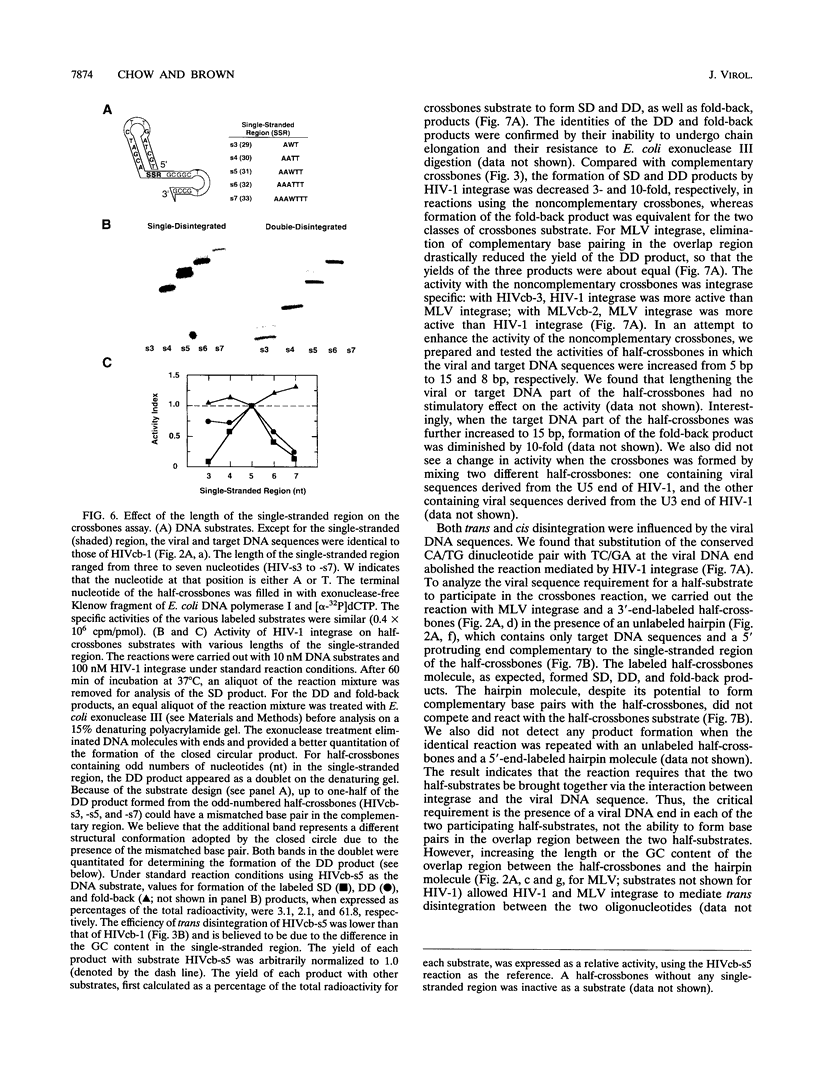
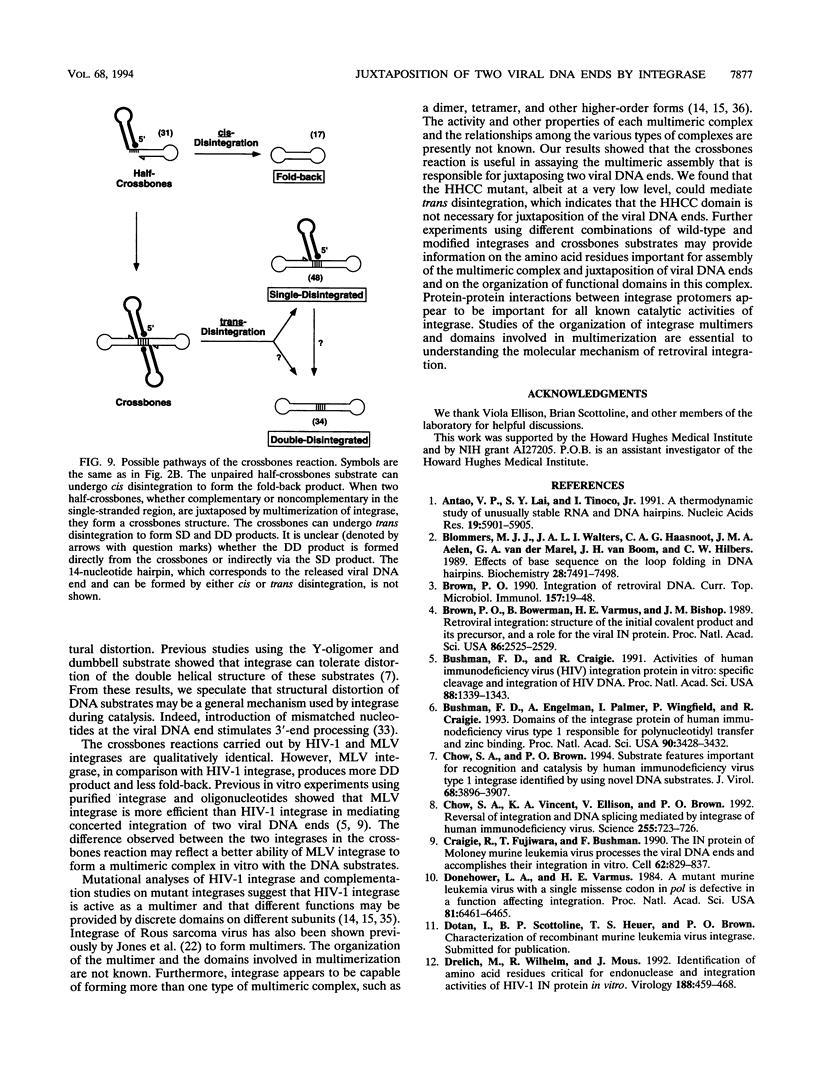
Abstract
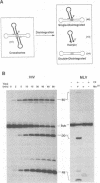
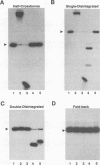
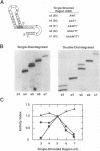
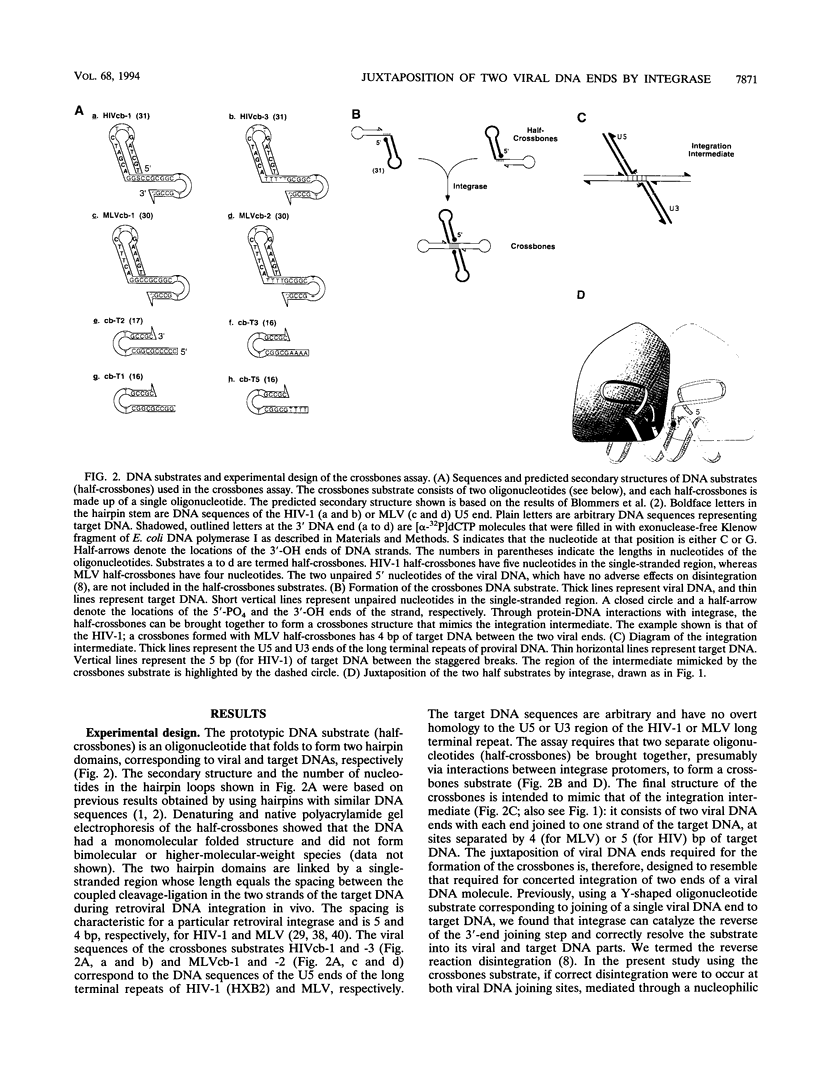
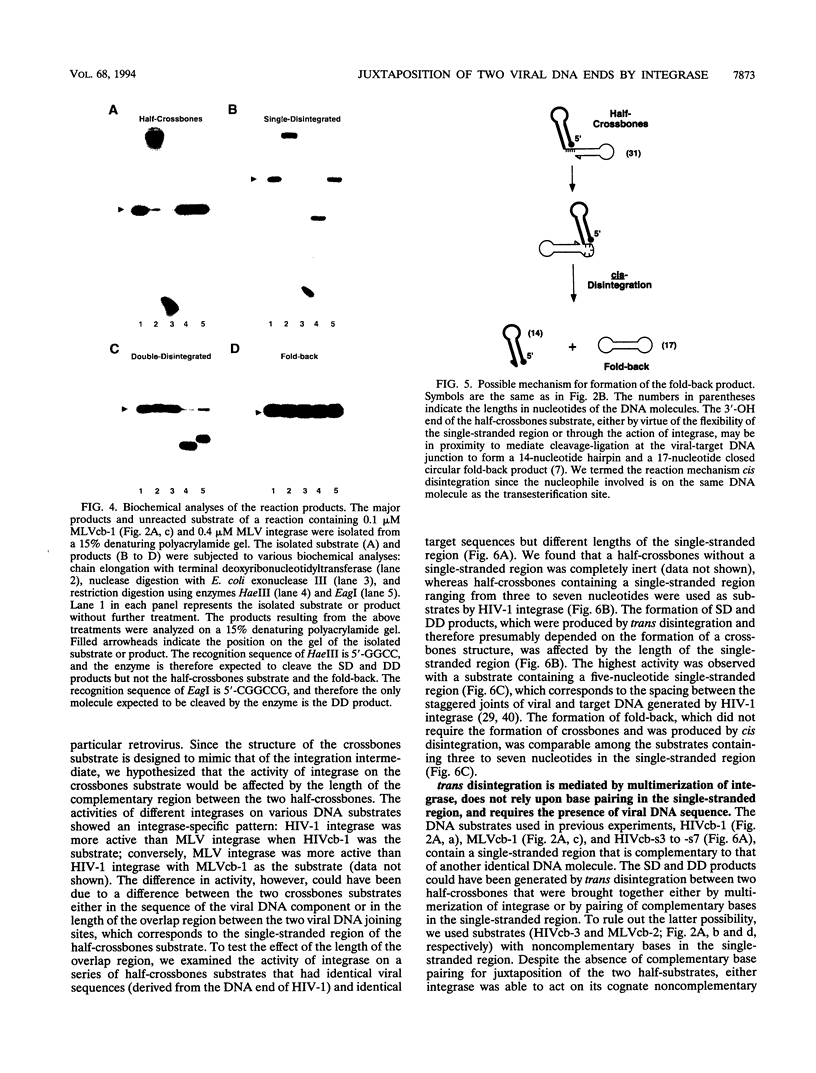
Integration of retroviral DNA involves a coordinated joining of the two ends of a viral DNA molecule into precisely spaced sites on target DNA. In this study, we designed an assay that requires two separate oligonucleotides to be brought together via interactions between integrase promoters to form a "crossbones" substrate that mimics the integration intermediate. The crossbones substrate contains two viral DNA ends, each joined to one strand of target DNA and separated by a defined length of target DNA. We showed that purified integrases of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and murine leukemia virus (MLV) could mediate a concerted strand cleavage-ligation between the two half-substrates at one or both viral DNA joining sites (trans disintegration). Another major product, termed fold-back, resulted from an intramolecular attack on the phosphodiester bond at the viral-target DNA junction by the 3'-OH group of the same DNA molecule (cis disintegration). The activity of integrase on the crossbones substrate depended on the presence of viral DNA sequences. For trans disintegration, the optimal length of target DNA between the viral DNA joining sites of the crossbones substrate corresponded to the spacing between the staggered joints formed on two opposite strands of target DNA during retroviral DNA integration in vivo. The activity of integrases on crossbones did not require complementary base pairing between the two half-substrates, indicating that the half-substrates were juxtaposed solely through protein-DNA interactions. The crossbones assay, therefore, measures the ability of integrase to juxtapose two viral DNA ends, an activity which heretofore has been difficult to detect by using purified integrase in conventional assays. Certain mutant integrases that were otherwise inactive with the crossbones substrate could complement one another, indicating that no single protomer in the integrase multimer requires a complete set of functional domains either for catalytic activity or for juxtaposition of the two viral DNA ends by the active multimer.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antao V. P., Lai S. Y., Tinoco I., Jr A thermodynamic study of unusually stable RNA and DNA hairpins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5901–5905. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blommers M. J., Walters J. A., Haasnoot C. A., Aelen J. M., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Hilbers C. W. Effects of base sequence on the loop folding in DNA hairpins. