Abstract
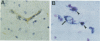
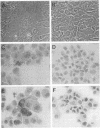
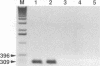
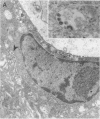
The perivascular location of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells suggests that the virus enters the central nervous system (CNS) by traversing the blood-brain barrier (BBB). In this study, the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) macaque model was used to determine whether SIV infects CNS endothelial cells. SIV RNA was detected in capillary endothelial cells in brain sections from animals parenterally inoculated with a neurovirulent strain of SIV by double immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization and by reverse transcriptase-in situ PCR. These in vivo observations were extended by examining whether SIV replicated productively in cultured macaque brain endothelial cells (MBEC). A neurovirulent strain, SIVmac239/17E-Br, replicated productively in MBEC as determined by the presence of viral cytopathic effect (syncytia), viral DNA by PCR, viral RNA by in situ hybridization, and viral antigen by immunohistochemistry and by the production of high titers of cell-free virus. Virus replication was confirmed by electron microscopy. In contrast, a nonneurovirulent strain, SIVmac239, did not infect MBEC. Infection of the endothelial cells was not blocked by soluble CD4. Thus, endothelial cells may provide a CD4-independent pathway of virus entry to the CNS. In addition, damage to the BBB as a result of endothelial cell infection may provide a mechanism for amplification of viral load in the CNS and may contribute to the CNS dysfunction that characterizes AIDS dementia and SIV encephalitis. These data suggest that MBEC may serve a selective role in determining virus entry to the CNS.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. G., Hauer D., Sharma D. P., Joag S. V., Narayan O., Zink M. C., Clements J. E. Analysis of envelope changes acquired by SIVmac239 during neuroadaption in rhesus macaques. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):616–626. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budka H. Neuropathology of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Brain Pathol. 1991 Apr;1(3):163–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1991.tb00656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilbott D. J., Peress N., Burger H., LaNeve D., Orenstein J., Gendelman H. E., Seidman R., Weiser B. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in spinal cords of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with myelopathy: expression and replication in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3337–3341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G. W., Asbury A. K., Diamond I. Pathogenesis of lead encephalopathy. Uptake of lead and reaction of brain capillaries. Arch Neurol. 1974 Dec;31(6):382–389. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490420048005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Cimino E. F., Robbins D. S., Broadwell R. D., Powers J. M., Ruscetti S. K. Cellular tropism and localization in the rodent nervous system of a neuropathogenic variant of Friend murine leukemia virus. Lab Invest. 1992 Sep;67(3):314–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalaria R. N., Gravina S. A., Schmidley J. W., Perry G., Harik S. I. The glucose transporter of the human brain and blood-brain barrier. Ann Neurol. 1988 Dec;24(6):757–764. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kure K., Lyman W. D., Weidenheim K. M., Dickson D. W. Cellular localization of an HIV-1 antigen in subacute AIDS encephalitis using an improved double-labeling immunohistochemical method. Am J Pathol. 1990 May;136(5):1085–1092. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafon M. E., Steffan A. M., Gendrault J. L., Klein-Soyer C., Gloeckler-Tondre L., Royer C., Kirn A. Interaction of human immunodeficiency virus with human macrovascular endothelial cells in vitro. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Sep;8(9):1567–1570. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. V., Bloom F. E., Pauza C. D., Nelson J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of human brain capillary endothelial cells occurs via a CD4/galactosylceramide-independent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10474–10478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray E. A., Rausch D. M., Lendvay J., Sharer L. R., Eiden L. E. Cognitive and motor impairments associated with SIV infection in rhesus monkeys. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1246–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.1546323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuwelt E. A., Pagel M. A., Dix R. D. Delivery of ultraviolet-inactivated 35S-herpesvirus across an osmotically modified blood-brain barrier. J Neurosurg. 1991 Mar;74(3):475–479. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.74.3.0475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. H., Lavi E., Blank K. J., Gaulton G. N. Intracerebral hemorrhages and syncytium formation induced by endothelial cell infection with a murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6015–6024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6015-6024.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petito C. K., Cash K. S. Blood-brain barrier abnormalities in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: immunohistochemical localization of serum proteins in postmortem brain. Ann Neurol. 1992 Nov;32(5):658–666. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power C., Kong P. A., Crawford T. O., Wesselingh S., Glass J. D., McArthur J. C., Trapp B. D. Cerebral white matter changes in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia: alterations of the blood-brain barrier. Ann Neurol. 1993 Sep;34(3):339–350. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Re M. C., Furlini G., Cenacchi G., Preda P., La Placa M. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of endothelial cells in vitro. Microbiologica. 1991 Apr;14(2):149–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. H. Evidence of serum-protein leakage across the blood-brain barrier in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1991 Mar;50(2):171–183. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199103000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostad S. W., Sumi S. M., Shaw C. M., Olson K., McDougall J. K. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in brains with AIDS-related leukoencephalopathy. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987;3(4):363–373. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharer L. R., Baskin G. B., Cho E. S., Murphey-Corb M., Blumberg B. M., Epstein L. G. Comparison of simian immunodeficiency virus and human immunodeficiency virus encephalitides in the immature host. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S108–S112. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharer L. R., Epstein L. G., Cho E. S., Joshi V. V., Meyenhofer M. F., Rankin L. F., Petito C. K. Pathologic features of AIDS encephalopathy in children: evidence for LAV/HTLV-III infection of brain. Hum Pathol. 1986 Mar;17(3):271–284. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., DeGirolami U., Hénin D., Bolgert F., Hauw J. J. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) leukoencephalopathy and the microcirculation. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1990 Jul;49(4):357–370. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199007000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffan A. M., Lafon M. E., Gendrault J. L., Schweitzer C., Royer C., Jaeck D., Arnaud J. P., Schmitt M. P., Aubertin A. M., Kirn A. Primary cultures of endothelial cells from the human liver sinusoid are permissive for human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1582–1586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoica G., Illanes O., Tasca S. I., Wong P. K. Temporal central and peripheral nervous system changes induced by a paralytogenic mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB. Lab Invest. 1993 Dec;69(6):724–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., O'Leary T. J., Baskin G. B., Benveniste R., Harris C. A., Nara P. L., Rhodes R. H. Immunohistochemical localization of human and simian immunodeficiency viral antigens in fixed tissue sections. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):199–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink M. C., Yager J. A., Myers J. D. Pathogenesis of caprine arthritis encephalitis virus. Cellular localization of viral transcripts in tissues of infected goats. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):843–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]