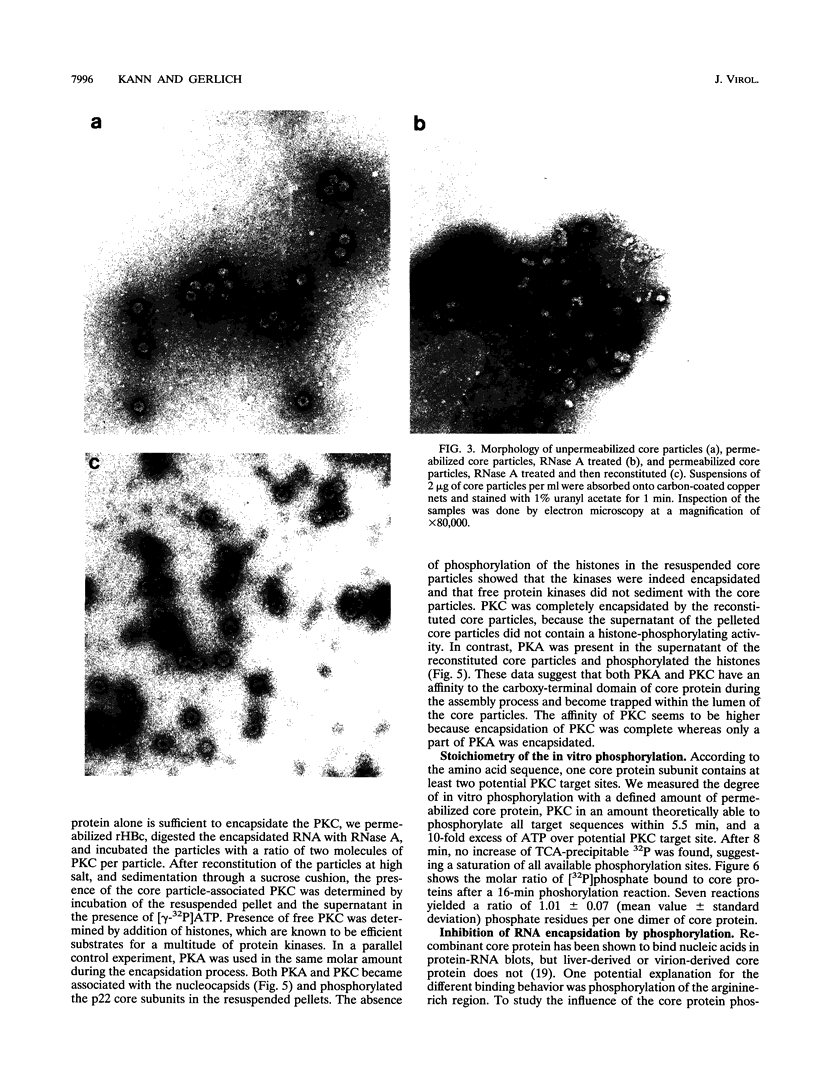
Abstract
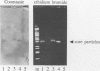
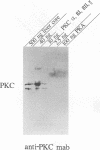
Phosphorylation of core particles derived either from hepatitis B viruses or from livers of hepatitis B-infected individuals has been long recognized, but the nature and function of the phosphorylating enzyme remained unknown. By immunoblotting with a monoclonal antibody, we have now detected protein kinase C within the liver-derived core particles. To study the significance of the encapsidated protein kinase C for the viral life cycle, we established an in vitro assembly system consisting of Escherichia coli-expressed core protein, protein kinase C, and in vitro-synthesized hepatitis B virus RNA. Phosphorylation of the core protein led to a reduced RNA encapsidation capacity of the core particles. Furthermore, RNA and protein kinase C competed for their target sequence, which is the carboxy-terminal arginine-rich domain of the core protein. This finding implies that phosphorylation of the nucleic acid binding site in the core protein occurs within the particles after encapsidation of protein kinase C, pregenomic RNA, and viral polymerase at a later step during viral genome maturation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albin C., Robinson W. S. Protein kinase activity in hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):297–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.297-302.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartenschlager R., Junker-Niepmann M., Schaller H. The P gene product of hepatitis B virus is required as a structural component for genomic RNA encapsidation. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5324-5332.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beames B., Lanford R. E. Carboxy-terminal truncations of the HBV core protein affect capsid formation and the apparent size of encapsidated HBV RNA. Virology. 1993 Jun;194(2):597–607. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum F., Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid assembly: primary structure requirements in the core protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3319–3330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3319-3330.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisova G. P., Pumpen P. P., Bychko V. V., Pushko P. M., Kalis Ia V. Struktura i ékspressiia v kletkakh Escherichia coli gena kor-antigena virusa gepatitia B (HBV) cheloveka. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1984;279(5):1245–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Kiselev N. A., Böttcher B., Berriman J. A., Borisova G. P., Ose V., Pumpens P. Three-dimensional structure of hepatitis B virus core particles determined by electron cryomicroscopy. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):943–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitelson M. A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Core particles of hepatitis B virus and ground squirrel hepatitis virus. II. Characterization of the protein kinase reaction associated with ground squirrel hepatitis virus and hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):741–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.741-748.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallina A., Bonelli F., Zentilin L., Rindi G., Muttini M., Milanesi G. A recombinant hepatitis B core antigen polypeptide with the protamine-like domain deleted self-assembles into capsid particles but fails to bind nucleic acids. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4645–4652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4645-4652.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Goldmann U., Müller R., Stibbe W., Wolff W. Specificity and localization of the hepatitis B virus-associated protein kinase. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):761–766. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.761-766.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton T., Zhou S., Standring D. N. RNA- and DNA-binding activities in hepatitis B virus capsid protein: a model for their roles in viral replication. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5232–5241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5232-5241.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. C., Lavine J. E., Chang L. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as wel as for reverse transcription. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):552–555. doi: 10.1038/344552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker-Niepmann M., Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. A short cis-acting sequence is required for hepatitis B virus pregenome encapsidation and sufficient for packaging of foreign RNA. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3389–3396. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kann M., Thomssen R., Köchel H. G., Gerlich W. H. Characterization of the endogenous protein kinase activity of the hepatitis B virus. Arch Virol Suppl. 1993;8:53–62. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9312-9_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köchel H. G., Kann M., Thomssen R. Identification of a binding site in the hepatitis B virus RNA pregenome for the viral Pol gene product. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):94–101. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90652-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Notvall L. Expression of hepatitis B virus core and precore antigens in insect cells and characterization of a core-associated kinase activity. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):222–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90247-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida A., Ohnuma H., Tsuda F., Yoshikawa A., Hoshi Y., Tanaka T., Kishimoto S., Akahane Y., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Phosphorylation in the carboxyl-terminal domain of the capsid protein of hepatitis B virus: evaluation with a monoclonal antibody. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6024–6030. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6024-6030.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassal M., Rieger A., Steinau O. Topological analysis of the hepatitis B virus core particle by cysteine-cysteine cross-linking. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 20;225(4):1013–1025. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90101-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassal M. The arginine-rich domain of the hepatitis B virus core protein is required for pregenome encapsidation and productive viral positive-strand DNA synthesis but not for virus assembly. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4107–4116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4107-4116.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus core protein contains a highly phosphorylated C terminus that is essential for replication but not for RNA packaging. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2995–3000. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2995-3000.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifer M., Standring D. N. A protease-sensitive hinge linking the two domains of the hepatitis B virus core protein is exposed on the viral capsid surface. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5548–5555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5548-5555.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifer M., Standring D. N. Recombinant human hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase is active in the absence of the nucleocapsid or the viral replication origin, DR1. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4513–4520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4513-4520.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifer M., Zhou S., Standring D. N. A micromolar pool of antigenically distinct precursors is required to initiate cooperative assembly of hepatitis B virus capsids in Xenopus oocytes. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):249–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.249-257.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavis J. E., Ganem D. Expression of functional hepatitis B virus polymerase in yeast reveals it to be the sole viral protein required for correct initiation of reverse transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4107–4111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uy A., Bruss V., Gerlich W. H., Köchel H. G., Thomssen R. Precore sequence of hepatitis B virus inducing e antigen and membrane association of the viral core protein. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. H., Seeger C. The reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B virus acts as a protein primer for viral DNA synthesis. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):663–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90599-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh C. T., Wong S. W., Fung Y. K., Ou J. H. Cell cycle regulation of nuclear localization of hepatitis B virus core protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6459–6463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M., Summers J. A domain of the hepadnavirus capsid protein is specifically required for DNA maturation and virus assembly. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2511–2517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2511-2517.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M., Summers J. Phosphorylation of the duck hepatitis B virus capsid protein associated with conformational changes in the C terminus. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):2965–2969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.5.2965-2969.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou S. L., Standring D. N. Production of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsidlike core particles in Xenopus oocytes: assembly occurs mainly in the cytoplasm and does not require the nucleus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5457–5464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5457-5464.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou S., Standring D. N. Hepatitis B virus capsid particles are assembled from core-protein dimer precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10046–10050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]