Abstract
Expression of alpha interferon (IFN-alpha)-, IFN-beta-, and IFN-alpha/beta-induced genes was monitored during the development of lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) to assess whether a restricted influence of these antiviral cytokines could be found in the central nervous system (CNS). High levels of IFN-alpha (83 +/- 42 U/ml) were present in the blood of LCM virus-infected mice 3 days postinfection, whereas IFN-beta was not detected (< 1.0 U/ml) at any time point. Spleens contained high levels of IFN-alpha and IFN-beta mRNAs at days 1 and 3 postinfection, whereas no IFN-alpha mRNA and only low levels of IFN-beta mRNA were detected in brains. In situ hybridization showed IFN-alpha mRNA-expressing cells in the marginal zones of the spleen and in the subcapsular sinus and outer cortex of cervical lymph nodes. The expression of 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase (2',5'-OAS) mRNA followed the expression of IFN-beta mRNA in the brain, whereas 2',5'-OAS mRNA in the periphery was associated with systemic IFN-alpha. The localization of IFN-alpha-expressing cells in the spleen and lymph nodes in proximity to T- and B-cell compartments is consistent with a role for these cytokines in immune regulation. Furthermore, the absence of IFN-alpha and the relatively low level and delayed expression of IFN-beta in the brain suggest that the CNS is an especially vulnerable organ for virus replication. With certain strains of LCM virus, the absence of early antiviral IFN-alpha/beta activity and preferential virus growth in the brain might lead to targeted T-cell inflammation of the CNS, resulting in death of the animal.
Full text
PDF

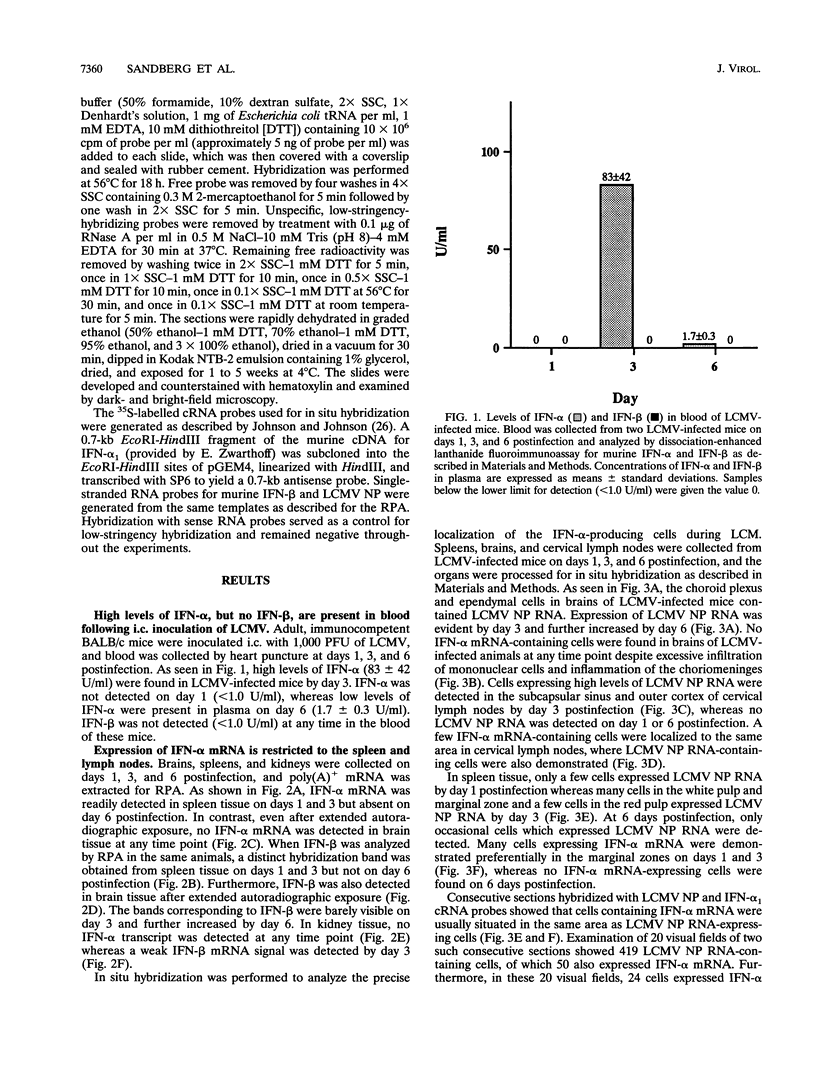
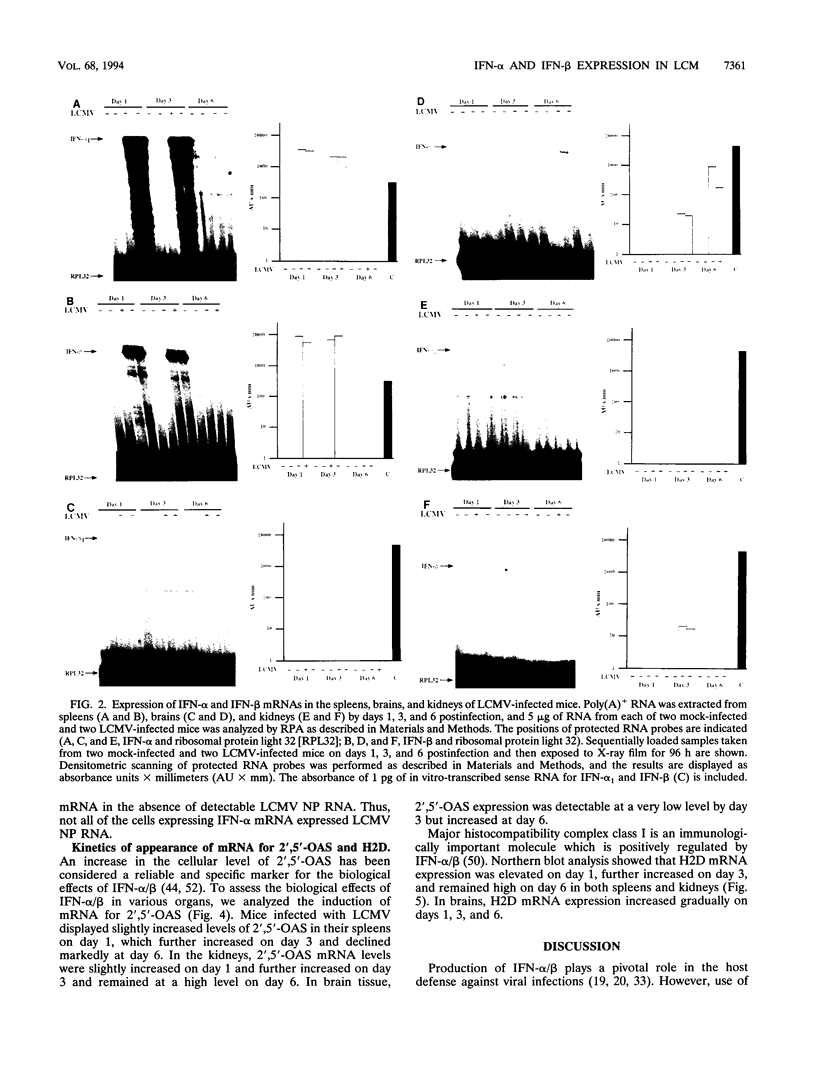
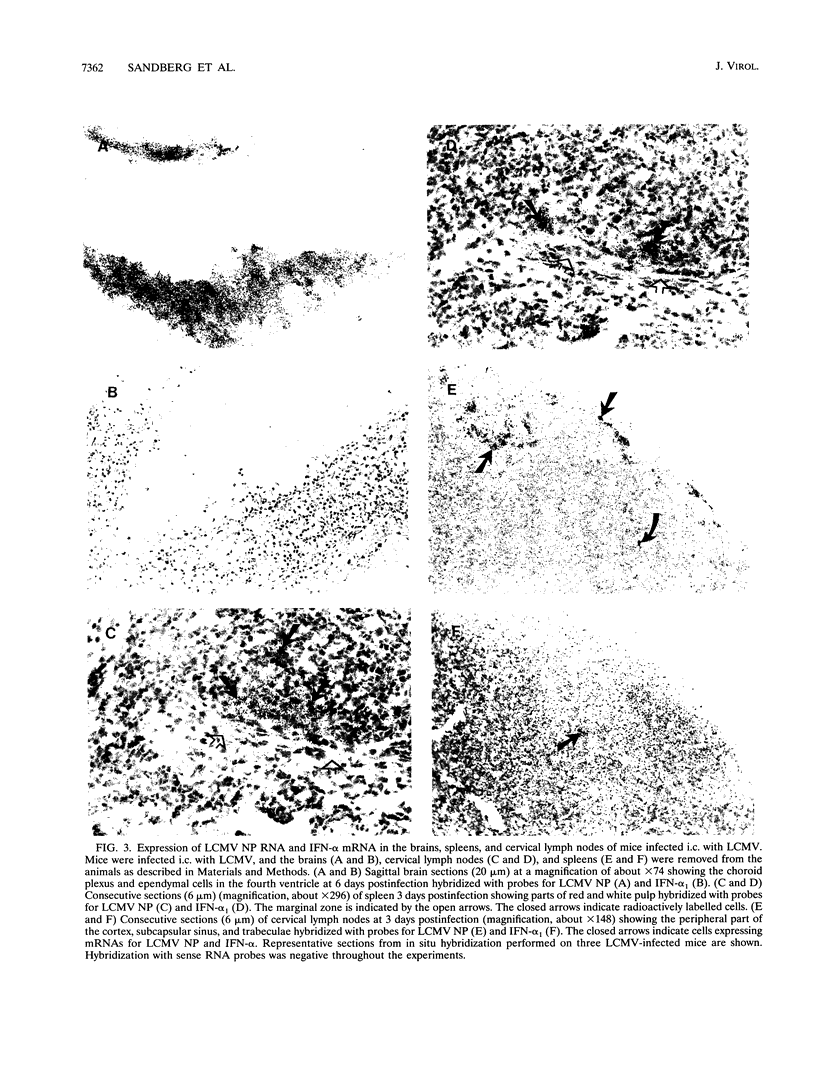

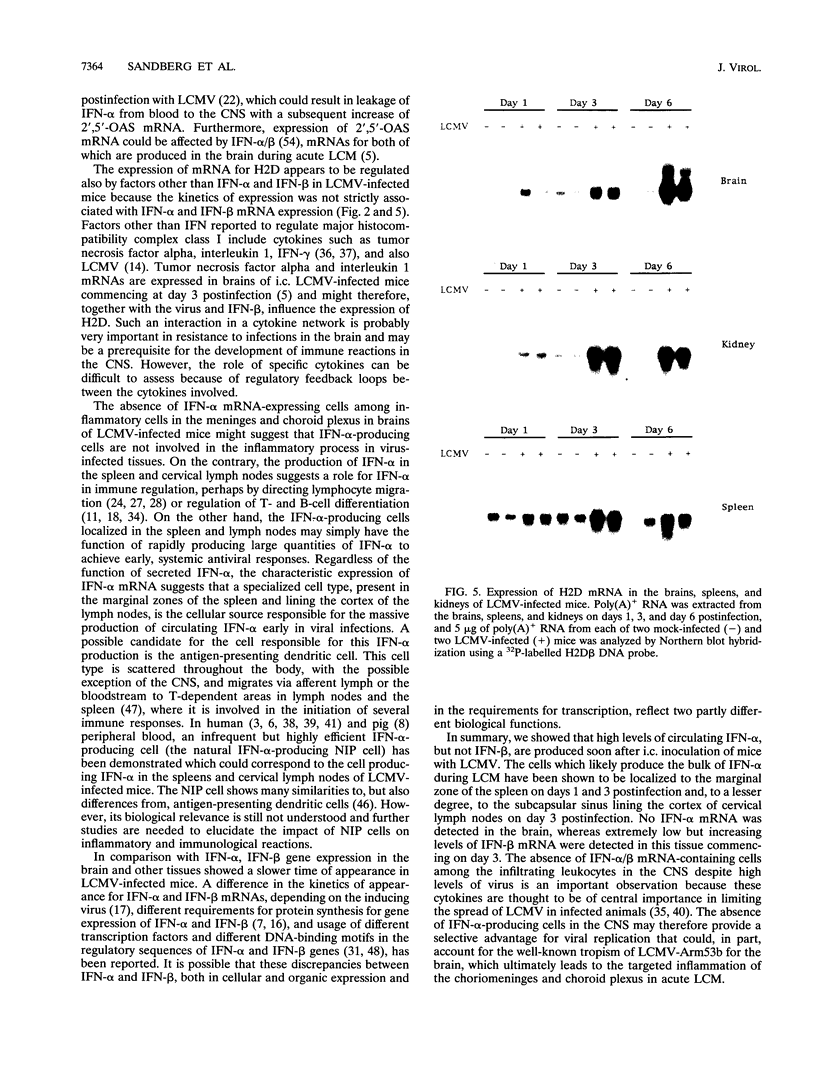


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackrill A. M., Blair G. E. Interferon-gamma regulation of major histocompatibility class I gene expression in rat cells containing the adenovirus 12 E1A oncogene. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen I. H., Marker O., Thomsen A. R. Breakdown of blood-brain barrier function in the murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection mediated by virus-specific CD8+ T cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Feb;31(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley J. E., Bishop G. A., St John T., Frelinger J. A. A simple, rapid method for the purification of poly A+ RNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):114–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay S., Perussia B., Trinchieri G., Miller D. S., Starr S. E. Requirement for HLA-DR+ accessory cells in natural killing of cytomegalovirus-infected fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):180–195. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Hobbs M. V., Kemper P., Oldstone M. B. Cerebral expression of multiple cytokine genes in mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 15;152(2):716–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederblad B., Alm G. V. Infrequent but efficient interferon-alpha-producing human mononuclear leukocytes induced by herpes simplex virus in vitro studied by immuno-plaque and limiting dilution assays. J Interferon Res. 1990 Feb;10(1):65–73. doi: 10.1089/jir.1990.10.