Abstract
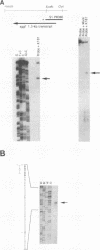
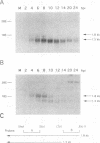
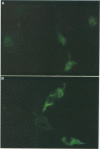
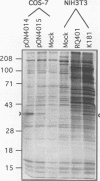
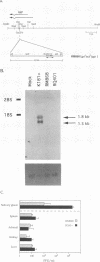
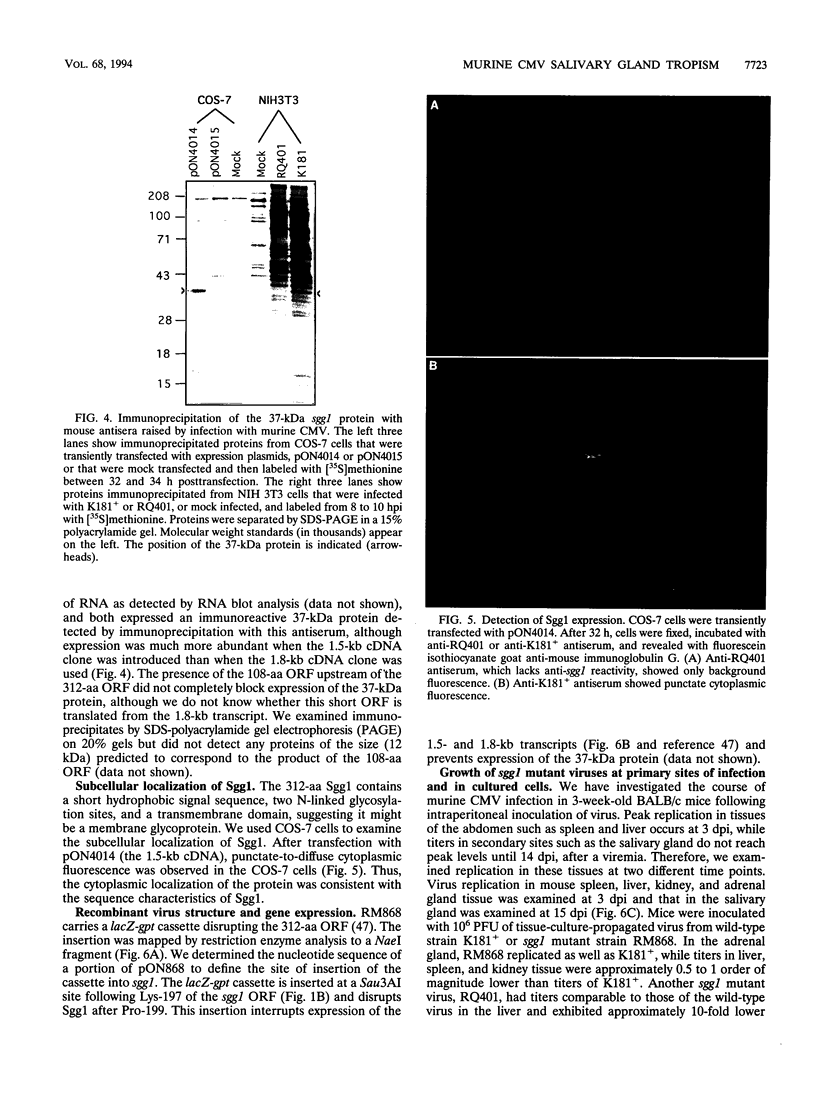
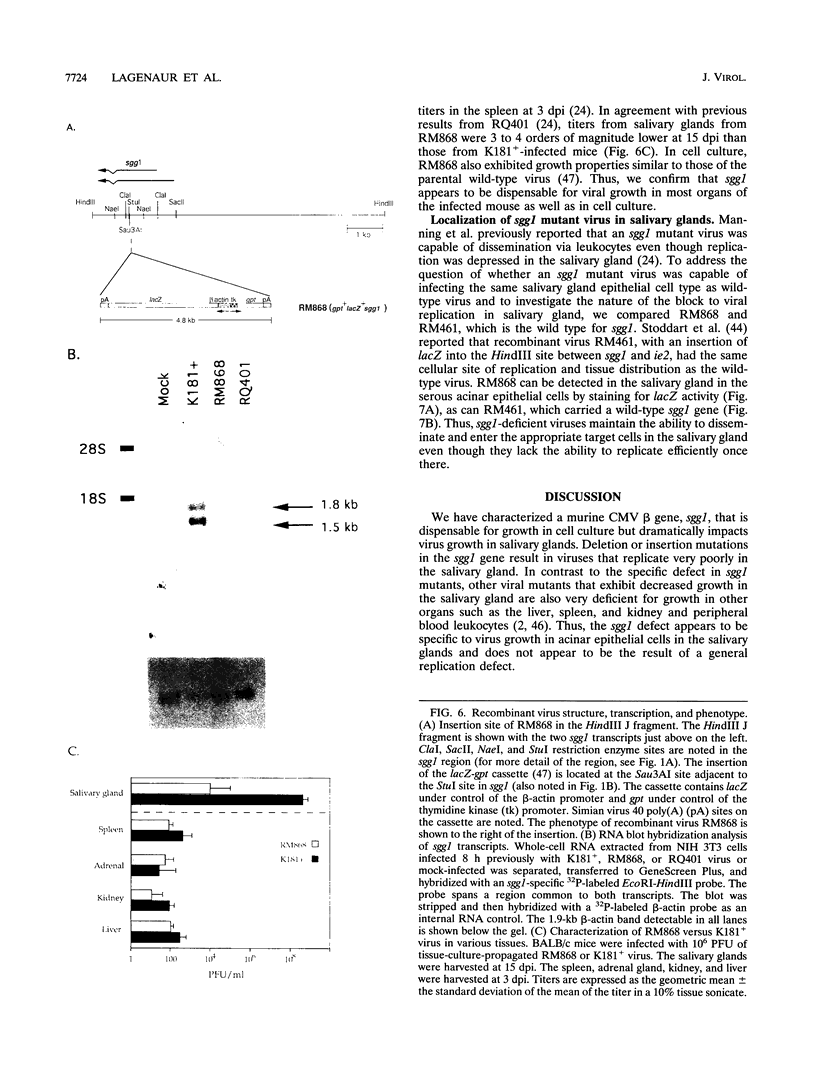
The salivary gland has long been recognized as an important target organ for cytomegalovirus replication in the infected host. A viral gene, denoted sgg1, plays an important role for replication in the salivary gland even though it is dispensable for growth in other organs or in cultured cells. The nucleotide sequence of this gene and of cDNA clones representing two spliced transcripts (1.5 and 1.8 kb in size) has been determined. The more abundant 1.5-kb transcript contains a 312-amino-acid (aa) open reading frame (ORF) and encodes the corresponding 37-kDa protein (Sgg1) when expressed in transfected COS-7 cells. The 1.8-kb transcript initiates upstream of the 1.5-kb transcript and contains a 108-aa ORF in addition to the 312-aa ORF. This longer cDNA also encodes the 37-kDa protein Sgg1, although at lower abundance than the 1.5-kb cDNA. Sgg1 localizes to the cytoplasm of COS-7 cells, which is consistent with the predicted structural characteristics of the 312-aa ORF: a type 1 integral membrane protein. During viral infection, expression of both sgg1 transcripts is highest at early times (8 to 12 h) after infection; only the 1.5-kb transcript is present, at low levels, late in infection. A recombinant virus, RM868, carrying a lacZ-gpt insertion within sgg1, fails to express Sgg1 protein and exhibits reduced growth in the salivary gland. RM868 retains the capacity to disseminate in the infected mouse and to enter serous acinar cells, although it fails to replicate efficiently in this cell type. These results suggest that sgg1 is critical for high levels of viral replication in the salivary gland.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boname J. M., Chantler J. K. Characterization of a strain of murine cytomegalovirus which fails to grow in the salivary glands of mice. J Gen Virol. 1992 Aug;73(Pt 8):2021–2029. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-8-2021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Kern E. R., Whitley R. J., Roizman B. Mapping of herpes simplex virus-1 neurovirulence to gamma 134.5, a gene nonessential for growth in culture. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1262–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.2173860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Santomenna L. D., Harlow P. P., Benfield P. A., Tenney D. J. Human cytomegalovirus US3 and UL36-38 immediate-early proteins regulate gene expression. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):95–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.95-105.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A., Goldman A. Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:321–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Leach F. S., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus late gene expression: gamma genes are controlled by posttranscriptional events. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):864–874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.864-874.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Mocarski E. S. Translational control of cytomegalovirus gene expression is mediated by upstream AUG codons. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3334–3340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3334-3340.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. A cis-acting element within the 5' leader of a cytomegalovirus beta transcript determines kinetic class. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):865–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson D., Strano A. J. Mouse cytomegalovirus. Necrosis of infected and morphologically normal submaxillary gland acinar cells during termination of chronic infection. Am J Pathol. 1972 Jul;68(1):183–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. Y., Mocarski E. S. Beta-galactosidase as a marker in the peripheral and neural tissues of the herpes simplex virus-infected mouse. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. Y., Mocarski E. S. Herpes simplex virus latent RNA (LAT) is not required for latent infection in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7596–7600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B. The murine cytomegalovirus as a model for the study of viral pathogenesis and persistent infections. Arch Virol. 1979;62(1):1–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01314900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. C., Takagi J. L. Virulence characteristics of murine cytomegalovirus in cell and organ cultures. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):841–843. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.841-843.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszinowski U. H., Del Val M., Reddehase M. J. Cellular and molecular basis of the protective immune response to cytomegalovirus infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:189–220. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning W. C., Mocarski E. S. Insertional mutagenesis of the murine cytomegalovirus genome: one prominent alpha gene (ie2) is dispensable for growth. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning W. C., Stoddart C. A., Lagenaur L. A., Abenes G. B., Mocarski E. S. Cytomegalovirus determinant of replication in salivary glands. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3794–3802. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3794-3802.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. A., Marks J. R., Spector D. H. Molecular cloning and restriction endonuclease mapping of the murine cytomegalovirus genome (Smith Strain). Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):94–106. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messerle M., Bühler B., Keil G. M., Koszinowski U. H. Structural organization, expression, and functional characterization of the murine cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene 3. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):27–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.27-36.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messerle M., Keil G. M., Koszinowski U. H. Structure and expression of murine cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene 2. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1638–1643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1638-1643.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messerle M., Keil G. M., Schneider K., Koszinowski U. H. Characterization of the murine cytomegalovirus genes encoding the major DNA binding protein and the ICP18.5 homolog. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A., Gould J. Infection of salivary glands, kidneys, adrenals, ovaries and epithelia by murine cytomegalovirus. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Feb;12(1):113–122. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Walker D. L. Virulence and attenuation of murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):228–236. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.228-236.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer G. Cytomegaloviruses of man and animals. Prog Med Virol. 1973;15:92–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE W. P., HARTLEY J. W., CRAMBLETT H. G., MASTROTA F. M. Detection of human salivary gland virus in the mouth and urine of children. Am J Hyg. 1958 Jan;67(1):57–65. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH M. G. Propagation in tissue cultures of a cytopathogenic virus from human salivary gland virus (SGV) disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jun;92(2):424–430. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH M. G. Propagation of salivary gland virus of the mouse in tissue cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Jul;86(3):435–440. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleiss M. R., Degnin C. R., Geballe A. P. Translational control of human cytomegalovirus gp48 expression. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6782–6789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6782-6789.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression: alpha and beta promoters are trans activated by viral functions in permissive human fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.135-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Synthesis of proteins and glycoproteins in cells infected with human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):751–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.751-767.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoddart C. A., Cardin R. D., Boname J. M., Manning W. C., Abenes G. B., Mocarski E. S. Peripheral blood mononuclear phagocytes mediate dissemination of murine cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1994 Oct;68(10):6243–6253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.10.6243-6253.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonari Y., Minamishima Y. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of temperature-sensitive mutants of murine cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Sep;64(Pt 9):1983–1990. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-9-1983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Farrell H. E., Rawlinson W. D., Mocarski E. S. Genes in the HindIII J fragment of the murine cytomegalovirus genome are dispensable for growth in cultured cells: insertion mutagenesis with a lacZ/gpt cassette. J Virol. 1994 Aug;68(8):4837–4846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.4837-4846.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J., Dallas P. B., Lyons P. A., Shellam G. R., Scalzo A. A. Identification of the glycoprotein H gene of murine cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jul;73(Pt 7):1849–1854. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-7-1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]