Abstract
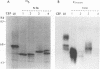
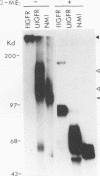
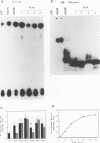
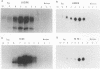
We reported previously that an N-terminally truncated insulinlike growth factor I receptor (IGFR) fused to avian sarcoma virus UR2 gag p19 had a greater transforming potential than did the native IGFR, but it failed to cause tumors in vivo. To investigate whether the 36 amino acids (aa) of the IGFR extracellular (EC) sequence in the gag-IGFR fusion protein encoded by the retrovirus UIGFR have a modulatory effect on the biological and biochemical properties of the protein, four mutants, NM1, NM2, NM3, and NM4 of the EC sequence were constructed. NM1 lacks the entire 36 aa residues; NM2 lacks the N-terminal 16 aa residues (aa 870 to 885), including two potential N-linked glycosylation sites of the EC sequence; NM3 contains a deletion of the C-terminal 20 aa residues (aa 886 to 905) of the EC sequence; and NM4 contains N-to-Q substitutions at both N-linked glycosylation sites. NM1 was the strongest of the four mutants in promoting anchorage-independent growth of transfected chicken embryo fibroblasts, while NM2 and NM4 had weaker transforming potential than did the original UIGFR virus. Only NM1 and NM3 were able to induce sarcomas in chickens. The four NM mutant-transformed cells expressed the expected proteins with comparable steady-state levels. The in vitro tyrosine kinase activity of P53NM1 was about fourfold higher than that of the parental P57-75UIGFR, whereas NM2 and NM4 proteins exhibited four- to fivefold-lower kinase activities. Despite lacking the IGFR EC sequence, P53NM1 formed covalent dimers similar to those formed by the parental P57-75UIGFR. Increased phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase activity was found to be associated with the mutant IGFR proteins. Among NM4 proteins. Elevated tyrosine phosphorylation of cellular proteins of 35, 120, 140, 160, and 170 kDa was detected in all mutant IGFR-transformed cells. We conclude that the EC 36-aa sequence of IGFR in the gag-IGFR fusion protein exerts intricate modulatory effects on the protein's transforming and tumorigenic potential. The 20 aa residues immediately upstream of the transmembrane domain have an inhibitory effect on the tumorigenic potential of gag-IGFR, whereas N-linked glycosylation within the EC sequence appears to have a positive effect on the transforming potential of UIGFR. Increased in vitro kinase activity and, to a lesser extent, in vivo tyrosine phosphorylation as well as the elevated association of PI 3-kinase activity with IGFR proteins seem to be correlated with the transforming potential of IGFR mutant proteins.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accili D., Perrotti N., Rees-Jones R., Taylor S. I. Tissue distribution and subcellular localization of an endogenous substrate (pp 120) for the insulin receptor-associated tyrosine kinase. Endocrinology. 1986 Sep;119(3):1274–1280. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-3-1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adari H., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M., Der C. J., McCormick F. Guanosine triphosphatase activating protein (GAP) interacts with the p21 ras effector binding domain. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2833817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auger K. R., Serunian L. A., Soltoff S. P., Libby P., Cantley L. C. PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balduzzi P. C., Notter M. F., Morgan H. R., Shibuya M. Some biological properties of two new avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):268–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.268-275.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballotti R., Lammers R., Scimeca J. C., Dull T., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Van Obberghen E. Intermolecular transphosphorylation between insulin receptors and EGF-insulin receptor chimerae. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3303–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorge J. D., Chan T. O., Antczak M., Kung H. J., Fujita D. J. Activated type I phosphatidylinositol kinase is associated with the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor following EGF stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3816–3820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Faletto D. L., Chan A. M., Kmiecik T. E., Vande Woude G. F., Aaronson S. A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1846706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Duckworth B. C., Auger K. R., Cohen B., Schaffhausen B. S., Cantley L. C. Purification and characterization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19704–19711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. M., Heller D., Poon B., Kang L., Wang L. H. The proto-oncogene c-ros codes for a transmembrane tyrosine protein kinase sharing sequence and structural homology with sevenless protein of Drosophila melanogaster. Oncogene. 1991 Feb;6(2):257–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Role of phosphatidylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.2466336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Signal transmission by the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Structural and functional homologies in the receptors for insulin and the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):8–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endemann G., Yonezawa K., Roth R. A. Phosphatidylinositol kinase or an associated protein is a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):396–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Kaplan D. R., Kavanaugh W. M., Turck C. W., Williams L. T. A phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase binds to platelet-derived growth factor receptors through a specific receptor sequence containing phosphotyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanciulli M., Paggi M. G., Mancini A., Del Carlo C., Floridi A., Taylor S. I., Perrotti N. rp-120: a common endogenous substrate for insulin and IGF-1 receptor-associated tyrosine kinase activity in the highly malignant AS-30D rat hepatoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 14;160(1):168–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91636-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activity associates with viral p60src protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1651–1658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Requirement of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase modification for its association with p60src. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1972–1979. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Kornbluth S., Jong S. M., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase type I activity associates with various oncogene products. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(4):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., O'Brien M. C., Hanafusa H. Deletions in the SH2 domain of p60v-src prevent association with the detergent-insoluble cellular matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1207–1213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgino F., Belfiore A., Milazzo G., Costantino A., Maddux B., Whittaker J., Goldfine I. D., Vigneri R. Overexpression of insulin receptors in fibroblast and ovary cells induces a ligand-mediated transformed phenotype. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Mar;5(3):452–459. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-3-452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H., Halpern C. C., Buchhagen D. L., Kawai S. Recovery of avian sarcoma virus from tumors induced by transformation-defective mutants. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1735–1747. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H. Rapid transformation of cells by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):318–325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence for epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced intermolecular autophosphorylation of the EGF receptors in living cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4035–4044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Interaction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-associated p85 with epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):981–990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E., Nocka K., Beier D. R., Chu T. Y., Buck J., Lahm H. W., Wellner D., Leder P., Besmer P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90303-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Cooperation between oncogenes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):249–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90637-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong S. M., Wang L. H. Role of gag sequence in the biochemical properties and transforming activity of the avian sarcoma virus UR2-encoded gag-ros fusion protein. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5997–6009. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5997-6009.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Koyasu S., Nishida E., Tobe K., Izumi T., Takaku F., Sakai H., Yahara I., Kasuga M. Tyrosine phosphorylation of common and specific sets of cellular proteins rapidly induced by insulin, insulin-like growth factor I, and epidermal growth factor in an intact cell. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7342–7350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Phosphorylation of the PDGF receptor beta subunit creates a tight binding site for phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3279–3286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma L. M., Weber M. J. Constitutive phosphorylation of the receptor for insulinlike growth factor I in cells transformed by the src oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3626–3634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers R., Van Obberghen E., Ballotti R., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Transphosphorylation as a possible mechanism for insulin and epidermal growth factor receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16886–16890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Kris R., Sasson I., Ullrich A., Hayman M. J., Beug H., Schlessinger J. Activation of c-erbB in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis leads to the expression of a truncated EGF receptor kinase. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3179–3182. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04062.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Schlessinger J. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced disulfide-linked dimerization of PDGF receptor in living cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3756–3761. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling L. E., Druker B. J., Cantley L. C., Roberts T. M. Transformation-defective mutants of polyomavirus middle T antigen associate with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) but are unable to maintain wild-type levels of PI 3-kinase products in intact cells. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1702–1708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1702-1708.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D., Rutter W. J., Wang L. H. Enhancement of transforming potential of human insulinlike growth factor 1 receptor by N-terminal truncation and fusion to avian sarcoma virus UR2 gag sequence. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):374–385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.374-385.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. Q., Pawson T. The epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylates GTPase-activating protein (GAP) at Tyr-460, adjacent to the GAP SH2 domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2511–2516. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Marinetti G. V., Balduzzi P. C. Transforming protein of avian sarcoma virus UR2 is associated with phosphatidylinositol kinase activity: possible role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Bellot F., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Zilberstein A. Tyrosine kinase activity is essential for the association of phospholipase C-gamma with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Reichman C. T., Hanafusa H. Biological and biochemical activity of v-Crk chimeras containing the SH2/SH3 regions of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C-gamma and Src. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):115–121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.115-121.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Wang L. H., Shibuya M. Human c-ros-1 gene homologous to the v-ros sequence of UR2 sarcoma virus encodes for a transmembrane receptorlike molecule. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):3000–3004. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Association of the v-crk oncogene product with phosphotyrosine-containing proteins and protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2638–2642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jackson P. K., Van Etten R. A., Baltimore D. Point mutations in the abl SH2 domain coordinately impair phosphotyrosine binding in vitro and transforming activity in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):609–618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlade C. J., Ellis C., Reedijk M., Anderson D., Mbamalu G., Reith A. D., Panayotou G., End P., Bernstein A., Kazlauskas A. SH2 domains of the p85 alpha subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulate binding to growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):991–997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckameyer W. S., Shibuya M., Hsu M. T., Wang L. H. Proto-oncogene c-ros codes for a molecule with structural features common to those of growth factor receptors and displays tissue specific and developmentally regulated expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1478–1486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckameyer W. S., Wang L. H. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus UR2 and comparison of its transforming sequence with those of other avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):914–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.914-921.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckameyer W. S., Wang L. H. Nucleotide sequence of avian sarcoma virus UR2 and comparison of its transforming gene with other members of the tyrosine protein kinase oncogene family. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):879–884. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.879-884.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. A., Perrotti N., Taylor S. I. Rat liver membranes contain a 120 kDa glycoprotein which serves as a substrate for the tyrosine kinases of the receptors for insulin and epidermal growth factor. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 9;212(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81573-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon B., Dixon D., Ellis L., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J., Wang L. H. Molecular basis of the activation of the tumorigenic potential of Gag-insulin receptor chimeras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):877–881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Kapeller R., White M. F., Cantley L. C. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson S. E., Chatterjee S., Chaudhuri M., White M. F. YMXM motifs of IRS-1 define substrate specificity of the insulin receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2027–2031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Erikson R. L. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activities in normal and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3194–3198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C: complete cDNA and protein sequences and sequence homology to tyrosine kinase-related oncogene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5419–5423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzman L., Ellis C., Lin L. L., Pawson T., Knopf J. Platelet-derived growth factor increases the in vivo activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 and phospholipase C-gamma 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2018–2025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Wong G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., Long C. M., Crosier W. J., Watt K., Koths K. Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1697–1700. doi: 10.1126/science.3201259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Druker B., Morrison D., Cantley L., Roberts T. The colony stimulating factor-1 receptor associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):699–702. doi: 10.1038/342699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Hanafusa H., Notter M. F., Balduzzi P. C. Genetic structure and transforming sequence of avian sarcoma virus UR2. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):833–841. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.833-841.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Lin B., Jong S. M., Dixon D., Ellis L., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Activation of transforming potential of the human insulin receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5725–5729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Livingston J. N., Backer J. M., Lauris V., Dull T. J., Ullrich A., Kahn C. R. Mutation of the insulin receptor at tyrosine 960 inhibits signal transmission but does not affect its tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):641–649. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D., Roberts T., Cantley L. Evidence for two distinct phosphatidylinositol kinases in fibroblasts. Implications for cellular regulation. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):165–174. doi: 10.1042/bj2470165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1443–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]