Abstract
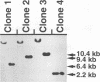
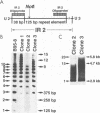
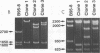
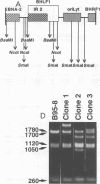
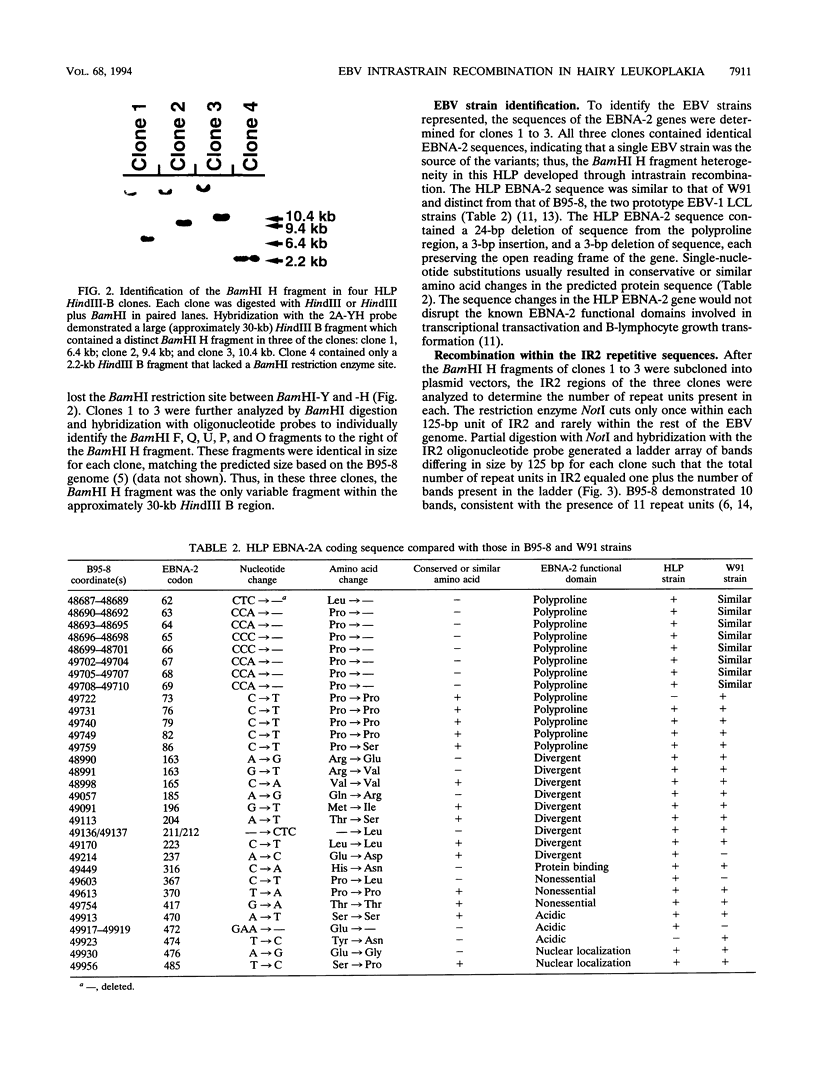
In laboratory lymphoblastoid cell lines and in natural human infections, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) strains have been identified by DNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms of the BamHI H fragment. Multiple, heterogeneous BamHI H fragments have been detected in oral hairy leukoplakia (HLP), raising the question of EBV coinfection with multiple strains. To investigate whether the heterogeneous BamHI H fragments represent different EBV strains or recombinant variants of the same strain, EBV DNA from HLP lesions was analyzed to characterize the viral strains and determine the source of possible recombinant variants. Clones of heterogeneous BamHI H fragments from a single HLP lesion were determined to have strain identity on the basis of sequence identity of the EBNA-2 genes. Intrastrain homologous recombination within the IR2 internal repeat region and nonhomologous recombination of other sequences accounted for the heterogeneity of the BamHI H fragments. PCR amplification from additional HLP specimens detected similar recombinant variants. A possible example of site-specific recombination joining the BamHI Y portion of the EBNA-2 gene to sequences within the BamHI S fragment was also detected in multiple HLP specimens. These data indicate that intrastrain recombination during productive replication confounds the use of restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the BamHI Y and H fragments to identify EBV strains in HLP. In patients with permissive epithelial EBV infections, EBV strains could be more accurately distinguished by sequence identity or divergence within known regions of genetic strain variation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Hamid M., Chen J. J., Constantine N., Massoud M., Raab-Traub N. EBV strain variation: geographical distribution and relation to disease state. Virology. 1992 Sep;190(1):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)91202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alsip G. R., Ench Y., Sumaya C. V., Boswell R. N. Increased Epstein-Barr virus DNA in oropharyngeal secretions from patients with AIDS, AIDS-related complex, or asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infections. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1072–1076. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armour J. A., Jeffreys A. J. Biology and applications of human minisatellite loci. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Dec;2(6):850–856. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayares D., Chekuri L., Song K. Y., Kucherlapati R. Sequence homology requirements for intermolecular recombination in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5199–5203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornkamm G. W., Delius H., Zimber U., Hudewentz J., Epstein M. A. Comparison of Epstein-Barr virus strains of different origin by analysis of the viral DNAs. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):603–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.603-618.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cen H., Breinig M. C., Atchison R. W., Ho M., McKnight J. L. Epstein-Barr virus transmission via the donor organs in solid organ transplantation: polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of IR2, IR3, and IR4. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):976–980. