Abstract
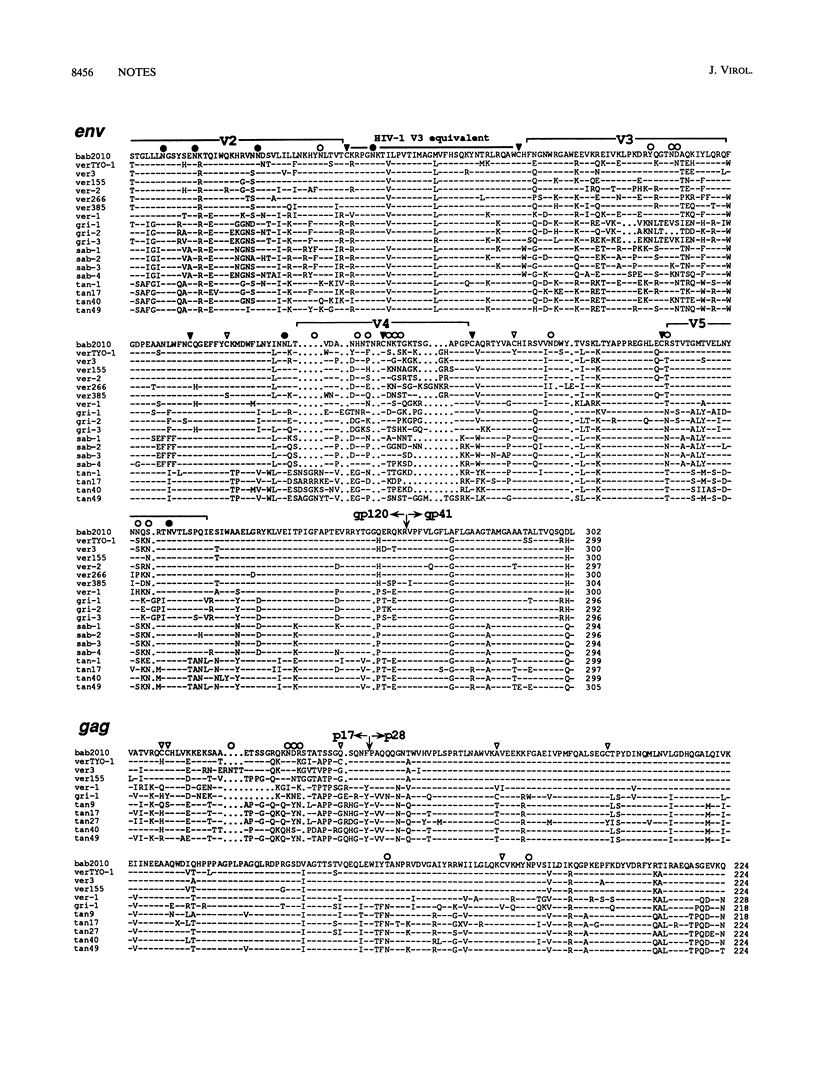
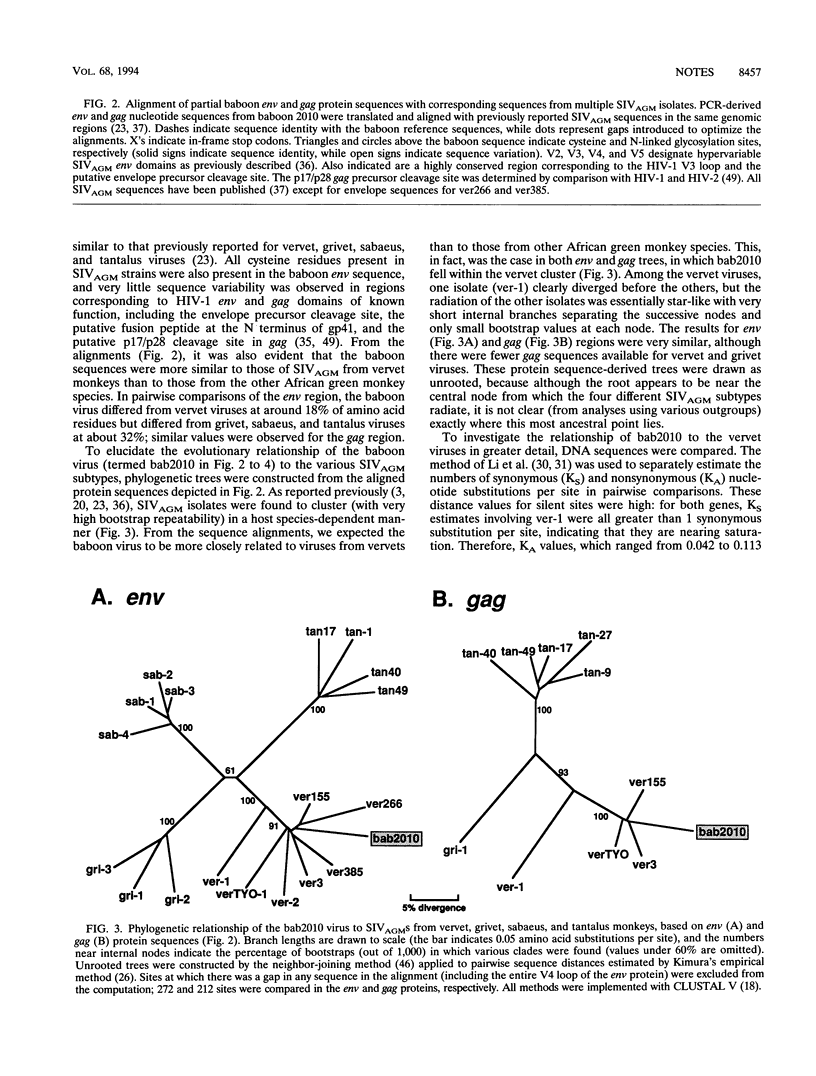
Many African primates are known to be naturally infected with simian immunodeficiency viruses (SIVs), but only a fraction of these viruses has been molecularly characterized. One primate species for which only serological evidence of SIV infection has been reported is the yellow baboon (Papio hamadryas cynocephalus). Two wild-living baboons with strong SIVAGM seroreactivity were previously identified in a Tanzanian national park where baboons and African green monkeys shared the same habitat (T. Kodama, D. P. Silva, M. D. Daniel, J. E. Phillips-Conroy, C. J. Jolly, J. Rogers, and R. C. Desrosiers, AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 5:337-343, 1989). To determine the genetic identity of the viruses infecting these animals, we used PCR to examine SIV sequences directly in uncultured leukocyte DNA. Targeting two different, nonoverlapping genomic regions, we amplified and sequenced a 673-bp gag gene fragment and a 908-bp env gene fragment from one of the two baboons. Phylo-genetic analyses revealed that this baboon was infected with an SIVAGM strain of the vervet subtype. These results provide the first direct evidence for simian-to-simian cross-species transmission of SIV in the wild.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J. S., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C., Cobb E. K., Anthony M., Eichberg J. W. Isolation and characterization of simian immunodeficiency viruses from two subspecies of African green monkeys. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Mar;6(3):275–285. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J. S., Short M., Taylor M. E., Su S., Hirsch V. M., Johnson P. R., Shaw G. M., Hahn B. H. Species-specific diversity among simian immunodeficiency viruses from African green monkeys. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2816–2828. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2816-2828.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Hill R. W., Knott W. B., Tsai C. C., Kuller L., Morton W. R. Detection of serum antibodies in Ethiopian baboons that cross-react with SIV, HTLV-I, and type D retroviral antigens. J Med Primatol. 1993 Feb-May;22(2-3):124–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro B. A., Nepomuceno M., Lerche N. W., Eichberg J. W., Levy J. A. Persistent infection of baboons and rhesus monkeys with different strains of HIV-2. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90838-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., King N. W., Kannagi M., Sehgal P. K., Hunt R. D., Kanki P. J., Essex M., Desrosiers R. C. Isolation of T-cell tropic HTLV-III-like retrovirus from macaques. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1201–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.3159089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C. The simian immunodeficiency viruses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:557–578. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estaquier J., Peeters M., Bedjabaga L., Honoré C., Bussi P., Dixson A., Delaporte E. Prevalence and transmission of simian immunodeficiency virus and simian T-cell leukemia virus in a semi-free-range breeding colony of mandrills in Gabon. AIDS. 1991 Nov;5(11):1385–1386. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199111000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa M., Miura T., Hasegawa A., Morikawa S., Tsujimoto H., Miki K., Kitamura T., Hayami M. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from African green monkey, a new member of the HIV/SIV group. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):457–461. doi: 10.1038/333457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F., Yue L., Robertson D. L., Hill S. C., Hui H., Biggar R. J., Neequaye A. E., Whelan T. M., Ho D. D., Shaw G. M. Genetic diversity of human immunodeficiency virus type 2: evidence for distinct sequence subtypes with differences in virus biology. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7433–7447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7433-7447.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F., Yue L., White A. T., Pappas P. G., Barchue J., Hanson A. P., Greene B. M., Sharp P. M., Shaw G. M., Hahn B. H. Human infection by genetically diverse SIVSM-related HIV-2 in west Africa. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):495–499. doi: 10.1038/358495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gürtler L. G., Hauser P. H., Eberle J., von Brunn A., Knapp S., Zekeng L., Tsague J. M., Kaptue L. A new subtype of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (MVP-5180) from Cameroon. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1581–1585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1581-1585.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainsey B. M., Hubbard G. B., Leland M. M., Brasky K. M. Clinical parameters of the normal baboons (Papio species) and chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). Lab Anim Sci. 1993 Jun;43(3):236–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry R. M., Wells M. A., Phelan M. A., Schneider A. L., Epstein J. S., Quinnan G. V. Antibodies to simian immunodeficiency virus in African green monkeys in Africa in 1957-62. Lancet. 1986 Aug 23;2(8504):455–455. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V. M., Dapolito G. A., Goldstein S., McClure H., Emau P., Fultz P. N., Isahakia M., Lenroot R., Myers G., Johnson P. R. A distinct African lentivirus from Sykes' monkeys. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1517–1528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1517-1528.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V. M., Olmsted R. A., Murphey-Corb M., Purcell R. H., Johnson P. R. An African primate lentivirus (SIVsm) closely related to HIV-2. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):389–392. doi: 10.1038/339389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet T., Cheynier R., Meyerhans A., Roelants G., Wain-Hobson S. Genetic organization of a chimpanzee lentivirus related to HIV-1. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):356–359. doi: 10.1038/345356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin M. J., Hui H., Robertson D. L., Müller M. C., Barré-Sinoussi F., Hirsch V. M., Allan J. S., Shaw G. M., Sharp P. M., Hahn B. H. Mosaic genome structure of simian immunodeficiency virus from west African green monkeys. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2935–2947. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Galvin T. A., Lowenstine L. J., Jennings M. B., Gardner M. B., Buckler C. E. A highly divergent simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVstm) recovered from stored stump-tailed macaque tissues. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):7061–7065. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.7061-7065.