Abstract
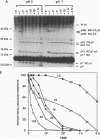
The proteolytic processing sites of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Gag precursor are cleaved in a sequential manner by the viral protease. We investigated the factors that regulate sequential processing. When full-length Gag protein was digested with recombinant HIV-1 protease in vitro, four of the five major processing sites in Gag were cleaved at rates that differ by as much as 400-fold. Three of these four processing sites were cleaved independently of the others. The CA/p2 site, however, was cleaved approximately 20-fold faster when the adjacent downstream p2/NC site was blocked from cleavage or when the p2 domain of Gag was deleted. These results suggest that the presence of a C-terminal p2 tail on processing intermediates slows cleavage at the upstream CA/p2 site. We also found that lower pH selectively accelerated cleavage of the CA/p2 processing site in the full-length precursor and as a peptide primarily by a sequence-based mechanism rather than by a change in protein conformation. Deletion of the p2 domain of Gag results in released virions that are less infectious despite the presence of the processed final products of Gag. These findings suggest that the p2 domain of HIV-1 Gag regulates the rate of cleavage at the CA/p2 processing site during sequential processing in vitro and in infected cells and that p2 may function in the proper assembly of virions.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bebenek K., Kunkel T. A. The use of native T7 DNA polymerase for site-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5408–5408. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billich A., Winkler G. Analysis of subsite preferences of HIV-1 proteinase using MA/CA junction peptides substituted at the P3-P1' positions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Oct;290(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90606-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billich S., Knoop M. T., Hansen J., Strop P., Sedlacek J., Mertz R., Moelling K. Synthetic peptides as substrates and inhibitors of human immune deficiency virus-1 protease. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17905–17908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., McGowan M. H., Kettner C. A., Schloss J. V., Erickson-Viitanen S., Yin F. H. High-level synthesis of recombinant HIV-1 protease and the recovery of active enzyme from inclusion bodies. Gene. 1990 Mar 15;87(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90308-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven R. C., Leure-duPree A. E., Erdie C. R., Wilson C. B., Wills J. W. Necessity of the spacer peptide between CA and NC in the Rous sarcoma virus gag protein. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6246–6252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6246-6252.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darke P. L., Nutt R. F., Brady S. F., Garsky V. M., Ciccarone T. M., Leu C. T., Lumma P. K., Freidinger R. M., Veber D. F., Sigal I. S. HIV-1 protease specificity of peptide cleavage is sufficient for processing of gag and pol polyproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):297–303. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80839-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiIanni C. L., Davis L. J., Holloway M. K., Herber W. K., Darke P. L., Kohl N. E., Dixon R. A. Characterization of an active single polypeptide form of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17348–17354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggleby R. G. Regression analysis of nonlinear Arrhenius plots: an empirical model and a computer program. Comput Biol Med. 1984;14(4):447–455. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(84)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis K. J., Morrison J. F. Buffers of constant ionic strength for studying pH-dependent processes. Methods Enzymol. 1982;87:405–426. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)87025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson-Viitanen S., Manfredi J., Viitanen P., Tribe D. E., Tritch R., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Loeb D. D., Swanstrom R. Cleavage of HIV-1 gag polyprotein synthesized in vitro: sequential cleavage by the viral protease. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Dec;5(6):577–591. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowda S. D., Stein B. S., Engleman E. G. Identification of protein intermediates in the processing of the p55 HIV-1 gag precursor in cells infected with recombinant vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8459–8462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. K., Deckman I. C., Minnich M. D., Culp J., Franklin S., Dreyer G. B., Tomaszek T. A., Jr, Debouck C., Meek T. D. Purification and biochemical characterization of recombinant simian immunodeficiency virus protease and comparison to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 27;30(34):8424–8434. doi: 10.1021/bi00098a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths J. T., Phylip L. H., Konvalinka J., Strop P., Gustchina A., Wlodawer A., Davenport R. J., Briggs R., Dunn B. M., Kay J. Different requirements for productive interaction between the active site of HIV-1 proteinase and substrates containing -hydrophobic*hydrophobic- or -aromatic*pro- cleavage sites. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 9;31(22):5193–5200. doi: 10.1021/bi00137a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlinger H. G., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Role of capsid precursor processing and myristoylation in morphogenesis and infectivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5781–5785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Benveniste R. E., Sowder R., Copeland T. D., Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. Molecular characterization of gag proteins from simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVMne). J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2587–2595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2587-2595.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Bowers M. A., Sowder R. C., 2nd, Serabyn S. A., Johnson D. G., Bess J. W., Jr, Arthur L. O., Bryant D. K., Fenselau C. Gag proteins of the highly replicative MN strain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: posttranslational modifications, proteolytic processings, and complete amino acid sequences. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1856–1865. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1856-1865.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyland L. J., Tomaszek T. A., Jr, Meek T. D. Human immunodeficiency virus-1 protease. 2. Use of pH rate studies and solvent kinetic isotope effects to elucidate details of chemical mechanism. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 27;30(34):8454–8463. doi: 10.1021/bi00098a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ido E., Han H. P., Kezdy F. J., Tang J. Kinetic studies of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease and its active-site hydrogen bond mutant A28S. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24359–24366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Power M. D., Masiarz F. R., Luciw P. A., Barr P. J., Varmus H. E. Characterization of ribosomal frameshifting in HIV-1 gag-pol expression. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):280–283. doi: 10.1038/331280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. H., Zack J. A., Knigge M., Paul D. A., Kempf D. J., Norbeck D. W., Swanstrom R. Partial inhibition of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease results in aberrant virus assembly and the formation of noninfectious particles. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4050–4055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4050-4055.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Kyushiki H., Sakamoto Y., Ikawa Y., Yoshinaka Y. Bovine leukemia virus matrix-associated protein MA(p15): further processing and formation of a specific complex with the dimer of the 5'-terminal genomic RNA fragment. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6845–6855. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6845-6855.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimpton J., Emerman M. Detection of replication-competent and pseudotyped human immunodeficiency virus with a sensitive cell line on the basis of activation of an integrated beta-galactosidase gene. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2232–2239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2232-2239.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler M., Katz R. A., Danho W., Leis J., Skalka A. M. Synthetic peptides as substrates and inhibitors of a retroviral protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4185–4189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Ingraham R. H., Skoog M. T., Wimmer E., Pallai P. V., Carter C. A. Activity of purified biosynthetic proteinase of human immunodeficiency virus on natural substrates and synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):807–811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Bebenek K., McClary J. Efficient site-directed mutagenesis using uracil-containing DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:125–139. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoote M. M., Coligan J. E., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Martin M. A., Venkatesan S. Structural characterization of reverse transcriptase and endonuclease polypeptides of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):771–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.771-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H., Farmerie W. G., Swanstrom R. Mutational analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease suggests functional homology with aspartic proteinases. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):111–121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.111-121.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louwagie J., McCutchan F. E., Peeters M., Brennan T. P., Sanders-Buell E., Eddy G. A., van der Groen G., Fransen K., Gershy-Damet G. M., Deleys R. Phylogenetic analysis of gag genes from 70 international HIV-1 isolates provides evidence for multiple genotypes. AIDS. 1993 Jun;7(6):769–780. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199306000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majer P., Urban J., Gregorová E., Konvalinka J., Novek P., Stehlíková J., Andreánsky M., Sedlácek J., Strop P. Specificity mapping of HIV-1 protease by reduced bond inhibitors. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Jul;304(1):1–8. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mervis R. J., Ahmad N., Lillehoj E. P., Raum M. G., Salazar F. H., Chan H. W., Venkatesan S. The gag gene products of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: alignment within the gag open reading frame, identification of posttranslational modifications, and evidence for alternative gag precursors. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3993–4002. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3993-4002.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. L., Bryan W. M., Fakhoury S. A., Magaard V. W., Huffman W. F., Dayton B. D., Meek T. D., Hyland L., Dreyer G. B., Metcalf B. W. Peptide substrates and inhibitors of the HIV-1 protease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):420–425. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J. C., Swanstrom R. A new pathway in the generation of defective retrovirus DNA. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.779-789.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Luftig R. B. Retroviral proteinases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:153–185. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partin K., Kräusslich H. G., Ehrlich L., Wimmer E., Carter C. Mutational analysis of a native substrate of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 proteinase. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3938–3947. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3938-3947.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Mattaliano R. J., Vogt V. M. Structure and processing of the p2 region of avian sarcoma and leukemia virus gag precursor polyproteins. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.50-58.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit S. C., Horwitz M. S., Engler J. A. Mutations of the precursor to the terminal protein of adenovirus serotypes 2 and 5. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5244–5250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5244-5250.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit S. C., Simsic J., Loeb D. D., Everitt L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Swanstrom R. Analysis of retroviral protease cleavage sites reveals two types of cleavage sites and the structural requirements of the P1 amino acid. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14539–14547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poorman R. A., Tomasselli A. G., Heinrikson R. L., Kézdy F. J. A cumulative specificity model for proteases from human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2, inferred from statistical analysis of an extended substrate data base. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14554–14561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Fisher A., Jagodzinski L. L., Mitsuya H., Liou R. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Complete nucleotide sequences of functional clones of the AIDS virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Spring;3(1):57–69. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. D., Phylip L. H., Farmerie W. G., Scarborough P. E., Alvarez A., Dunn B. M., Hirel P. H., Konvalinka J., Strop P., Pavlickova L. Sensitive, soluble chromogenic substrates for HIV-1 proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7733–7736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. D., Roberts R., Dunn B. M., Graves M. C., Kay J. Effective blocking of HIV-1 proteinase activity by characteristic inhibitors of aspartic proteinases. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 10;247(1):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter N. M., Eng G. Y., McCaslin D. R. Human skin tryptase: kinetic characterization of its spontaneous inactivation. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 16;32(10):2617–2625. doi: 10.1021/bi00061a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng N., Erickson-Viitanen S. Cleavage of p15 protein in vitro by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease is RNA dependent. J Virol. 1994 Oct;68(10):6207–6214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.10.6207-6214.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasselli A. G., Hui J. O., Sawyer T. K., Staples D. J., FitzGerald D. J., Chaudhary V. K., Pastan I., Heinrikson R. L. Interdomain hydrolysis of a truncated Pseudomonas exotoxin by the human immunodeficiency virus-1 protease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):408–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasselli A. G., Olsen M. K., Hui J. O., Staples D. J., Sawyer T. K., Heinrikson R. L., Tomich C. S. Substrate analogue inhibition and active site titration of purified recombinant HIV-1 protease. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):264–269. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaszek T. A., Jr, Moore M. L., Strickler J. E., Sanchez R. L., Dixon J. S., Metcalf B. W., Hassell A., Dreyer G. B., Brooks I., Debouck C. Proteolysis of an active site peptide of lactate dehydrogenase by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 27;31(42):10153–10168. doi: 10.1021/bi00157a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tritch R. J., Cheng Y. E., Yin F. H., Erickson-Viitanen S. Mutagenesis of protease cleavage sites in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gag polyprotein. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):922–930. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.922-930.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tözsér J., Bláha I., Copeland T. D., Wondrak E. M., Oroszlan S. Comparison of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 proteinases using oligopeptide substrates representing cleavage sites in Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tözsér J., Gustchina A., Weber I. T., Blaha I., Wondrak E. M., Oroszlan S. Studies on the role of the S4 substrate binding site of HIV proteinases. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):356–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80186-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tözsér J., Weber I. T., Gustchina A., Bláha I., Copeland T. D., Louis J. M., Oroszlan S. Kinetic and modeling studies of S3-S3' subsites of HIV proteinases. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4793–4800. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J., Konvalinka J., Stehlíková J., Gregorová E., Majer P., Soucek M., Andreánsky M., Fábry M., Strop P. Reduced-bond tight-binding inhibitors of HIV-1 protease. Fine tuning of the enzyme subsite specificity. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 17;298(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80010-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese F. D., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Biochemical and immunological analysis of human immunodeficiency virus gag gene products p17 and p24. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):795–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.795-801.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese F. D., Rahman R., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Immunological and chemical analysis of P6, the carboxyl-terminal fragment of HIV P15. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Fall;3(3):253–264. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. T., Stegeman-Olsen J., Zhang Y., Barklis E. Assembly of HIV GAG-B-galactosidase fusion proteins into virus particles. Virology. 1994 May 1;200(2):524–534. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S., Cramer W. A., Peterson A. A., Hermodson M., Montecucco C. Dynamic properties of membrane proteins: reversible insertion into membrane vesicles of a colicin E1 channel-forming peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7531–7535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Marzo Veronese F., Copeland T. D., DeVico A. L., Rahman R., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Characterization of highly immunogenic p66/p51 as the reverse transcriptase of HTLV-III/LAV. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1289–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.2418504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]