Abstract
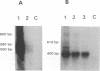
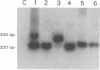
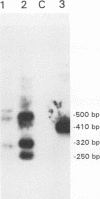
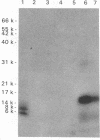
The polymerase chain reaction was used to detect and characterize low-abundance bovine leukemia virus (BLV) mRNAs. In infected cattle we could detect spliced mRNA with a splice pattern consistent with a Tax/Rex mRNA, as well as at least four alternatively spliced RNAs. Two of the alternatively spliced mRNAs encoded hitherto unrecognized BLV proteins, designated RIII and GIV. The Tax/Rex and alternatively spliced mRNAs could be detected at their highest levels in BLV-infected cell cultures; the next highest levels were found in samples from calves experimentally infected at 6 weeks postinoculation. Alternatively spliced mRNAs were also expressed, albeit at lower levels, in naturally infected animals; they were detected by a nested polymerase chain reaction. Interestingly, the GIV mRNA was specifically detected in naturally infected cows with persistent lymphocytosis and in two of five calves at 6 months after experimental infection with BLV. Furthermore, the calf with the strongest signal for GIV had the highest lymphocyte counts. These data may suggest a correlation between expression of the GIV product and development of persistent lymphocytosis. Some of the donor and acceptor sites in the alternatively spliced mRNAs were highly unusual. The biological mechanisms and significance of such a choice of unexpected splice sites are currently unknown.