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7491–7498. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O. Integration of retroviral DNA. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:19–48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Activities of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integration protein in vitro: specific cleavage and integration of HIV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1339–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Engelman A., Palmer I., Wingfield P., Craigie R. Domains of the integrase protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 responsible for polynucleotidyl transfer and zinc binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Brown P. O. Substrate features important for recognition and catalysis by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase identified by using novel DNA substrates. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3896–3907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3896-3907.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Vincent K. A., Ellison V., Brown P. O. Reversal of integration and DNA splicing mediated by integrase of human immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.1738845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Fujiwara T., Bushman F. The IN protein of Moloney murine leukemia virus processes the viral DNA ends and accomplishes their integration in vitro. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):829–837. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90126-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Varmus H. E. A mutant murine leukemia virus with a single missense codon in pol is defective in a function affecting integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6461–6465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drelich M., Wilhelm R., Mous J. Identification of amino acid residues critical for endonuclease and integration activities of HIV-1 IN protein in vitro. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90499-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison V., Abrams H., Roe T., Lifson J., Brown P. Human immunodeficiency virus integration in a cell-free system. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2711–2715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2711-2715.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Identification of discrete functional domains of HIV-1 integrase and their organization within an active multimeric complex. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3269–3275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Craigie R. Identification of conserved amino acid residues critical for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase function in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6361–6369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6361-6369.