Abstract
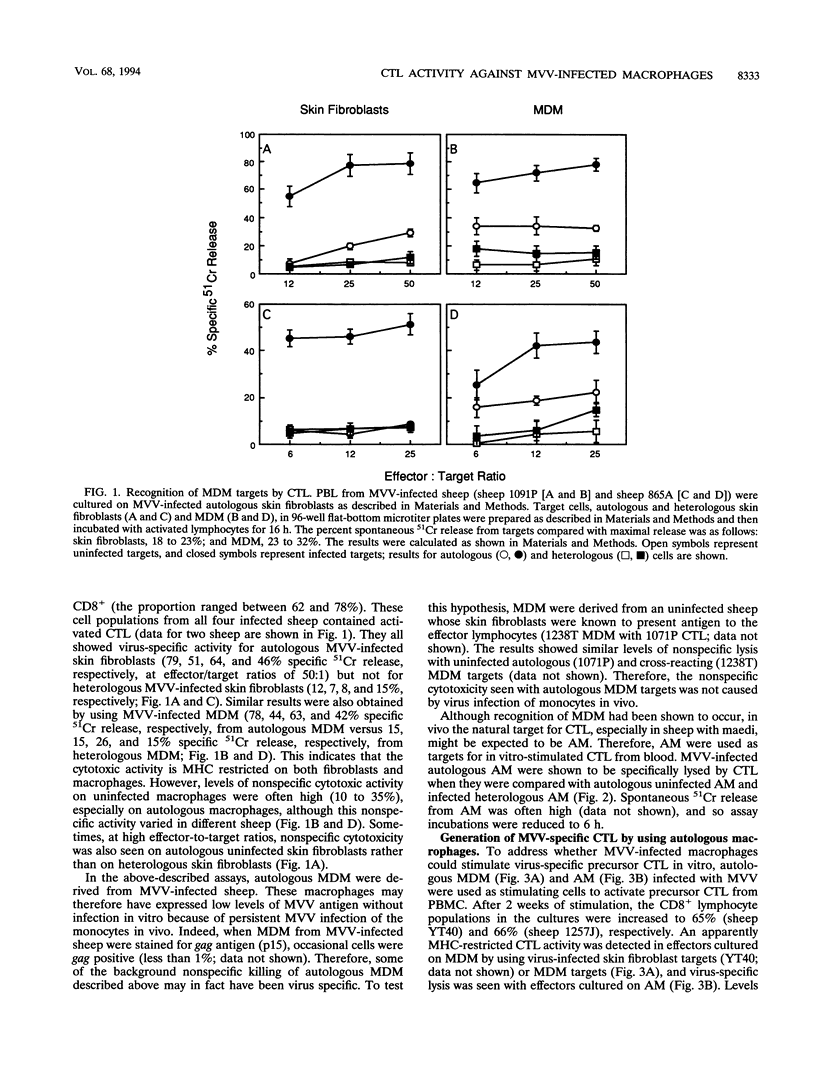
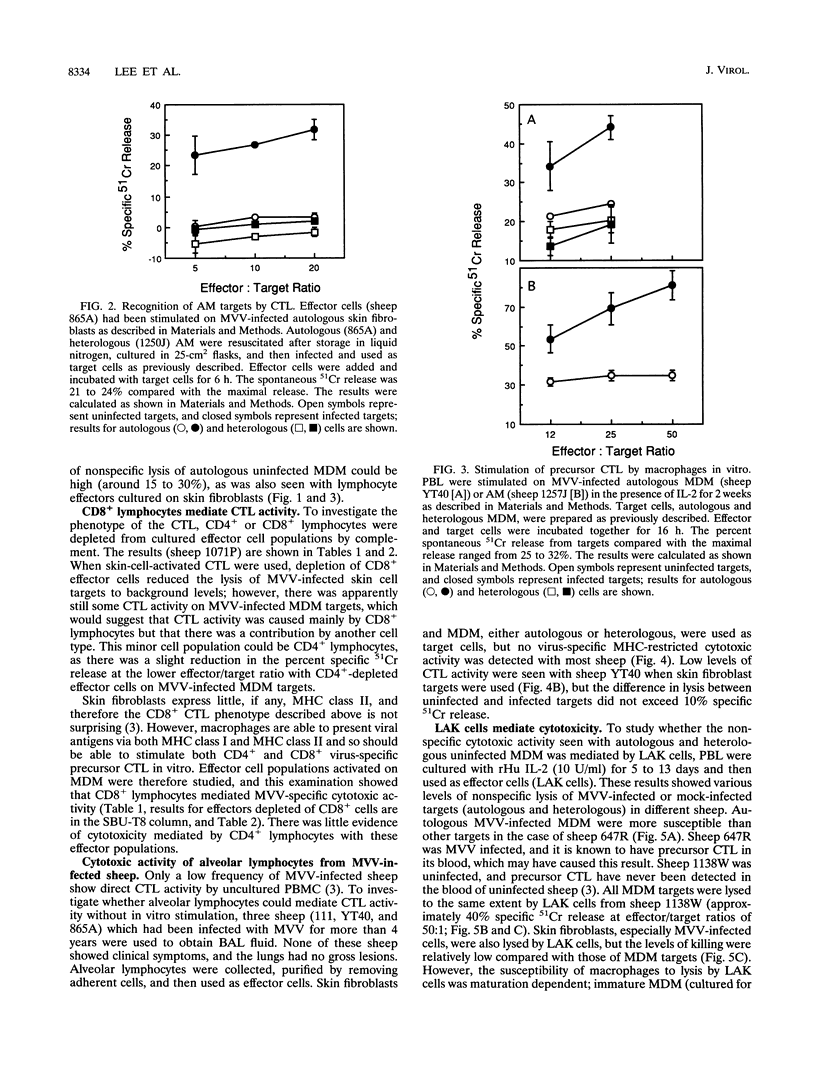
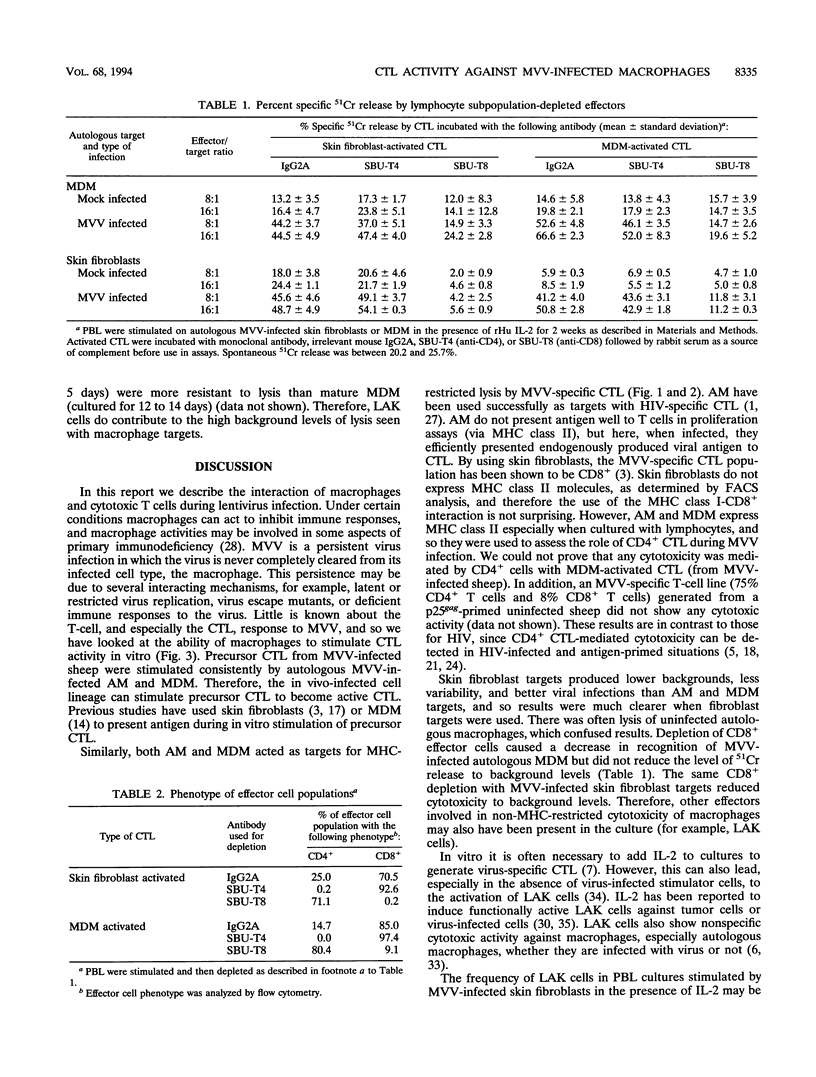
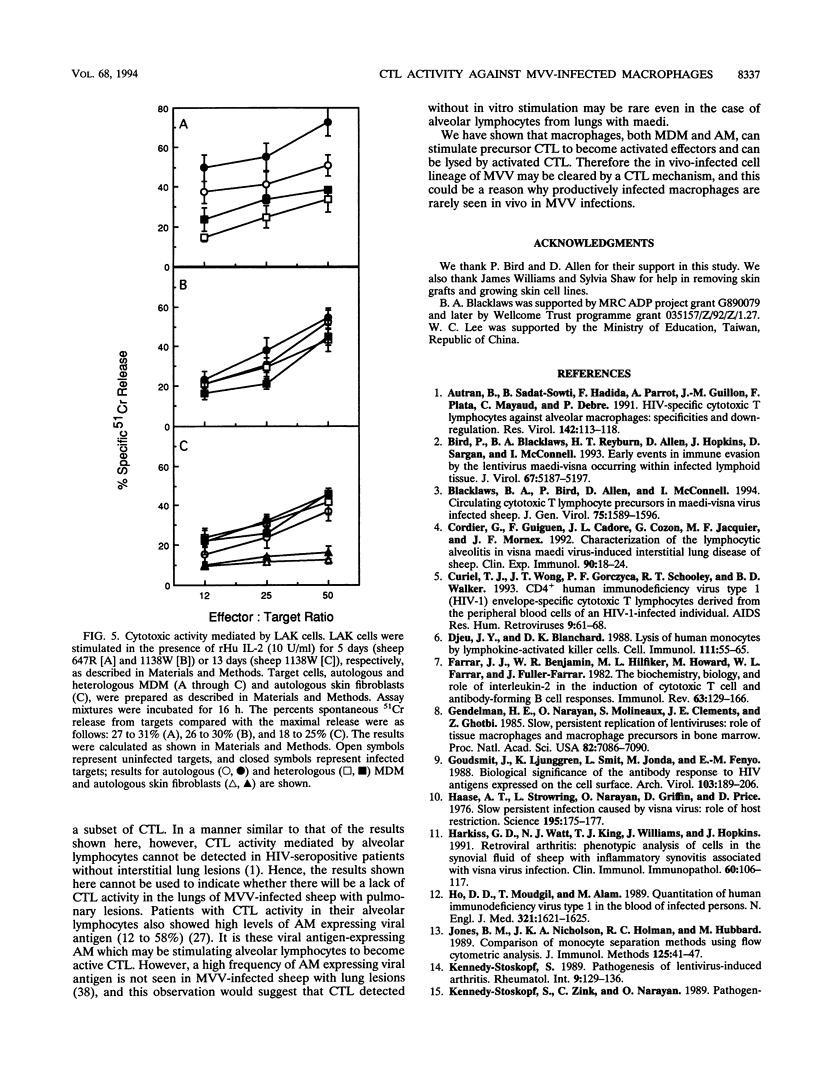
The cell type predominantly infected by maedi-visna virus (MVV) is the macrophage, and we have looked at the ability of MVV-infected macrophages to interact with cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), important effector cells against virus infections. MVV-specific CTL precursors were detected, after in vitro culture with MVV antigen and recombinant human interleukin-2, in peripheral blood lymphocytes of all MVV-infected sheep. MVV-infected monocyte-derived macrophages and alveolar macrophages were able to stimulate CTL activity in vitro and were targets for these activated CTL. The major effector cell population using MVV-infected macrophage targets was CD8+ lymphocytes, although another population, lymphokine-activated killer cells, may also have been involved. There was no direct cytotoxic activity found in alveolar lymphocytes from MVV-infected sheep without lung lesions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Autran B., Sadat-Sowti B., Hadida F., Parrot A., Guillon J. M., Plata F., Mayaud C., Debré P. HIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes against alveolar macrophages: specificities and downregulation. Res Virol. 1991 Mar-Jun;142(2-3):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(91)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird P., Blacklaws B., Reyburn H. T., Allen D., Hopkins J., Sargan D., McConnell I. Early events in immune evasion by the lentivirus maedi-visna occurring within infected lymphoid tissue. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5187–5197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5187-5197.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklaws B. A., Bird P., Allen D., McConnell I. Circulating cytotoxic T lymphocyte precursors in maedi-visna virus-infected sheep. J Gen Virol. 1994 Jul;75(Pt 7):1589–1596. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-7-1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier G., Guiguen F., Cadoré J. L., Cozon G., Jacquier M. F., Mornex J. F. Characterization of the lymphocytic alveolitis in visna-maedi virus-induced interstitial lung disease of sheep. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Oct;90(1):18–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiel T. J., Wong J. T., Gorczyca P. F., Schooley R. T., Walker B. D. CD4+ human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes derived from the peripheral blood cells of an HIV-1-infected individual. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Jan;9(1):61–68. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Blanchard D. K. Lysis of human monocytes by lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jan;111(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Benjamin W. R., Hilfiker M. L., Howard M., Farrar W. L., Fuller-Farrar J. The biochemistry, biology, and role of interleukin 2 in the induction of cytotoxic T cell and antibody-forming B cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:129–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Narayan O., Molineaux S., Clements J. E., Ghotbi Z. Slow, persistent replication of lentiviruses: role of tissue macrophages and macrophage precursors in bone marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7086–7090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Ljunggren K., Smit L., Jondal M., Fenyö E. M., Jonda M. Biological significance of the antibody response to HIV antigens expressed on the cell surface. Arch Virol. 1988;103(3-4):189–206. doi: 10.1007/BF01311092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Stowring L., Narayan P., Griffin D., Price D. Slow persistent infection caused by visna virus: role of host restriction. Science. 1977 Jan 14;195(4274):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.188133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkiss G. D., Watt N. J., King T. J., Williams J., Hopkins J. Retroviral arthritis: phenotypic analysis of cells in the synovial fluid of sheep with inflammatory synovitis associated with visna virus infection. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Jul;60(1):106–117. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90116-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Moudgil T., Alam M. Quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the blood of infected persons. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 14;321(24):1621–1625. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912143212401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. M., Nicholson J. K., Holman R. C., Hubbard M. Comparison of monocyte separation methods using flow cytometric analysis. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Dec 20;125(1-2):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy-Stoskopf S. Pathogenesis of lentivirus-induced arthritis. A review. Rheumatol Int. 1989;9(3-5):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00271869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlade-Demoyen P., Michel F., Hoffenbach A., Vilmer E., Dadaglio G., Garicia-Pons F., Mayaud C., Autran B., Wain-Hobson S., Plata F. Immune recognition of AIDS virus antigens by human and murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):1949–1957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtensteiger C. A., Cheevers W. P., Davis W. C. CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes against antigenic variants of caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1993 Oct;74(Pt 10):2111–2116. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-10-2111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littaua R. A., Oldstone M. B., Takeda A., Ennis F. A. A CD4+ cytotoxic T-lymphocyte clone to a conserved epitope on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 p24: cytotoxic activity and secretion of interleukin-2 and interleukin-6. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):608–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.608-611.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luján L., Begara I., Collie D. D., Watt N. J. Phenotypic analysis of cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood of maedi visna-infected sheep. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Feb;91(2):272–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox J. F., Mackay C. R., Brandon M. R. Surface antigens, SBU-T4 and SBU-T8, of sheep T lymphocyte subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):739–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Hoffenbach A., Froussard P., Langlade-Demoyen P., Kaczorek M., Kieny M. P., Plata F. HIV-1 env, nef, and gag-specific T-cell immunity in mice: conserved epitopes in nef p27 and gag p25 proteins. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Apr;8(4):469–478. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Clements J. E. Biology and pathogenesis of lentiviruses. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jul;70(Pt 7):1617–1639. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-7-1617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orentas R. J., Hildreth J. E., Obah E., Polydefkis M., Smith G. E., Clements M. L., Siliciano R. F. Induction of CD4+ human cytolytic T cells specific for HIV-infected cells by a gp160 subunit vaccine. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1234–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.2190315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Ab B. K., Van Embden J. D., Thole J. E., Kiessling R. The recombinant 65-kD heat shock protein of Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin/M. tuberculosis is a target molecule for CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes that lyse human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1947–1952. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Trinchieri G., Jackson A., Warner N. L., Faust J., Rumpold H., Kraft D., Lanier L. L. The Fc receptor for IgG on human natural killer cells: phenotypic, functional, and comparative studies with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):180–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata F., Autran B., Martins L. P., Wain-Hobson S., Raphaël M., Mayaud C., Denis M., Guillon J. M., Debré P. AIDS virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in lung disorders. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):348–351. doi: 10.1038/328348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riviere Y., Tanneau-Salvadori F., Regnault A., Lopez O., Sansonetti P., Guy B., Kieny M. P., Fournel J. J., Montagnier L. Human immunodeficiency virus-specific cytotoxic responses of seropositive individuals: distinct types of effector cells mediate killing of targets expressing gag and env proteins. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2270–2277. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2270-2277.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook A. H., Masur H., Lane H. C., Frederick W., Kasahara T., Macher A. M., Djeu J. Y., Manischewitz J. F., Jackson L., Fauci A. S. Interleukin-2 enhances the depressed natural killer and cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic activities of lymphocytes from patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):398–403. doi: 10.1172/JCI110981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargan D. R., Bennet I. D., Cousens C., Roy D. J., Blacklaws B. A., Dalziel R. G., Watt N. J., McConnell I. Nucleotide sequence of EV1, a British isolate of maedi-visna virus. J Gen Virol. 1991 Aug;72(Pt 8):1893–1903. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-8-1893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sissons J. G., Oldstone M. B. Antibody-mediated destruction of virus-infected cells. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:209–260. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60045-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondel P. M., Hank J. A., Kohler P. C., Chen B. P., Minkoff D. Z., Molenda J. A. Destruction of autologous human lymphocytes by interleukin 2-activated cytotoxic cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):502–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streck R. J., Helinski E. H., Ovak G. M., Pauly J. L. Lysis of autologous human macrophages by lymphokine-activated killer cells: interaction of effector cell and target cell conjugates analyzed by scanning electron microscopy. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Sep;48(3):237–246. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. K., Cohen J. J. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Jun;4(3):338–343. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90086-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanham G., Kestens L., Gigase P., Colebunders R., Vandenbruaene M., Brijs L., Ceuppens J. L. Evidence for circulating activated cytotoxic T cells in HIV-infected subjects before the onset of opportunistic infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Oct;82(1):3–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vowels B. R., Gershwin M. E., Gardner M. B., Ahmed-Ansari A., McGraw T. P. Characterization of simian immunodeficiency virus-specific T-cell-mediated cytotoxic response of infected rhesus macaques. AIDS. 1989 Dec;3(12):785–792. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198912000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt N. J., MacIntyre N., Collie D., Sargan D., McConnell I. Phenotypic analysis of lymphocyte populations in the lungs and regional lymphoid tissue of sheep naturally infected with maedi visna virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Nov;90(2):204–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb07929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinhold K. J., Lyerly H. K., Matthews T. J., Tyler D. S., Ahearne P. M., Stine K. C., Langlois A. J., Durack D. T., Bolognesi D. P. Cellular anti-GP120 cytolytic reactivities in HIV-1 seropositive individuals. Lancet. 1988 Apr 23;1(8591):902–905. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91713-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Miller M. D., Watkins D. I., Snyder G. B., Chase N. E., Mazzara G. P., Gritz L., Panicali D. L., Letvin N. L. Two distinct lymphocyte populations mediate simian immunodeficiency virus envelope-specific target cell lysis. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3740–3746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


