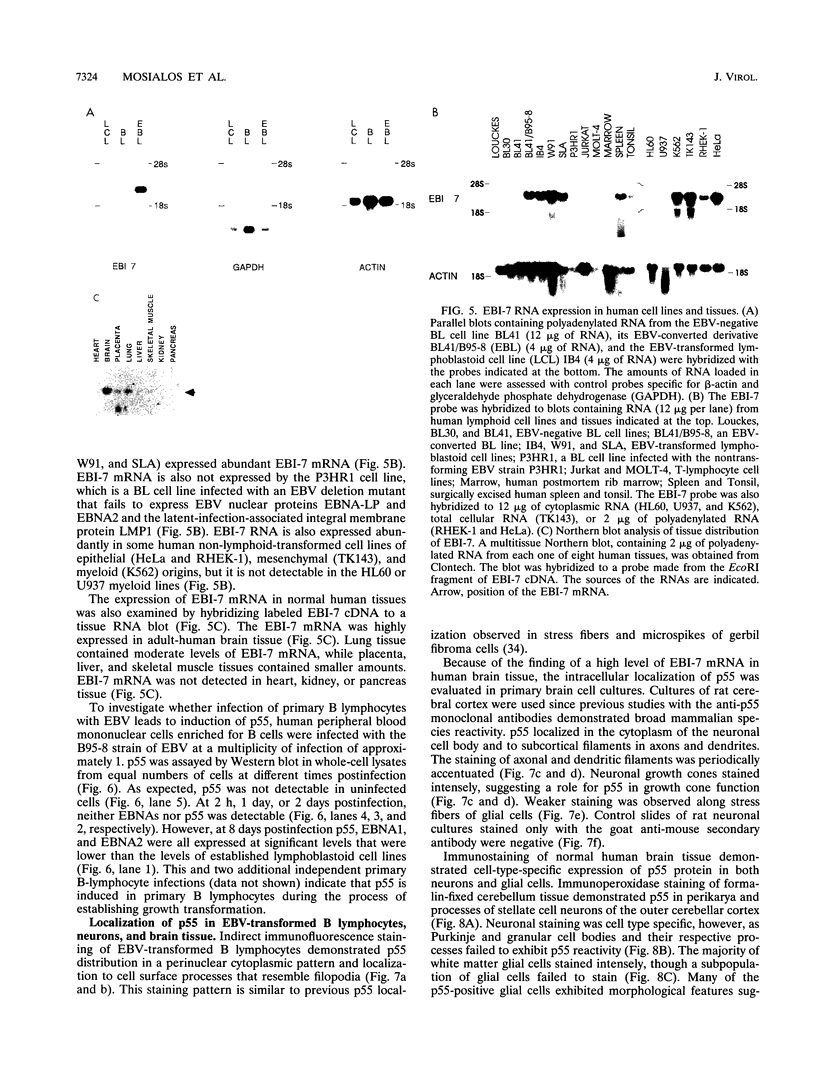
A novel human mRNA whose expression is induced over 200-fold in B lymphocytes by latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection was reverse transcribed, cloned, and sequenced. The mRNA is predicted to encode a protein containing four peptides which precisely match amino acid sequences from a previously identified 55-kDa actin-bundling protein, p55. In vitro translation of the cDNA results in a 55-kDa protein which binds to actin filaments in the presence of purified p55 from HeLa cells. The p55 mRNA is undetectable in non-EBV-infected B- and T-cell lines or in a myelomonocytic cell line (U937). Newly infected primary human B lymphocytes, EBV-transformed B-cell lines, latently infected Burkitt tumor cells expressing EBNA2 and LMP1, a chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line (K562), and an osteosarcoma cell line (TK143) contain high levels of p55 mRNA or protein. In EBV-transformed B cells, p55 localizes to perinuclear cytoplasm and to cell surface processes that resemble filopodia. The p55 mRNA is detected at high levels in spleen and brain tissues, at moderate levels in lung and placenta tissues, and at low levels in skeletal muscle, liver, and tonsil tissues and is undetectable in heart, kidney, pancreas, and bone marrow tissues. Immunohistochemical staining of human brain tissue demonstrates p55 localization to the perinuclear cytoplasm and dendritic processes of many, but not all, types of cortical or cerebellar neurons, to glial cells, and to capillary endothelial cells. In cultured primary rat neurons, p55 is distributed throughout the perinuclear cytoplasm and in subcortical filamentous structures of dendrites and growth cones. p55 is highly evolutionarily conserved since it shows 40% amino acid sequence identity to the Drosophila singed gene product and 37% identity to fascin, an echinoderm actin-bundling protein. The evolutionary conservation of p55 and its lack of extensive homology to other actin-binding proteins suggest that p55 has specific microfilament-associated functions in cells in which it is differentially expressed, including neural cells and EBV-transformed B lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Dubnick M., Kerlavage A. R., Moreno R., Kelley J. M., Utterback T. R., Nagle J. W., Fields C., Venter J. C. Sequence identification of 2,375 human brain genes. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):632–634. doi: 10.1038/355632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams M. D., Kelley J. M., Gocayne J. D., Dubnick M., Polymeropoulos M. H., Xiao H., Merril C. R., Wu A., Olde B., Moreno R. F. Complementary DNA sequencing: expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1651–1656. doi: 10.1126/science.2047873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aderem A. The MARCKS brothers: a family of protein kinase C substrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90546-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenbach M., Josefsen K., Yalamanchili R., Lenoir G., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus-induced genes: first lymphocyte-specific G protein-coupled peptide receptors. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2209–2220. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2209-2220.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenbach M., Liebowitz D., Wang F., Sample J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein increases vimentin expression in human B-cell lines. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4079–4084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4079-4084.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Edwards R., Matsudaira P., Otto J., Wulfkuhle J. Fascin, an echinoid actin-bundling protein, is a homolog of the Drosophila singed gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9115–9119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Zimber U., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Banchereau J., Tursz T., Bornkamm G., Lenoir G. M. Stable transfection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2 in lymphoma cells containing the EBV P3HR1 genome induces expression of B-cell activation molecules CD21 and CD23. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1002–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1002-1013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friederich E., Vancompernolle K., Huet C., Goethals M., Finidori J., Vandekerckhove J., Louvard D. An actin-binding site containing a conserved motif of charged amino acid residues is essential for the morphogenic effect of villin. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90535-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutzeit H. O. The role of microfilaments in cytoplasmic streaming in Drosophila follicles. J Cell Sci. 1986 Feb;80:159–169. doi: 10.1242/jcs.80.