Abstract
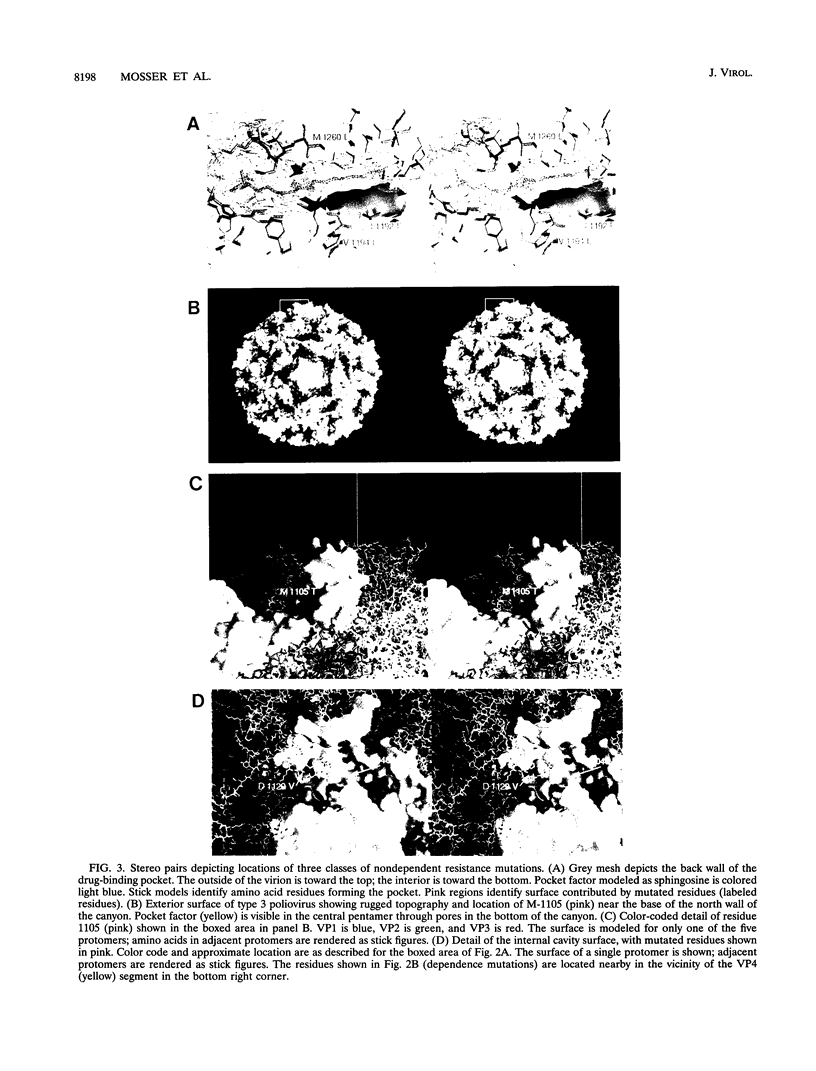
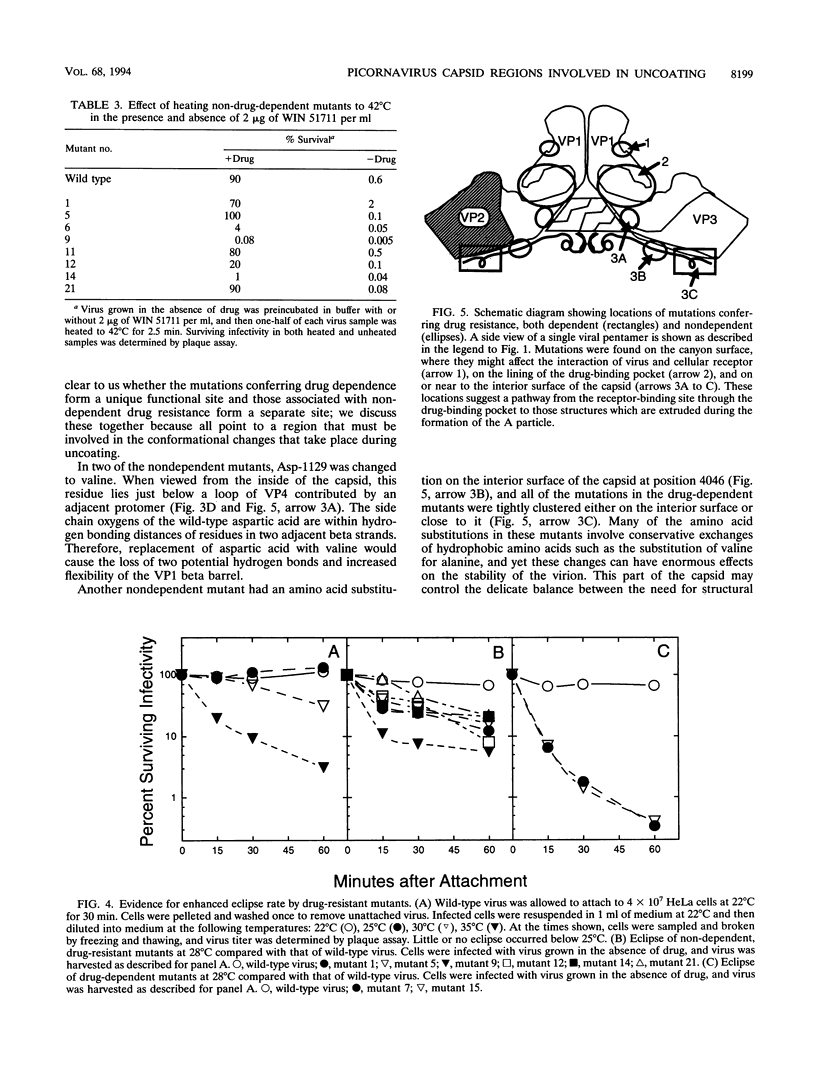
We have previously described the use of an uncoating inhibitor, WIN 51711, to select drug-resistant mutants of the Sabin strain of poliovirus type 3. Two-thirds of the mutants proved to be dependent on the drug for plaque formation because of extreme thermolability (A. G. Mosser and R. R. Rueckert, J. Virol. 67:1246-1254, 1993). Here we report the responsible mutations; all were traced to single amino acid substitutions. Mutations conferring dependence and thermolability occurred in all four capsid proteins (VP1 to VP4), but all were clustered near residue 53 of VP4 at the inner capsid surface. Amino acid substitutions of the remaining non-drug-dependent mutants were mapped to three distinct loci: (i) on or near the inner capsid surface, at VP4 residue 46 or VP1 residue 129, in the vicinity of the drug dependence substitutions; (ii) at residues 192, 194, and 260 in the lining of the VP1 beta barrel, which is the drug-binding site; and (iii) at VP1 residue 105 on the edge of the canyon surrounding the fivefold axis of symmetry, the putative receptor-binding site. All of the mutations increased the eclipse rate of cell-attached virus. Such mutants help identify parts of the capsid that play a role in viral uncoating functions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Air G. M. Nucleotide sequence coding for the "signal peptide" and N terminus of the hemagglutinin from an asian (H2N2) strain of influenza virus. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):468–472. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger J., Minor I., Kremer M. J., Oliveira M. A., Smith T. J., Griffith J. P., Guerin D. M., Krishnaswamy S., Luo M., Rossmann M. G. Structural analysis of a series of antiviral agents complexed with human rhinovirus 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3304–3308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., McSharry J. J., Lawrence G. W. Effect of arildone on modifications of poliovirus in vitro. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Condra J. H., Mizutani S., Callahan P. L., Davies M. E., Murcko M. A. Evidence for the direct involvement of the rhinovirus canyon in receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couderc T., Hogle J., Le Blay H., Horaud F., Blondel B. Molecular characterization of mouse-virulent poliovirus type 1 Mahoney mutants: involvement of residues of polypeptides VP1 and VP2 located on the inner surface of the capsid protein shell. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3808–3817. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3808-3817.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sena J., Mandel B. Studies on the in vitro uncoating of poliovirus. II. Characteristics of the membrane-modified particle. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):554–566. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everaert L., Vrijsen R., Boeyé A. Eclipse products of poliovirus after cold-synchronized infection of HeLa cells. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90512-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichot O., Girard M. An improved method for sequencing of RNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6162–6162. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filman D. J., Syed R., Chow M., Macadam A. J., Minor P. D., Hogle J. M. Structural factors that control conformational transitions and serotype specificity in type 3 poliovirus. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1567–1579. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox M. P., Otto M. J., McKinlay M. A. Prevention of rhinovirus and poliovirus uncoating by WIN 51711, a new antiviral drug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricks C. E., Hogle J. M. Cell-induced conformational change in poliovirus: externalization of the amino terminus of VP1 is responsible for liposome binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1934–1945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1934-1945.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Davis G., Meyer A. M., Forte C. P., Yost S. C., Marlor C. W., Kamarck M. E., McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberger M., Pevear D., Diana G. D., Kuechler E., Blaas D. Stabilization of human rhinovirus serotype 2 against pH-induced conformational change by antiviral compounds. J Gen Virol. 1991 Feb;72(Pt 2):431–433. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-2-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez Yafal A., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Hogle J. M. Characterization of poliovirus conformational alteration mediated by soluble cell receptors. Virology. 1993 Nov;197(1):501–505. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz B. A., Rueckert R. R., Shepard D. A., Dutko F. J., McKinlay M. A., Fancher M., Rossmann M. G., Badger J., Smith T. J. Genetic and molecular analyses of spontaneous mutants of human rhinovirus 14 that are resistant to an antiviral compound. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2476–2485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2476-2485.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K., DARNELL J. E., Jr The adsorption and early fate of purified poliovirus in HeLa cells. Virology. 1961 Apr;13:439–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Freistadt M. S., Racaniello V. R. Neutralization of poliovirus by cell receptors expressed in insect cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4697–4702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4697-4702.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K. Mutations in VP1 of poliovirus specifically affect both encapsidation and release of viral RNA. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):195–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.195-206.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. M., Monroe S. S., Rueckert R. R. Role of maturation cleavage in infectivity of picornaviruses: activation of an infectosome. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2110–2122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2110-2122.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Yafal A. G., Lee Y. M., Hogle J., Chow M. Poliovirus neutralization by antibodies to internal epitopes of VP4 and VP1 results from reversible exposure of these sequences at physiological temperature. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3965–3970. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3965-3970.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Gosser L. B., Kauer J. C. Early alteration of poliovirus in infected cells and its specific inhibition. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jun;27(3):329–342. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macadam A. J., Arnold C., Howlett J., John A., Marsden S., Taffs F., Reeve P., Hamada N., Wareham K., Almond J. Reversion of the attenuated and temperature-sensitive phenotypes of the Sabin type 3 strain of poliovirus in vaccinees. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):408–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Wychowski C., Couderc T., Crainic R., Hogle J., Girard M. Engineering a poliovirus type 2 antigenic site on a type 1 capsid results in a chimaeric virus which is neurovirulent for mice. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2839–2847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinlay M. A. WIN 51711, a new systematically active broad-spectrum antipicornavirus agent. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Sep;16(3):284–286. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medappa K. C., McLean C., Rueckert R. R. On the structure of rhinovirus 1A. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Dunn G., Evans D. M., Magrath D. I., John A., Howlett J., Phillips A., Westrop G., Wareham K., Almond J. W. The temperature sensitivity of the Sabin type 3 vaccine strain of poliovirus: molecular and structural effects of a mutation in the capsid protein VP3. J Gen Virol. 1989 May;70(Pt 5):1117–1123. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-5-1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscufo N., Yafal A. G., Rogove A., Hogle J., Chow M. A mutation in VP4 defines a new step in the late stages of cell entry by poliovirus. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):5075–5078. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.5075-5078.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss E. G., Racaniello V. R. Host range determinants located on the interior of the poliovirus capsid. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1067–1074. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08046.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser A. G., Rueckert R. R. WIN 51711-dependent mutants of poliovirus type 3: evidence that virions decay after release from cells unless drug is present. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1246–1254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1246-1254.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira M. A., Zhao R., Lee W. M., Kremer M. J., Minor I., Rueckert R. R., Diana G. D., Pevear D. C., Dutko F. J., McKinlay M. A. The structure of human rhinovirus 16. Structure. 1993 Sep 15;1(1):51–68. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson N. H., Kolatkar P. R., Oliveira M. A., Cheng R. H., Greve J. M., McClelland A., Baker T. S., Rossmann M. G. Structure of a human rhinovirus complexed with its receptor molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):507–511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevear D. C., Fancher M. J., Felock P. J., Rossmann M. G., Miller M. S., Diana G., Treasurywala A. M., McKinlay M. A., Dutko F. J. Conformational change in the floor of the human rhinovirus canyon blocks adsorption to HeLa cell receptors. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2002–2007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2002-2007.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rombaut B., Andries K., Boeyé A. A comparison of WIN 51711 and R 78206 as stabilizers of poliovirus virions and procapsids. J Gen Virol. 1991 Sep;72(Pt 9):2153–2157. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-9-2153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard D. A., Heinz B. A., Rueckert R. R. WIN 52035-2 inhibits both attachment and eclipse of human rhinovirus 14. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2245–2254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2245-2254.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Kremer M. J., Luo M., Vriend G., Arnold E., Kamer G., Rossmann M. G., McKinlay M. A., Diana G. D., Otto M. J. The site of attachment in human rhinovirus 14 for antiviral agents that inhibit uncoating. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1286–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.3018924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]