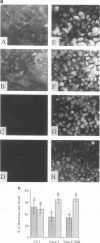
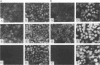
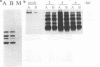
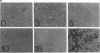
Abstract
The interactions of viruses with polarized epithelial cells are of some significance to the pathogenesis of disease because these cell types comprise the primary barrier to many virus infections and also serve as the sites for virus release from the host. Poliovirus-epithelial cell interactions are of particular interest since this virus is an important enteric pathogen and the host cell receptor has been identified. In this study, poliovirus was observed to adsorb to both the apical and basolateral surfaces of polarized monkey kidney (Vero C1008) and human intestinal (Caco-2) epithelial cells but exhibited preferential binding to the basolateral surfaces of both cell types. Localization of the poliovirus receptor by a receptor-specific monoclonal antibody (D171) revealed a similar distribution predominantly on basolateral membranes, and treatment of cells with antibody D171 inhibited virus adsorption to both membrane surfaces. Poliovirus was able to initiate infection with similar efficiency following adsorption to either surface, and infection was blocked at both surfaces by D171, indicating that functional receptor molecules are expressed on both surfaces at sufficient density to mediate efficient infection at the apical and basolateral plasma membranes. Poliovirus infection resulted in a decrease in transepithelial resistance which was inhibited by prior treatment with monoclonal antibody D171 and occurred prior to other visible cytopathic effects. These results have interesting implications for viral pathogenesis in the human gut.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amerongen H. M., Weltzin R., Farnet C. M., Michetti P., Haseltine W. A., Neutra M. R. Transepithelial transport of HIV-1 by intestinal M cells: a mechanism for transmission of AIDS. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(8):760–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BODIAN D. Poliovirus in chimpanzee tissues after virus feeding. Am J Hyg. 1956 Sep;64(2):181–197. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. M., Trier J. S., Dambrauskas R., Wolf J. L. Reovirus type I infection of small intestinal epithelium in suckling mice and its effect on M cells. Lab Invest. 1988 Feb;58(2):226–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan M. J., Anderson H. C., Palade G. E., Jamieson J. D. Intracellular sorting and polarized cell surface delivery of (Na+,K+)ATPase, an endogenous component of MDCK cell basolateral plasma membranes. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):623–631. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90888-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan M. J., Stow J. L., Newman A. P., Madri J., Anderson H. C., Farquhar M. G., Palade G. E., Jamieson J. D. Dependence on pH of polarized sorting of secreted proteins. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):632–635. doi: 10.1038/329632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Otero M. J., Castrillo J. L. Modification of membrane permeability by animal viruses. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;40(2):171–212. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. D., Tang J. P., Julian J., Glasser S. R. Vectorial secretion of proteoglycans by polarized rat uterine epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2425–2435. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereijido M., Contreras R. G., Gonzalez-Mariscal L. Development and alteration of polarity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:785–795. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.004033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereijido M., Robbins E. S., Dolan W. J., Rotunno C. A., Sabatini D. D. Polarized monolayers formed by epithelial cells on a permeable and translucent support. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):853–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayson E. T., Compans R. W. Entry of simian virus 40 is restricted to apical surfaces of polarized epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3391–3396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compans R. W., Srinivas R. V. Protein sorting in polarized epithelial cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;170:141–181. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76389-2_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE SOMER P., PRINZIE A., SCHONNE E. Infectivity of polio virus ribonucleic acid for embryonated eggs and unsusceptible cell lines. Nature. 1959 Aug 22;184(Suppl 9):652–653. doi: 10.1038/184652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantini J., Yahi N., Chermann J. C. Human immunodeficiency virus can infect the apical and basolateral surfaces of human colonic epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9297–9301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J., Fogh J. M., Orfeo T. One hundred and twenty-seven cultured human tumor cell lines producing tumors in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):221–226. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freistadt M. S., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R. Heterogeneous expression of poliovirus receptor-related proteins in human cells and tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5700–5706. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukudome K., Yoshie O., Konno T. Comparison of human, simian, and bovine rotaviruses for requirement of sialic acid in hemagglutination and cell adsorption. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):196–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S., von Bonsdorff C. H., Simons K. Vesicular stomatitis virus infects and matures only through the basolateral surface of the polarized epithelial cell line, MDCK. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb T. A., Beaudry G., Rizzolo L., Colman A., Rindler M., Adesnik M., Sabatini D. D. Secretion of endogenous and exogenous proteins from polarized MDCK cell monolayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2100–2104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gstraunthaler G. J. Epithelial cells in tissue culture. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1988 Jan-Feb;11(1-2):1–42. doi: 10.1159/000173147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., McLAREN L. C., SYVERTON J. T. Mammalian cell-virus relationship. III. Poliovirus production by non-primate cells exposed to poliovirus ribonucleic acid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Apr;100(4):843–845. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler J. S., Preston A. S., Steele R. E. Factors affecting the differentiation of epithelial transport and responsiveness to hormones. Fed Proc. 1984 May 15;43(8):2221–2224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harouse J. M., Bhat S., Spitalnik S. L., Laughlin M., Stefano K., Silberberg D. H., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Inhibition of entry of HIV-1 in neural cell lines by antibodies against galactosyl ceramide. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):320–323. doi: 10.1126/science.1857969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo I. J., Raub T. J., Borchardt R. T. Characterization of the human colon carcinoma cell line (Caco-2) as a model system for intestinal epithelial permeability. Gastroenterology. 1989 Mar;96(3):736–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Stieger B., Bartles J. R. Biogenesis of endogenous plasma membrane proteins in epithelial cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:755–770. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.003543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN A. S. Comparison of susceptible and resistant cells to infection with poliomyelitis virus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Sep 27;61(4):830-8; discussion, 838-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb42539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Horie H., Ise I., Okitsu A., Yoshida M., Iizuka N., Takeuchi K., Takegami T., Nomoto A. The poliovirus receptor protein is produced both as membrane-bound and secreted forms. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3217–3224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondor-Koch C., Bravo R., Fuller S. D., Cutler D., Garoff H. Exocytotic pathways exist to both the apical and the basolateral cell surface of the polarized epithelial cell MDCK. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Vancell R., Beaty G., Stefani E., Rodríguez-Boulan E. E., Cereijido M. Changes in paracellular and cellular ionic permeabilities of monolayers of MDCK cells infected with influenza or vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):171–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01868711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. The interaction of neutralized poliovirus with HeLa cells. I. Adsorption. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLAREN L. C., HOLLAND J. J., SYVERTON J. T. The mammalian cell-virus relationship. I. Attachment of poliovirus to cultivated cells of primate and non-primate origin. J Exp Med. 1959 May 1;109(5):475–485. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.5.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C., Johnson B., Lionetti K. A., Nobis P., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Transformation of a human poliovirus receptor gene into mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7845–7849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulos G., Pitot H. C. Primary culture of parenchymal liver cells on collagen membranes. Morphological and biochemical observations. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Aug;94(1):70–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90532-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt D. S., Hamamoto S. T., Pitelka D. R. Transepithelial transport in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1212–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobis P., Zibirre R., Meyer G., Kühne J., Warnecke G., Koch G. Production of a monoclonal antibody against an epitope on HeLa cells that is the functional poliovirus binding site. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2563–2569. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabenandrasana C., Baghdiguian S., Marvaldi J., Fantini J. CD4 molecules are restricted to the basolateral membrane domain of in vitro differentiated human colon cancer cells (HT29-D4). FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 4;265(1-2):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80887-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B. Pathogenesis of poliomyelitis; reappraisal in the light of new data. Science. 1956 Jun 29;123(3209):1151–1157. doi: 10.1126/science.123.3209.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears A. E., McGwire B. S., Roizman B. Infection of polarized MDCK cells with herpes simplex virus 1: two asymmetrically distributed cell receptors interact with different viral proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5087–5091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon J. M., Pitelka D. R. The influence of cell shape on the induction of functional differentiation in mouse mammary cells in vitro. In Vitro. 1981 Nov;17(11):1016–1028. doi: 10.1007/BF02618428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. Pathogenesis of viral infections. Basic concepts derived from the reovirus model. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 21;312(8):486–497. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502213120806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siciński P., Rowiński J., Warchoł J. B., Jarzabek Z., Gut W., Szczygieł B., Bielecki K., Koch G. Poliovirus type 1 enters the human host through intestinal M cells. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jan;98(1):56–58. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91290-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Fuller S. D. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Wandinger-Ness A. Polarized sorting in epithelia. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90357-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., van Meer G. Lipid sorting in epithelial cells. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6197–6202. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Mosher D. F., Rapraeger A. Heparan sulfate-mediated binding of epithelial cell surface proteoglycan to thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2885–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson L., Finlay B. B., Bass D., von Bonsdorff C. H., Greenberg H. B. Symmetric infection of rotavirus on polarized human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4190–4197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4190-4197.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J. P., Julian J., Glasser S. R., Carson D. D. Heparan sulfate proteoglycan synthesis and metabolism by mouse uterine epithelial cells cultured in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12832–12842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker S. P., Melsen L. R., Compans R. W. Migration of polarized epithelial cells through permeable membrane substrates of defined pore size. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;58(2):280–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Bye W. A. The membranous epithelial (M) cell and the mucosal immune system. Annu Rev Med. 1984;35:95–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.35.020184.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Dambrauskas R., Sharpe A. H., Trier J. S. Adherence to and penetration of the intestinal epithelium by reovirus type 1 in neonatal mice. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):82–91. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90842-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Kauffman R. S., Finberg R., Dambrauskas R., Fields B. N., Trier J. S. Determinants of reovirus interaction with the intestinal M cells and absorptive cells of murine intestine. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):291–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Rubin D. H., Finberg R., Kauffman R. S., Sharpe A. H., Trier J. S., Fields B. N. Intestinal M cells: a pathway for entry of reovirus into the host. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):471–472. doi: 10.1126/science.6259737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WuDunn D., Spear P. G. Initial interaction of herpes simplex virus with cells is binding to heparan sulfate. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.52-58.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zibert A., Selinka H. C., Elroy-Stein O., Moss B., Wimmer E. Vaccinia virus-mediated expression and identification of the human poliovirus receptor. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):250–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90668-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Simons K. Viruses budding from either the apical or the basolateral plasma membrane domain of MDCK cells have unique phospholipid compositions. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):847–852. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bonsdorff C. H., Fuller S. D., Simons K. Apical and basolateral endocytosis in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells grown on nitrocellulose filters. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2781–2792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]