Abstract
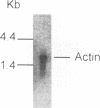
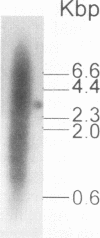
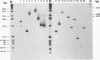
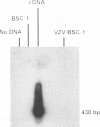
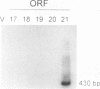
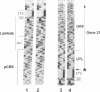
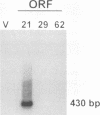
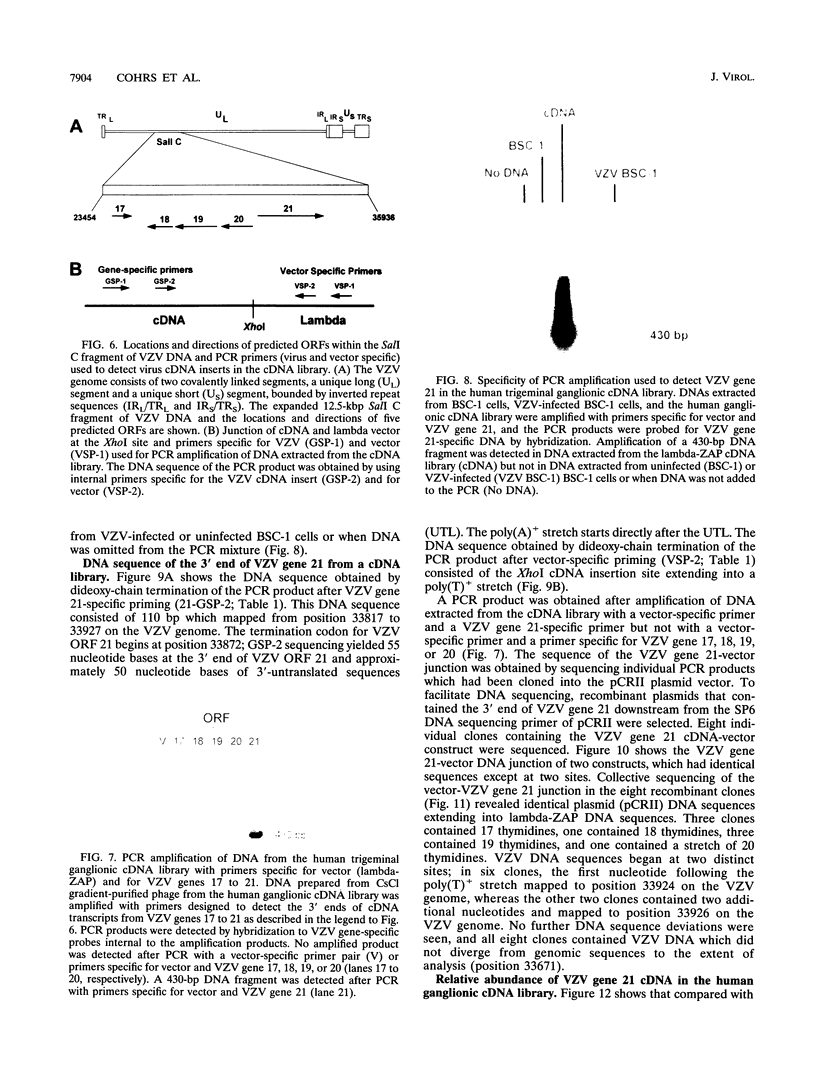
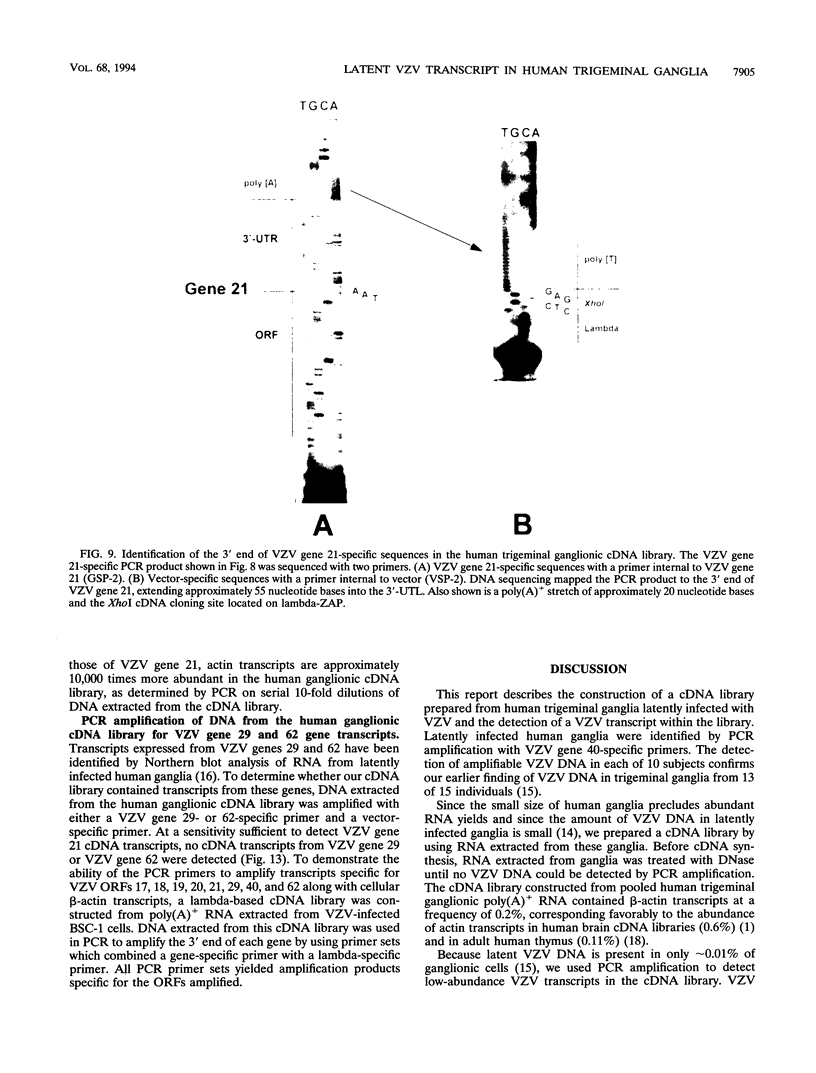
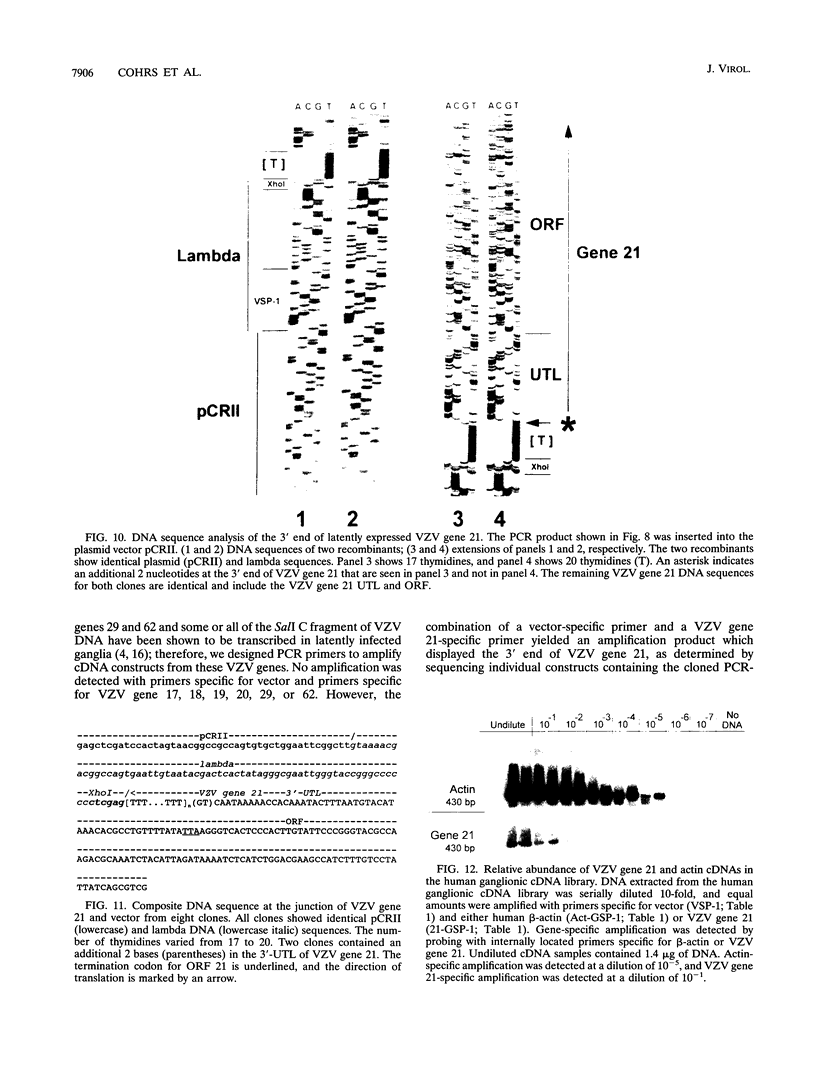
The entire varicella-zoster virus (VZV) genome appears to be present in latently infected human ganglia, but the extent of virus DNA transcription is unknown. Conventional methods to study virus gene transcripts by Northern (RNA) blotting are not feasible, since ganglia are small and VZV DNA is not abundant. To circumvent this problem, we prepared radiolabeled cDNA from ganglionic RNA, hybridized it to Southern blots containing VZV DNA, and demonstrated the presence of a transcript within the SalI C fragment of the virus genome (R. Cohrs, R. Mahalingam, A. N. Dueland, W. Wolf, M. Wellish, and D. H. Gilden, J. Infect. Dis. 166:S24-S29, 1992). To further map VZV transcripts, in the work described here we constructed a cDNA library from poly(A)+ RNA obtained from latently infected human ganglia. Phage DNA isolated from the library was used in PCR amplifications to detect VZV-specific inserts. The specificity of the PCRs was provided by selection of a primer specific for VZV gene 17, 18, 19, 20, or 21 and a second vector-specific primer. VZV gene 21-specific sequences were identified by PCR amplification. The PCR product contained the XhoI cloning site and poly(A)+ sequences between vector and VZV gene 21 sequences. The sequence motif at the 3' end of VZV gene 21, determined by cloning and sequencing of the PCR product, consisted of 49 to 51 nucleotide bases of 3'-untranslated DNA, the termination codon for the VZV gene 21 open reading frame, and DNA sequences reading into the VZV gene 21 open reading frame.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Dubnick M., Kerlavage A. R., Moreno R., Kelley J. M., Utterback T. R., Nagle J. W., Fields C., Venter J. C. Sequence identification of 2,375 human brain genes. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):632–634. doi: 10.1038/355632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright A. G., Jenkins F. J. The herpes simplex virus UL37 protein is phosphorylated in infected cells. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4842–4847. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4842-4847.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratanich A. C., Hanson N. D., Jones C. J. The latency-related gene of bovine herpesvirus 1 inhibits the activity of immediate-early transcription unit 1. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):988–991. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90278-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohrs R., Mahalingam R., Dueland A. N., Wolf W., Wellish M., Gilden D. H. Restricted transcription of varicella-zoster virus in latently infected human trigeminal and thoracic ganglia. J Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;166 (Suppl 1):S24–S29. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.supplement_1.s24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Straus S. E. Patterns of gene expression and sites of latency in human nerve ganglia are different for varicella-zoster and herpes simplex viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9773–9777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Dupuis K. W., Schmidt N. J. Varicella-zoster viral glycoproteins analyzed with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):55–62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.55-62.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. W., Block T. M., Spivack J. G. The latency-associated transcripts of herpes simplex virus: RNA in search of function. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90160-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Hayward A. R., Krupp J., Hunter-Laszlo M., Huff J. C., Vafai A. Varicella-zoster virus infection of human mononuclear cells. Virus Res. 1987 Apr;7(2):117–129. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Mahalingam R., Dueland A. N., Cohrs R. Herpes zoster: pathogenesis and latency. Prog Med Virol. 1992;39:19–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Shtram Y., Friedmann A., Wellish M., Devlin M., Cohen A., Fraser N., Becker Y. Extraction of cell-associated varicella-zoster virus DNA with triton X-100-NaCl. J Virol Methods. 1982 May;4(4-5):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutish G., Mainprize T., Rock D. Characterization of the latency-related transcriptionally active region of the bovine herpesvirus 1 genome. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5730–5737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5730-5737.