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King N. W., Chalifoux L. V., Ringler D. J., Wyand M. S., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., Desrosiers R. C., Blake B. J., Hunt R. D. Comparative biology of natural and experimental SIVmac infection in macaque monkeys: a review. J Med Primatol. 1990;19(2):109–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Silva D. P., Daniel M. D., Phillips-Conroy J. E., Jolly C. J., Rogers J., Desrosiers R. C. Prevalence of antibodies to SIV in baboons in their native habitat. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Jun;5(3):337–343. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H. Unbiased estimation of the rates of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution. J Mol Evol. 1993 Jan;36(1):96–99. doi: 10.1007/BF02407308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Wu C. I., Luo C. C. A new method for estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous rates of nucleotide substitution considering the relative likelihood of nucleotide and codon changes. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Mar;2(2):150–174. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Naidu Y. M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Extensive genetic variability of simian immunodeficiency virus from African green monkeys. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1800–1802. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1800-1802.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstine L. J., Pedersen N. C., Higgins J., Pallis K. C., Uyeda A., Marx P., Lerche N. W., Munn R. J., Gardner M. B. Seroepidemiologic survey of captive Old-World primates for antibodies to human and simian retroviruses, and isolation of a lentivirus from sooty mangabeys (Cercocebus atys). Int J Cancer. 1986 Oct 15;38(4):563–574. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx P. A., Li Y., Lerche N. W., Sutjipto S., Gettie A., Yee J. A., Brotman B. H., Prince A. M., Hanson A., Webster R. G. Isolation of a simian immunodeficiency virus related to human immunodeficiency virus type 2 from a west African pet sooty mangabey. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4480–4485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4480-4485.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeating J. A., Willey R. L. Structure and function of the HIV envelope. AIDS. 1989;3 (Suppl 1):S35–S41. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198901001-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers G., MacInnes K., Korber B. The emergence of simian/human immunodeficiency viruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Mar;8(3):373–386. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. C., Saksena N. K., Nerrienet E., Chappey C., Hervé V. M., Durand J. P., Legal-Campodonico P., Lang M. C., Digoutte J. P., Georges A. J. Simian immunodeficiency viruses from central and western Africa: evidence for a new species-specific lentivirus in tantalus monkeys. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1227–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1227-1235.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N., McGann K. A., Wilesmith J., Desrosiers R. C., Brookmeyer R. The evolution of virus diseases: their emergence, epidemicity, and control. Virus Res. 1993 Jul;29(1):3–20. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(93)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novembre F. J., Hirsch V. M., McClure H. M., Fultz P. N., Johnson P. R. SIV from stump-tailed macaques: molecular characterization of a highly transmissible primate lentivirus. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):783–787. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90047-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta Y., Masuda T., Tsujimoto H., Ishikawa K., Kodama T., Morikawa S., Nakai M., Honjo S., Hayami M. Isolation of simian immunodeficiency virus from African green monkeys and seroepidemiologic survey of the virus in various non-human primates. Int J Cancer. 1988 Jan 15;41(1):115–122. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters M., Fransen K., Delaporte E., Van den Haesevelde M., Gershy-Damet G. M., Kestens L., van der Groen G., Piot P. Isolation and characterization of a new chimpanzee lentivirus (simian immunodeficiency virus isolate cpz-ant) from a wild-captured chimpanzee. AIDS. 1992 May;6(5):447–451. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199205000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips-Conroy J. E., Jolly C. J., Petros B., Allan J. S., Desrosiers R. C. Sexual transmission of SIVagm in wild grivet monkeys. J Med Primatol. 1994 Jan;23(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0684.1994.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatak M., Jr, Saag M. S., Yang L. C., Clark S. J., Kappes J. C., Luk K. C., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Lifson J. D. High levels of HIV-1 in plasma during all stages of infection determined by competitive PCR. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1749–1754. doi: 10.1126/science.8096089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Kidd K. K. Nuclear DNA polymorphisms in a wild population of yellow baboons (Papio hamadryas cynocephalus) from Mikumi National Park, Tanzania. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1993 Apr;90(4):477–486. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330900407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonaga K., Katahira J., Fukasawa M., Hassan M. A., Kawamura M., Akari H., Miura T., Goto T., Nakai M., Suleman M. Isolation and characterization of simian immunodeficiency virus from African white-crowned mangabey monkeys (Cercocebus torquatus lunulatus). Arch Virol. 1993;129(1-4):77–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01316886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto H., Hasegawa A., Maki N., Fukasawa M., Miura T., Speidel S., Cooper R. W., Moriyama E. N., Gojobori T., Hayami M. Sequence of a novel simian immunodeficiency virus from a wild-caught African mandrill. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):539–541. doi: 10.1038/341539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tözsér J., Bláha I., Copeland T. D., Wondrak E. M., Oroszlan S. Comparison of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 proteinases using oligopeptide substrates representing cleavage sites in Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanden Haesevelde M., Decourt J. L., De Leys R. J., Vanderborght B., van der Groen G., van Heuverswijn H., Saman E. Genomic cloning and complete sequence analysis of a highly divergent African human immunodeficiency virus isolate. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1586–1596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1586-1596.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