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Mizuuchi K., Craigie R. HIV-1 DNA integration: mechanism of viral DNA cleavage and DNA strand transfer. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90297-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M. L., Vora A. C., Zeh W. G., Grandgenett D. P. Concerted integration of viral DNA termini by purified avian myeloblastosis virus integrase. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6257–6263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6257-6263.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Integration of mini-retroviral DNA: a cell-free reaction for biochemical analysis of retroviral integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3065–3069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Mumm S. R. Unraveling retrovirus integration. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90707-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. S., Coleman J., Merkel G. W., Laue T. M., Skalka A. M. Retroviral integrase functions as a multimer and can turn over catalytically. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16037–16040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson C. B., Roth M. J. Role of the His-Cys finger of Moloney murine leukemia virus integrase protein in integration and disintegration. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5562–5571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5562-5571.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Merkel G., Kulkosky J., Leis J., Skalka A. M. The avian retroviral IN protein is both necessary and sufficient for integrative recombination in vitro. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90290-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkosky J., Jones K. S., Katz R. A., Mack J. P., Skalka A. M. Residues critical for retroviral integrative recombination in a region that is highly conserved among retroviral/retrotransposon integrases and bacterial insertion sequence transposases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2331–2338. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R. L., Schneider C. L., Robbins H. L., Callahan P. L., LeGrow K., Roth E., Schleif W. A., Emini E. A. Requirement of active human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase enzyme for productive infection of human T-lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7414–7419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7414-7419.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt A. D., Shiue L., Varmus H. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of HIV-1 integrase demonstrates differential effects on integrase functions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2113–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder A., Engelman A., Craigie R., Fesen M., Pommier Y. Intermolecular disintegration and intramolecular strand transfer activities of wild-type and mutant HIV-1 integrase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 25;22(6):1037–1043. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.6.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. The retrovirus pol gene encodes a product required for DNA integration: identification of a retrovirus int locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7885–7889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Schwartzberg P. L., Goff S. P. Structure of the termini of DNA intermediates in the integration of retroviral DNA: dependence on IN function and terminal DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Construction and analysis of deletion mutations in the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus: a new viral function required for productive infection. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent K. A., Ellison V., Chow S. A., Brown P. O. Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase expressed in Escherichia coli and analysis of variants with amino-terminal mutations. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):425–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.425-437.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent K. A., York-Higgins D., Quiroga M., Brown P. O. Host sequences flanking the HIV provirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6045–6047. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Oude Groeneger A. M., Plasterk R. H. Identification of the catalytic and DNA-binding region of the human immunodeficiency virus type I integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 25;21(6):1419–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.6.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Plasterk R. H. The human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein. Trends Genet. 1993 Dec;9(12):433–438. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90107-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D. C., Elgersma Y., Bolk M. W., Vink C., Plasterk R. H. DNA binding properties of the integrase proteins of human immunodeficiency viruses types 1 and 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3821–3827. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D. C., Groeneger A. A., Plasterk R. H. Mutational analysis of the integrase protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9598–9602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D. C., Vink C., Groeneger A. A., Plasterk R. H. Complementation between HIV integrase proteins mutated in different domains. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3261–3267. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]