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahalingam R., Wellish M., Lederer D., Forghani B., Cohrs R., Gilden D. Quantitation of latent varicella-zoster virus DNA in human trigeminal ganglia by polymerase chain reaction. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2381–2384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2381-2384.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahalingam R., Wellish M., Wolf W., Dueland A. N., Cohrs R., Vafai A., Gilden D. Latent varicella-zoster viral DNA in human trigeminal and thoracic ganglia. N Engl J Med. 1990 Sep 6;323(10):627–631. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009063231002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J. L., Holman R. P., Croen K. D., Smialek J. E., Straus S. E. Varicella-zoster virus transcription in human trigeminal ganglia. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):193–200. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima-Iijima S., Hamada H., Reddy P., Kakunaga T. Molecular structure of the human cytoplasmic beta-actin gene: interspecies homology of sequences in the introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6133–6137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patanjali S. R., Parimoo S., Weissman S. M. Construction of a uniform-abundance (normalized) cDNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1943–1947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priola S. A., Gustafson D. P., Wagner E. K., Stevens J. G. A major portion of the latent pseudorabies virus genome is transcribed in trigeminal ganglia of pigs. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4755–4760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4755-4760.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton L. S., Pensiero M. N., Jenkins F. J. Identification and characterization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 protein encoded by the UL37 open reading frame. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6101–6109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6101-6109.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G. B., Cook M. L., Feldman L. T. RNA complementary to a herpesvirus alpha gene mRNA is prominent in latently infected neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2434993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]