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.976-980.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman S. H., Henle W., Rubin R. H., Tolkoff-Rubin N. E., Cosimi B., Cantell K., Winkle S., Herrin J. T., Black P. H., Russell P. S. Epstein-Barr virus infection in renal transplant recipients. Effects of antithymocyte globulin and interferon. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):39–42. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho M. S., Bornkamm G. W., zur Hausen H. Structure of defective DNA molecules in Epstein-Barr virus preparations from P3HR-1 cells. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):199–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.199-207.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 domain essential for transformation is a direct transcriptional activator. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5880–5885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5880-5885.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 mutations define essential domains for transformation and transactivation. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2545–2554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2545-2554.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T. R., Kieff E. Identification and nucleotide sequences of two similar tandem direct repeats in Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):823–833. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.823-833.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Beisel C., Hummel M., King W., Fennewald S., Cheung A., Heller M., Raab-Traub N., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (B95-8) DNA VII: molecular cloning and detailed mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Hennessy K., Chamnankit L., Kieff E. U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA may encode Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. A. DNA fingerprints: Victims or perpetrators of DNA turnover? Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):347–348. doi: 10.1038/342347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutch R. E., Bruckner R. C., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus type 1 recombination: role of DNA replication and viral a sequences. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):277–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.277-285.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan K., Rajadurai P., Resnick L., Raab-Traub N. Epstein-Barr virus small nuclear RNAs are not expressed in permissively infected cells in AIDS-associated leukoplakia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8790–8794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
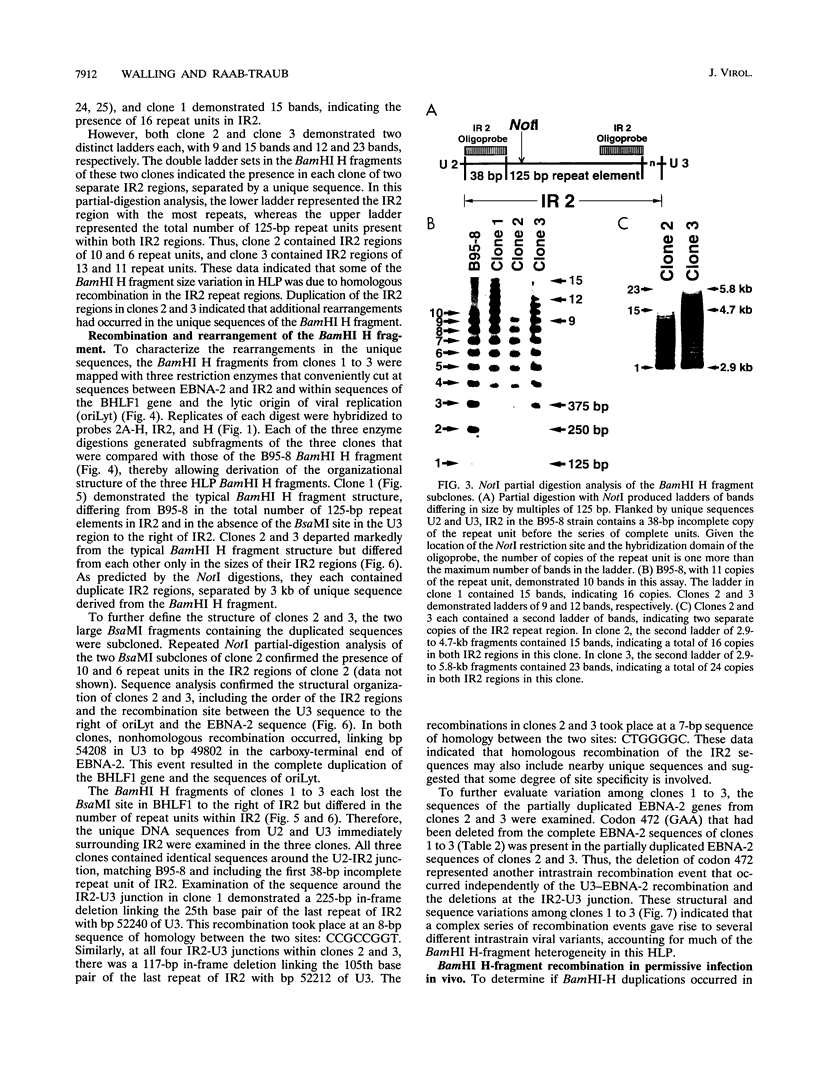
- Gratama J. W., Oosterveer M. A., Klein G., Ernberg I. EBNA size polymorphism can be used to trace Epstein-Barr virus spread within families. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4703–4708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4703-4708.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Oosterveer M. A., Lepoutre J. M., van Rood J. J., Zwaan F. E., Vossen J. M., Kapsenberg J. G., Richel D., Klein G., Ernberg I. Serological and molecular studies of Epstein-Barr virus infection in allogeneic marrow graft recipients. Transplantation. 1990 Apr;49(4):725–730. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199004000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Oosterveer M. A., Weimar W., Sintnicolaas K., Sizoo W., Bolhuis R. L., Ernberg I. Detection of multiple 'Ebnotypes' in individual Epstein-Barr virus carriers following lymphocyte transformation by virus derived from peripheral blood and oropharynx. J Gen Virol. 1994 Jan;75(Pt 1):85–94. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
