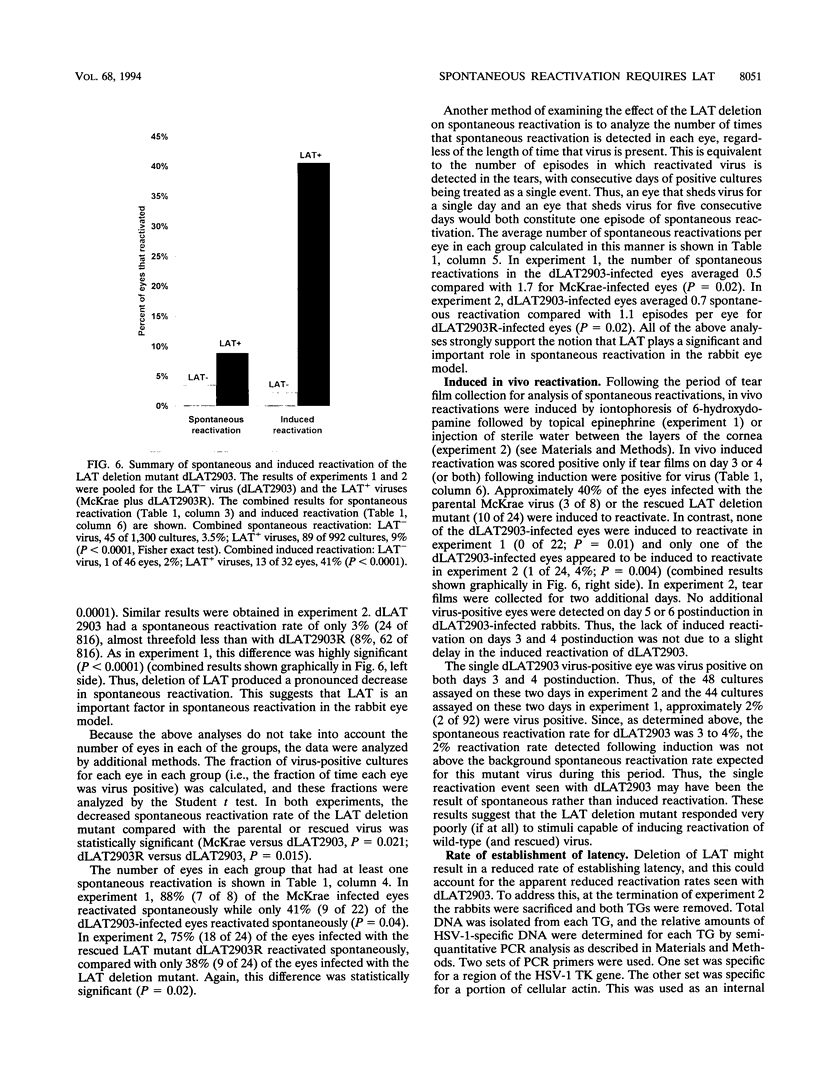
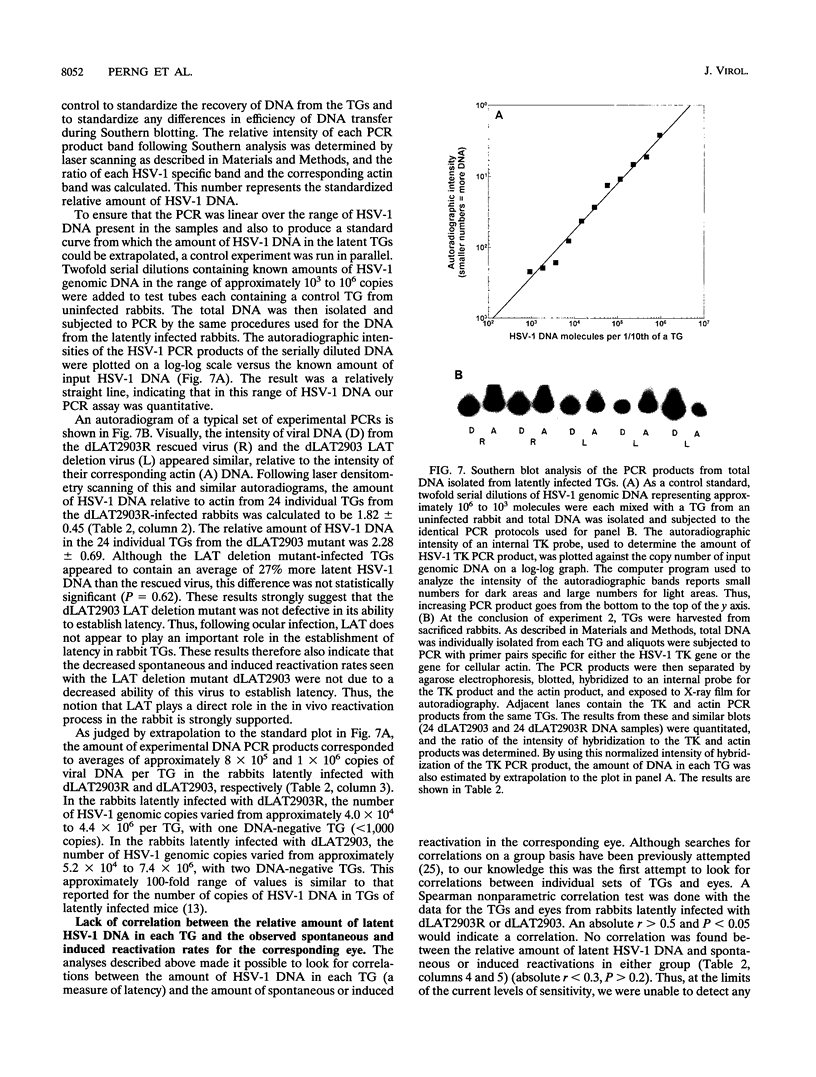
Abstract
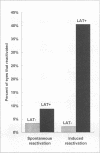
During herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) neuronal latency, the only viral RNA detected is from the latency-associated transcript (LAT) gene. We have made a LAT deletion mutant of McKrae, an HSV-1 strain with a very high in vivo spontaneous reactivation rate. This mutant (dLAT2903) lacks the LAT promoter and the first 1.6 kb of the 5' end of LAT. dLAT2903 was compared with its parental virus and with a rescued virus containing a restored LAT gene (dLAT2903R). Replication of the LAT mutant in tissue culture, rabbit eyes, and rabbit trigeminal ganglia was similar to that of the rescued and parental viruses. On the basis of semiquantitative PCR analysis of the amount of HSV-1 DNA in trigeminal ganglia, the LAT mutant was unimpaired in its ability to establish latency. In contrast, spontaneous reactivation of dLAT2903 in the rabbit ocular model of HSV-1 latency and reactivation was decreased to approximately 33% of normal. This decrease was highly significant (P < 0.0001) and demonstrates that in an HSV-1 strain with a high spontaneous reactivation rate, deletion of LAT can dramatically decrease in vivo spontaneous reactivation. We also report here that deletion of LAT appeared to eliminate rather than just reduce in vivo induced reactivation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block T. M., Spivack J. G., Steiner I., Deshmane S., McIntosh M. T., Lirette R. P., Fraser N. W. A herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript mutant reactivates with normal kinetics from latent infection. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3417–3426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3417-3426.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom D. C., Devi-Rao G. B., Hill J. M., Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K. Molecular analysis of herpes simplex virus type 1 during epinephrine-induced reactivation of latently infected rabbits in vivo. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1283–1292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1283-1292.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Smialek J. E., Straus S. E. Latent herpes simplex virus in human trigeminal ganglia. Detection of an immediate early gene "anti-sense" transcript by in situ hybridization. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 3;317(23):1427–1432. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712033172302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R., Seamans C., Lomedico P., McAndrew S. Versatile expression vectors for high-level synthesis of cloned gene products in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson A. T., Sederati F., Devi-Rao G., Flanagan W. M., Farrell M. J., Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Feldman L. T. Identification of the latency-associated transcript promoter by expression of rabbit beta-globin mRNA in mouse sensory nerve ganglia latently infected with a recombinant herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3844–3851. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3844-3851.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goins W. F., Sternberg L. R., Croen K. D., Krause P. R., Hendricks R. L., Fink D. J., Straus S. E., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. A novel latency-active promoter is contained within the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL flanking repeats. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2239–2252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2239-2252.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon Y. J., Johnson B., Romanowski E., Araullo-Cruz T. RNA complementary to herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0 gene demonstrated in neurons of human trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1832–1835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1832-1835.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon Y. J., Romanowski E., Araullo-Cruz T. A fast, simple reactivation method for the study of HSV-1 latency in the rabbit ocular model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990 May;31(5):921–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. M., Sedarati F., Javier R. T., Wagner E. K., Stevens J. G. Herpes simplex virus latent phase transcription facilitates in vivo reactivation. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. Y., Mocarski E. S. Herpes simplex virus latent RNA (LAT) is not required for latent infection in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7596–7600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javier R. T., Stevens J. G., Dissette V. B., Wagner E. K. A herpes simplex virus transcript abundant in latently infected neurons is dispensable for establishment of the latent state. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):254–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J. P., Bodin E. T., Coen D. M. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of herpes simplex virus DNA in ganglia of mice infected with replication-incompetent mutants. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4288–4295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4288-4295.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leib D. A., Bogard C. L., Kosz-Vnenchak M., Hicks K. A., Coen D. M., Knipe D. M., Schaffer P. A. A deletion mutant of the latency-associated transcript of herpes simplex virus type 1 reactivates from the latent state with reduced frequency. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2893–2900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2893-2900.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leib D. A., Nadeau K. C., Rundle S. A., Schaffer P. A. The promoter of the latency-associated transcripts of herpes simplex virus type 1 contains a functional cAMP-response element: role of the latency-associated transcripts and cAMP in reactivation of viral latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):48–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesburn A. B., Robinson C., Dickinson R. Adenine arabinoside effect on experimental idoxuridine-resistant herpes simplex infection. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Apr;13(4):302–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perng G. C., Ghiasi H., Kaiwar R., Nesburn A. B., Wechsler S. L. An improved method for cloning portions of the repeat regions of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol Methods. 1994 Feb;46(2):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(94)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., McGeoch D. J. The DNA sequences of the long repeat region and adjoining parts of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Nov;69(Pt 11):2831–2846. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-11-2831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock D. L., Nesburn A. B., Ghiasi H., Ong J., Lewis T. L., Lokensgard J. R., Wechsler S. L. Detection of latency-related viral RNAs in trigeminal ganglia of rabbits latently infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3820–3826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3820-3826.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawtell N. M., Thompson R. L. Herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcription unit promotes anatomical site-dependent establishment and reactivation from latency. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2157–2169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2157-2169.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimozuma M., Drew W. L., Miner R. C., Epstein W. L., Fukuyama K. Direct inactivation of herpes simplex virus type-2 by rat epidermal protein. Antiviral Res. 1992 Jun;18(2):179–189. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(92)90037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Fraser N. W. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcripts in the trigeminal ganglia of mice during acute infection and reactivation of latent infection. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1479–1485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1479-1485.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Spivack J. G., Lirette R. P., Brown S. M., MacLean A. R., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Fraser N. W. Herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcripts are evidently not essential for latent infection. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):505–511. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Spivack J. G., O'Boyle D. R., 2nd, Lavi E., Fraser N. W. Latent herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription in human trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3493–3496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3493-3496.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G. B., Cook M. L., Feldman L. T. RNA complementary to a herpesvirus alpha gene mRNA is prominent in latently infected neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2434993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasu T., Furuta Y., Sato K. C., Fukuda S., Inuyama Y., Nagashima K. Detection of latent herpes simplex virus DNA and RNA in human geniculate ganglia by the polymerase chain reaction. Acta Otolaryngol. 1992 Nov;112(6):1004–1011. doi: 10.3109/00016489209137502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trousdale M. D., Steiner I., Spivack J. G., Deshmane S. L., Brown S. M., MacLean A. R., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Fraser N. W. In vivo and in vitro reactivation impairment of a herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript variant in a rabbit eye model. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6989–6993. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6989-6993.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G., Feldman L. T., Dobson A. T., Zhang Y. F., Flanagan W. M., Stevens J. G. Physical characterization of the herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript in neurons. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1194–1202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1194-1202.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. K., Flanagan W. M., Devi-Rao G., Zhang Y. F., Hill J. M., Anderson K. P., Stevens J. G. The herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript is spliced during the latent phase of infection. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4577–4585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4577-4585.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Nesburn A. B., Watson R., Slanina S. M., Ghiasi H. Fine mapping of the latency-related gene of herpes simplex virus type 1: alternative splicing produces distinct latency-related RNAs containing open reading frames. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4051–4058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4051-4058.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Nesburn A. B., Watson R., Slanina S., Ghiasi H. Fine mapping of the major latency-related RNA of herpes simplex virus type 1 in humans. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):3101–3106. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-3101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Nesburn A. B., Zwaagstra J., Ghiasi H. Sequence of the latency-related gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):168–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaagstra J. C., Ghiasi H., Nesburn A. B., Wechsler S. L. Identification of a major regulatory sequence in the latency associated transcript (LAT) promoter of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Virology. 1991 May;182(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90672-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaagstra J. C., Ghiasi H., Slanina S. M., Nesburn A. B., Wheatley S. C., Lillycrop K., Wood J., Latchman D. S., Patel K., Wechsler S. L. Activity of herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript (LAT) promoter in neuron-derived cells: evidence for neuron specificity and for a large LAT transcript. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5019–5028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5019-5028.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaagstra J., Ghiasi H., Nesburn A. B., Wechsler S. L. In vitro promoter activity associated with the latency-associated transcript gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):2163–2169. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-2163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]