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederblad B., Gobl A. E., Alm G. V. The induction of interferon-alpha and interferon-beta mRNA in human natural interferon-producing blood leukocytes requires de novo protein synthesis. J Interferon Res. 1991 Dec;11(6):371–377. doi: 10.1089/jir.1991.11.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charley B., Lavenant L. Characterization of blood mononuclear cells producing IFN alpha following induction by coronavirus-infected cells (porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus). Res Immunol. 1990 Feb;141(2):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(90)90133-J. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Allan J. E., Lynch F., Ceredig R. Dissection of an inflammatory process induced by CD8+ T cells. Immunol Today. 1990 Feb;11(2):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. Genomic and biological variation among commonly used lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus strains. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1689–1698. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman F. D., Svetic A., Gresser I., Snapper C., Holmes J., Trotta P. P., Katona I. M., Gause W. C. Regulation by interferon alpha of immunoglobulin isotype selection and lymphokine production in mice. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1179–1188. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flenniken A. M., Galabru J., Rutherford M. N., Hovanessian A. G., Williams B. R. Expression of interferon-induced genes in different tissues of mice. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3077–3083. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3077-3083.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Leist T. P., Meager A., Gallo P., Leppert D., Zinkernagel R. M., Fontana A. Production of B cell stimulatory factor-2 and interferon gamma in the central nervous system during viral meningitis and encephalitis. Evaluation in a murine model infection and in patients. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):449–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gairin J. E., Joly E., Oldstone M. B. Persistent infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus enhances expression of MHC class I glycoprotein on cultured mouse brain endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3953–3957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Robert N., Buffet-Janvresse C., Rivière Y., Hovanessian A. G. Continuous production of interferon in normal mice: effect of anti-interferon globulin, sex, age, strain and environment on the levels of 2-5A synthetase and p67K kinase. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):711–718. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobl A. E., Cederblad B., Sandberg K., Alm G. V. Interferon-alpha but not -beta genes require de novo protein synthesis for efficient expression in human monocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Feb;35(2):177–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb02848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobl A. E., Funa K., Alm G. V. Different induction patterns of mRNA for IFN-alpha and -beta in human mononuclear leukocytes after in vitro stimulation with herpes simplex virus-infected fibroblasts and Sendai virus. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3605–3609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Carnaud C., Maury C., Sala A., Eid P., Woodrow D., Maunoury M. T., Belardelli F. Host humoral and cellular immune mechanisms in the continued suppression of Friend erythroleukemia metastases after interferon alpha/beta treatment in mice. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1193–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Bandu M. E., Maury C., Brouty-Boyé D. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. I. Rapid evolution of encephalomyocarditis virus infection. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1305–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Maury C., Bandu M. T. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. II. Studies with herpes simplex, Moloney sarcoma, vesicular stomatitis, Newcastle disease, and influenza viruses. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1316–1323. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannigan G., Williams B. R. Transcriptional regulation of interferon-responsive genes is closely linked to interferon receptor occupancy. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1607–1613. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04403.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs M. V., Weigle W. O., Noonan D. J., Torbett B. E., McEvilly R. J., Koch R. J., Cardenas G. J., Ernst D. N. Patterns of cytokine gene expression by CD4+ T cells from young and old mice. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3602–3614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa R., Biron C. A. IFN induction and associated changes in splenic leukocyte distribution. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):3713–3727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Friedman R. M., Pfau C. J. Interferon induction by lymphocytic choriomeningitis viruses correlates with maximum virulence. J Gen Virol. 1981 Dec;57(Pt 2):275–283. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-2-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korngold R., Blank K. J., Murasko D. M. Effect of interferon on thoracic duct lymphocyte output: induction with either poly I:poly C or vaccinia virus. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2236–2240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korngold R., Doherty P. C. Treatment of mice with polyinosinic-polycytidilic polyribonucleotide reduces T-cell involvement in a localized inflammatory response to vaccinia virus challenge. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):489–494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.489-494.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist T. P., Aguet M., Hässig M., Pevear D. C., Pfau C. J., Zinkernagel R. M. Lack of correlation between serum titres of interferon alpha, beta, natural killer cell activity and clinical susceptibility in mice infected with two isolates of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Aug;68(Pt 8):2213–2218. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-8-2213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist T. P., Eppler M., Zinkernagel R. M. Enhanced virus replication and inhibition of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus disease in anti-gamma interferon-treated mice. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2813–2819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2813-2819.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald N. J., Kuhl D., Maguire D., Näf D., Gallant P., Goswamy A., Hug H., Büeler H., Chaturvedi M., de la Fuente J. Different pathways mediate virus inducibility of the human IFN-alpha 1 and IFN-beta genes. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90091-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C., Oldstone M. B., Welsh R. M. Interferon production during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of nude and normal mice. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):67–68. doi: 10.1038/268067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis D., Battegay M., Bruendler M. A., Laine E., Gresser I., Zinkernagel R. M. Resistance of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus to alpha/beta interferon and to gamma interferon. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1951–1955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1951-1955.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parronchi P., De Carli M., Manetti R., Simonelli C., Sampognaro S., Piccinni M. P., Macchia D., Maggi E., Del Prete G., Romagnani S. IL-4 and IFN (alpha and gamma) exert opposite regulatory effects on the development of cytolytic potential by Th1 or Th2 human T cell clones. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):2977–2983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfau C. J., Gresser I., Hunt K. D. Lethal role of interferon in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-induced encephalitis. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1827–1830. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Scheurich P., Schlüter C., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor enhances HLA-A,B,C and HLA-DR gene expression in human tumor cells. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):975–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnblom L., Ramstedt U., Alm G. V. Properties of human natural interferon-producing cells stimulated by tumor cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jun;13(6):471–476. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg K., Gobl A. E., Funa K., Alm G. V. Characterization of the blood mononuclear leucocytes producing alpha interferon after stimulation with herpes simplex virus in vitro, by means of combined immunohistochemical staining and in situ RNA-RNA hybridization. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jun;29(6):651–658. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg K., Kemper P., Stalder A., Zhang J., Hobbs M. V., Whitton J. L., Campbell I. L. Altered tissue distribution of viral replication and T cell spreading is pivotal in the protection against fatal lymphocytic choriomeningitis in mice after neutralization of IFN-alpha/beta. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 1;153(1):220–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg K., Matsson P., Alm G. V. A distinct population of nonphagocytic and low level CD4+ null lymphocytes produce IFN-alpha after stimulation by herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):1015–1020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C. Mechanism of interferon action: progress toward its understanding. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1982;27:105–156. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60599-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Ransohoff R. M. Interferon-induced antiviral actions and their regulation. Adv Virus Res. 1993;42:57–102. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Bandyopadhyay S., Shanmugam V., Hassan N., Douglas S., Jackson S. J., Trinchieri G., Chehimi J. Morphological and functional differences between HLA-DR+ peripheral blood dendritic cells and HLA-DR+ IFN-alpha producing cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;329:173–178. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2930-9_29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. L., Grossberg S. E. Recent progress in interferon research: molecular mechanisms of regulation, action, and virus circumvention. Virus Res. 1990 Jan;15(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga K., Taniguchi H., Yoda K., Shimizu M., Sakiyama S. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for mouse cytoskeletal beta-actin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2829–2829. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignaux F., Gresser I. Enhanced expression of histocompatibility antigens on interferon-treated mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Mar;157(3):456–460. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-40076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodjdani G., Coulombel C., Doly J. Structure and characterization of a murine chromosomal fragment containing the interferon beta gene. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90571-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathelet M. G., Clauss I. M., Content J., Huez G. A. Regulation of two interferon-inducible human genes by interferon, poly(rI).poly(rC) and viruses. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jun 1;174(2):323–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille A., Gessner A., Lother H., Lehmann-Grube F. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection. VIII. Treatment of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-infected mice with anti-interferon-gamma monoclonal antibody blocks generation of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes and virus elimination. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1283–1288. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Tumour necrosis factors alpha and beta inhibit virus replication and synergize with interferons. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):819–822. doi: 10.1038/323819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]