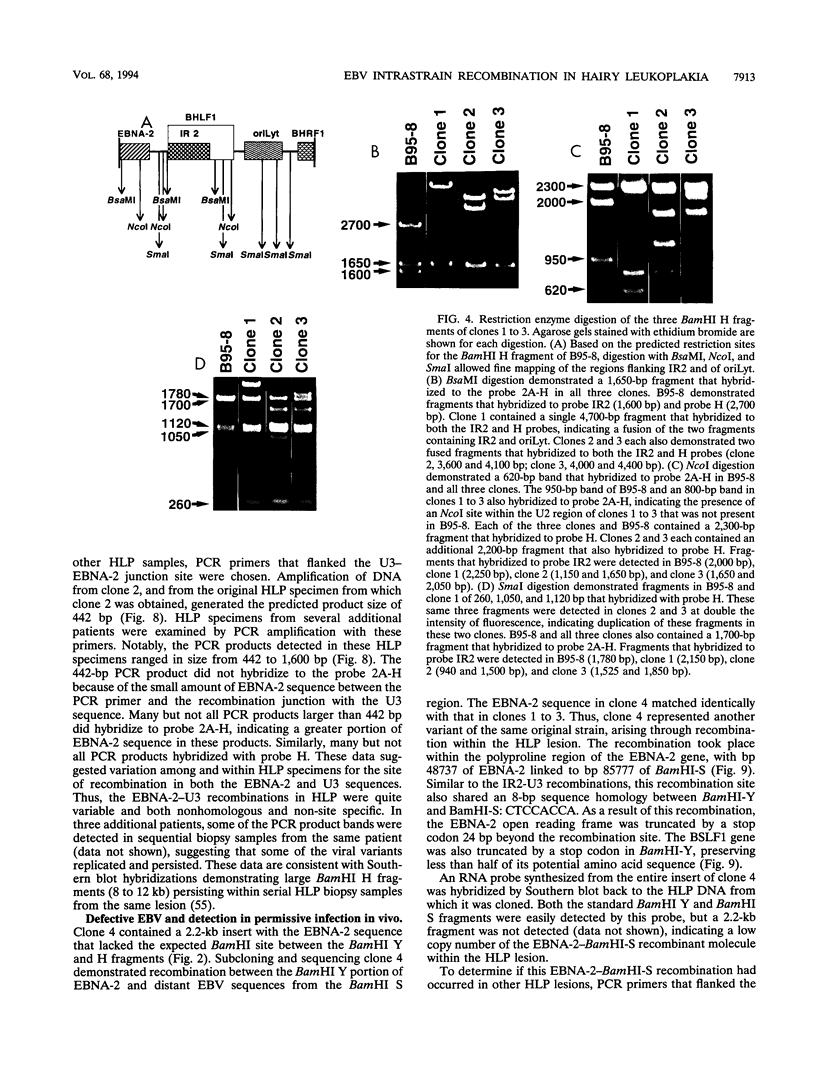
- Gratama J. W., Oosterveer M. A., Zwaan F. E., Lepoutre J., Klein G., Ernberg I. Eradication of Epstein-Barr virus by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: implications for sites of viral latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8693–8696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan J. S., Greenspan D., Lennette E. T., Abrams D. I., Conant M. A., Petersen V., Freese U. K. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus within the epithelial cells of oral "hairy" leukoplakia, an AIDS-associated lesion. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 19;313(25):1564–1571. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512193132502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Dambaugh T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus DNA. IX. Variation among viral DNAs from producer and nonproducer infected cells. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):632–648. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.632-648.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Hayward S. D. Organization of the Epstein-Barr virus DNA molecule. III. Location of the P3HR-1 deletion junction and characterization of the NotI repeat units that form part of the template for an abundant 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced mRNA transcript. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):135–148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.135-148.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenson H. B., Farrell P. J., Miller G. Sequences of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) large internal repeat form the center of a 16-kilobase-pair palindrome of EBV (P3HR-1) heterogeneous DNA. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1495–1506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1495-1506.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B. Z., Niederman J. C., Olson B. A., Miller G. Fragment length polymorphisms among independent isolates of Epstein-Barr virus from immunocompromised and normal hosts. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):299–308. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf C. W. Recombinational hotspots within the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene? Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7647–7648. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyaw M. T., Hurren L., Evans L., Moss D. J., Cooper D. A., Benson E., Esmore D., Sculley T. B. Expression of B-type Epstein-Barr virus in HIV-infected patients and cardiac transplant recipients. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Nov;8(11):1869–1874. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling P. D., Rawlins D. R., Hayward S. D. The Epstein-Barr virus immortalizing protein EBNA-2 is targeted to DNA by a cellular enhancer-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9237–9241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling P. D., Ryon J. J., Hayward S. D. EBNA-2 of herpesvirus papio diverges significantly from the type A and type B EBNA-2 proteins of Epstein-Barr virus but retains an efficient transactivation domain with a conserved hydrophobic motif. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):2990–3003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.2990-3003.