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Rowe M., Gregory C., Croom-Carter D., Wang F., Longnecker R., Kieff E., Rickinson A. Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90007-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C. The level of c-fgr RNA is increased by EBNA-2, an Epstein-Barr virus gene required for B-cell immortalization. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2530–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2530-2536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiri K. F., Gordon-Weeks P. R. GAP-43 in growth cones is associated with areas of membrane that are tightly bound to substrate and is a component of a membrane skeleton subcellular fraction. J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;10(1):256–266. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-01-00256.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overton J. The fine structure of developing bristles in wild type and mutant Drosophila melanogaster. J Morphol. 1967 Aug;122(4):367–379. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051220406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson J., O'Hare K. Structure and transcription of the singed locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1991 Dec;129(4):1073–1084. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.4.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrimon N., Gans M. Clonal analysis of the tissue specificity of recessive female-sterile mutations of Drosophila melanogaster using a dominant female-sterile mutation Fs(1)K1237. Dev Biol. 1983 Dec;100(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson E. S., Tomkinson B., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus with a 58-kilobase-pair deletion that includes BARF0 transforms B lymphocytes in vitro. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1449–1458. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1449-1458.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen A., Keenan K. F., Thelen M., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. Activation of protein kinase C results in the displacement of its myristoylated, alanine-rich substrate from punctate structures in macrophage filopodia. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1211–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Graff J. M., Albert K. A., Greengard P., Blackshear P. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and expression of a cDNA encoding the "80- to 87-kDa" myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate: a major cellular substrate for protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4012–4016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson B., Robertson E., Yalamanchili R., Longnecker R., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus recombinants from overlapping cosmid fragments. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7298–7306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7298-7306.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Wang F., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Larson R., Springer T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4173–4184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4173-4184.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C., Sample C., Rowe M., Liebowitz D., Murray R., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2309–2318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2309-2318.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Tsang S. F., Kurilla M. G., Cohen J. I., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates latent membrane protein LMP1. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3407–3416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3407-3416.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro-Matsumura S., Matsumura F. Intracellular localization of the 55-kD actin-bundling protein in cultured cells: spatial relationships with actin, alpha-actinin, tropomyosin, and fimbrin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):631–640. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro-Matsumura S., Matsumura F. Purification and characterization of an F-actin-bundling 55-kilodalton protein from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5087–5097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., Goodman D. W., Karns L. R., Fishman M. C. The neuronal growth-associated protein GAP-43 induces filopodia in non-neuronal cells. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1193–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.2658062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]