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liskay R. M., Letsou A., Stachelek J. L. Homology requirement for efficient gene conversion between duplicated chromosomal sequences in mammalian cells. Genetics. 1987 Jan;115(1):161–167. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little P. F., Cross S. H. A cosmid vector that facilitates restriction enzyme mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3159–3163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Chang R. S., Jones J. H. Genetic polymorphism of natural Epstein-Barr virus isolates from infectious mononucleosis patients and healthy carriers. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3862–3866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3862-3866.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Chang R. S. Longitudinal study of Epstein-Barr virus genotypes associated with infectious mononucleosis patients and healthy carriers. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):994–995. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Li S. B., Chang R. S. Study of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transmission by EBV genotyping. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):213–214. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons K. M., Stein J. H., Smithies O. Length polymorphisms in human proline-rich protein genes generated by intragenic unequal crossing over. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):267–278. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Heston L., Countryman J. P3HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA is an independent replicon maintained by cell-to-cell spread. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):45–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.45-52.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Rabson M., Heston L. Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA disrupts latency. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):174–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.174-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. E., Edwards R. H., Walling D. M., Raab-Traub N. Sequence variation in the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1. J Gen Virol. 1994 Oct;75(Pt 10):2729–2740. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-10-2729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Deiss L. P., Frenkel N. Nucleotide sequence and structural features of a novel US-a junction present in a defective herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):140–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.140-146.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton D. F., Shirley P., Raab-Traub N., Resnick L., Sixbey J. W. Defective viral DNA in Epstein-Barr virus-associated oral hairy leukoplakia. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):397–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.397-400.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C., Howe J. G., Speck S. H., Miller G. Influence of Burkitt's lymphoma and primary B cells on latent gene expression by the nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1531–1539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1531-1539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubnitz J., Subramani S. The minimum amount of homology required for homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2253–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Young L., Martin B., Chatman T., Kieff E., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus types 1 and 2 differ in their EBNA-3A, EBNA-3B, and EBNA-3C genes. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4084–4092. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4084-4092.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvej K., Krenács L., Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Rindum J. L., Pindborg J. J., Pallesen G. Epstein-Barr virus latent and replicative gene expression in oral hairy leukoplakia. Histopathology. 1992 May;20(5):387–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1992.tb01008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarisky R. T., Weber P. C. Requirement for double-strand breaks but not for specific DNA sequences in herpes simplex virus type 1 genome isomerization events. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):34–47. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.34-47.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculley T. B., Apolloni A., Hurren L., Moss D. J., Cooper D. A. Coinfection with A- and B-type Epstein-Barr virus in human immunodeficiency virus-positive subjects. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):643–648. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Shirley P., Chesney P. J., Buntin D. M., Resnick L. Detection of a second widespread strain of Epstein-Barr virus. Lancet. 1989 Sep 30;2(8666):761–765. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90829-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Shirley P., Sloas M., Raab-Traub N., Israele V. A transformation-incompetent, nuclear antigen 2-deleted Epstein-Barr virus associated with replicative infection. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1008–1015. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch B., Andrews L. L., Siegel N., Miller G. Oropharyngeal excretion of Epstein-Barr virus by renal transplant recipients and other patients treated with immunosuppressive drugs. Lancet. 1974 Feb 16;1(7851):234–237. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92546-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Felix D. H., Wray D., Southam J. C., Cubie H. A., Crawford D. H. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression and epithelial cell differentiation in oral hairy leukoplakia. Am J Pathol. 1991 Dec;139(6):1369–1380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson B., Robertson E., Yalamanchili R., Longnecker R., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus recombinants from overlapping cosmid fragments. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7298–7306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7298-7306.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walling D. M., Edmiston S. N., Sixbey J. W., Abdel-Hamid M., Resnick L., Raab-Traub N. Coinfection with multiple strains of the Epstein-Barr virus in human immunodeficiency virus-associated hairy leukoplakia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6560–6564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Q. Y., Rowe M., Martin B., Young L. S., Rickinson A. B. The Epstein-Barr virus carrier state: dominance of a single growth-transforming isolate in the blood and in the oropharynx of healthy virus carriers. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jul;72(Pt 7):1579–1590. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-7-1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Dawson C. W., Clark D., Rupani H., Busson P., Tursz T., Johnson A., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Gen Virol. 1988 May;69(Pt 5):1051–1065. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-5-1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]