Full text
PDF

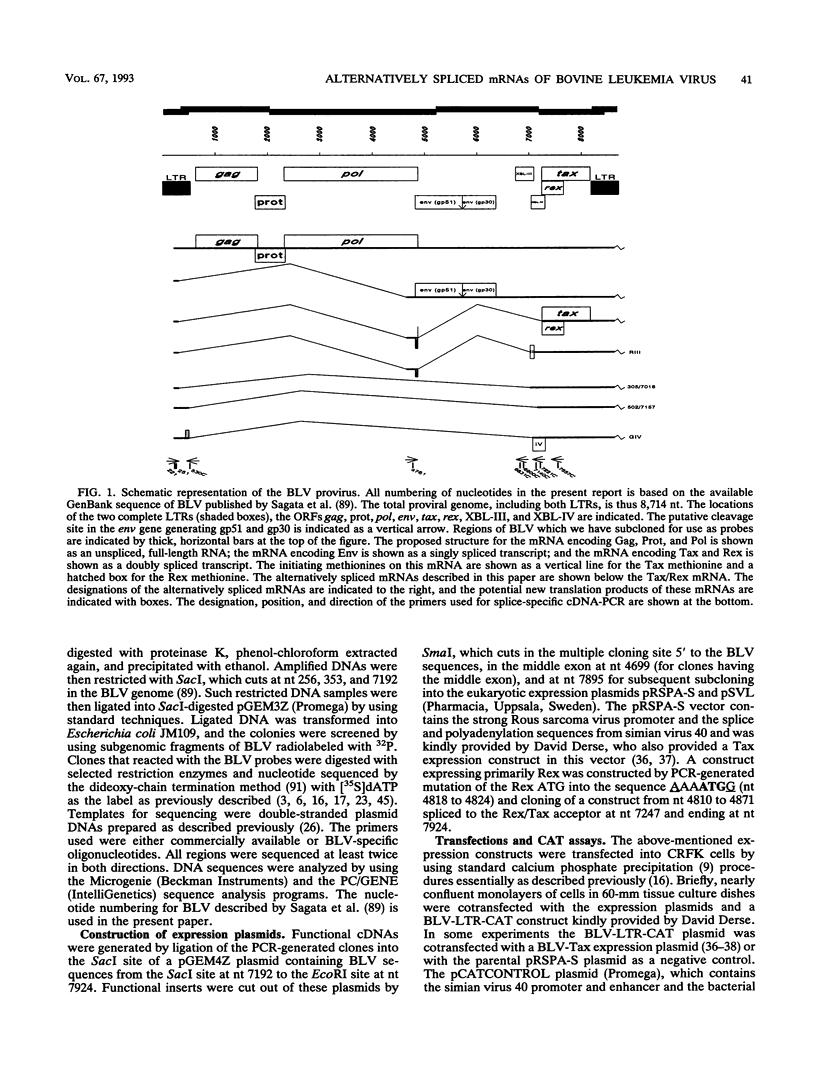
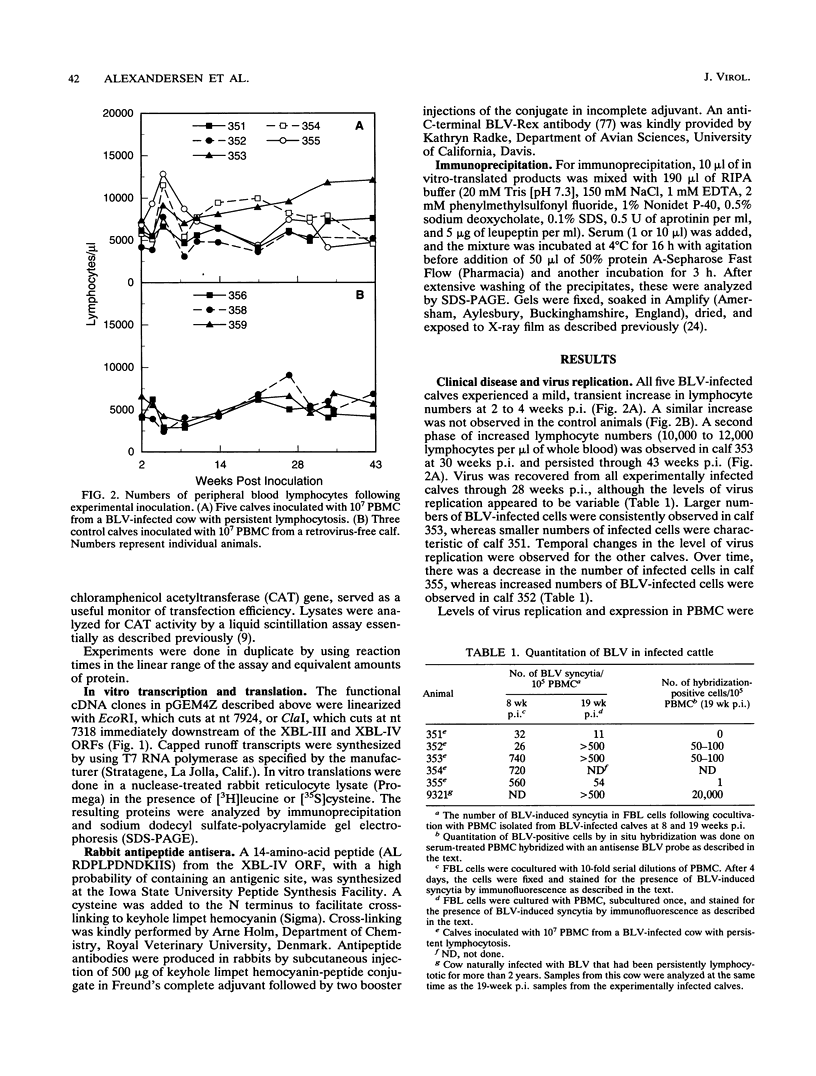

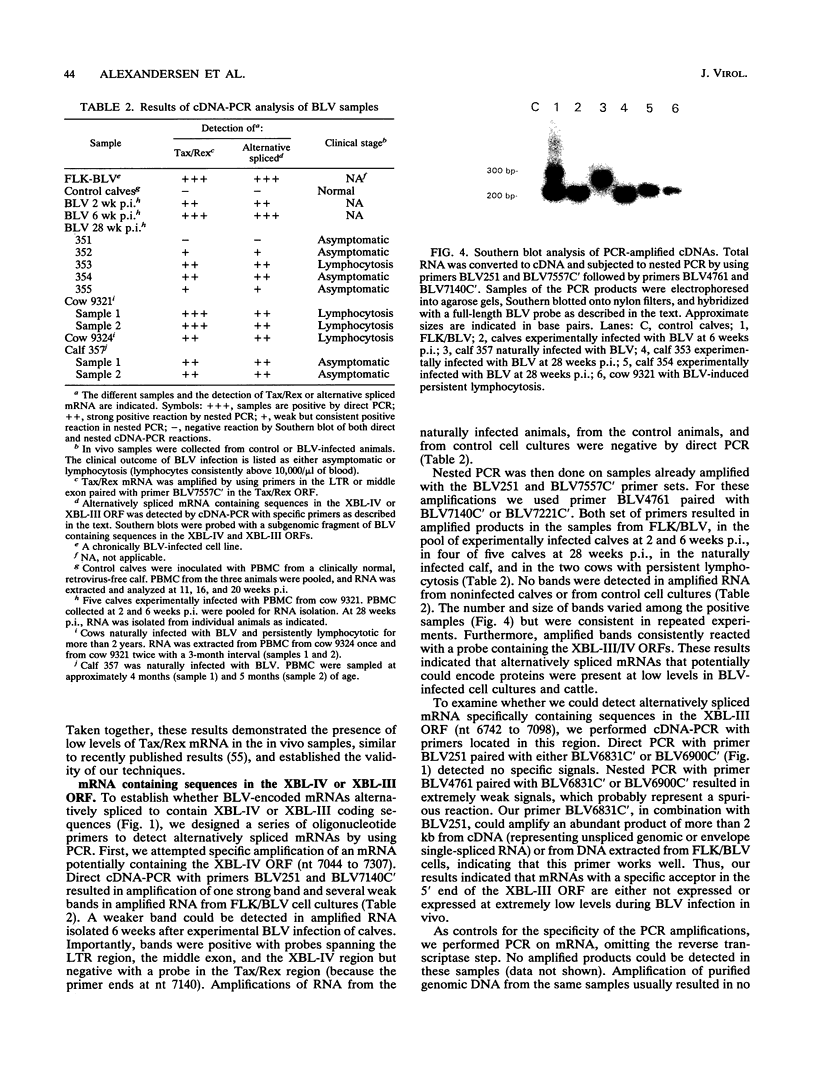

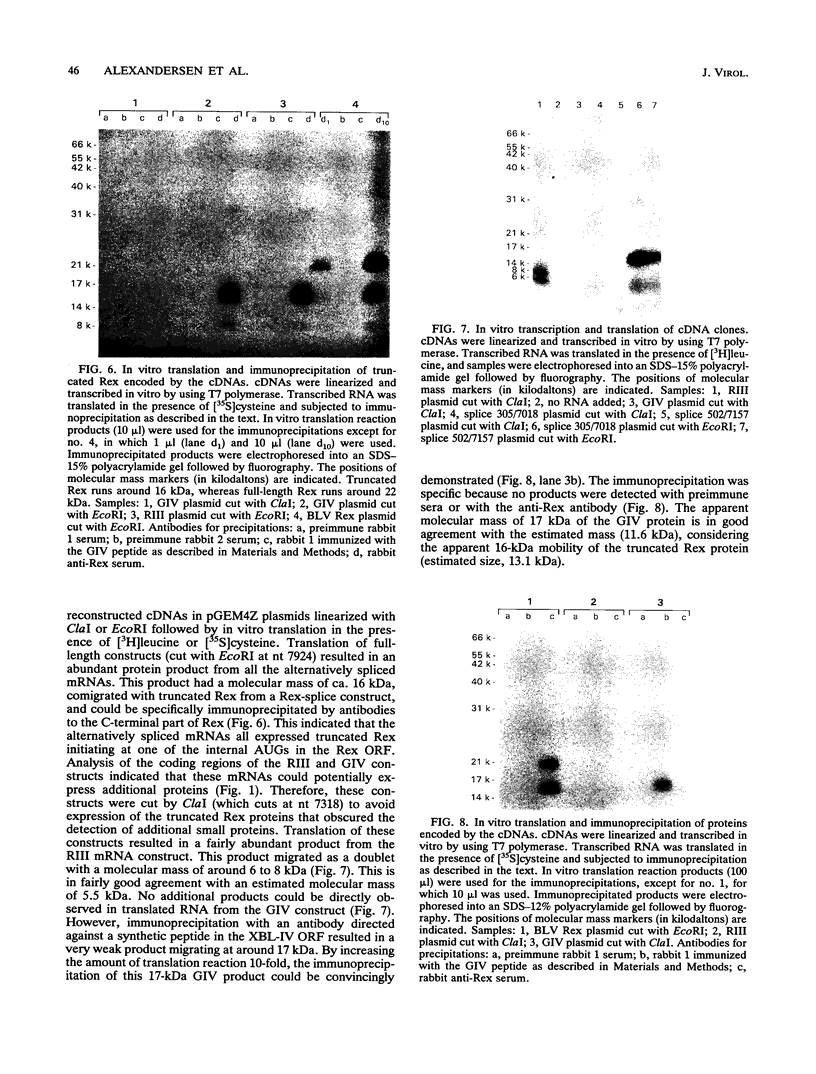






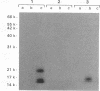
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed Y. F., Hanly S. M., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Structure-function analyses of the HTLV-I Rex and HIV-1 Rev RNA response elements: insights into the mechanism of Rex and Rev action. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1014–1022. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Perryman S. Detailed transcription map of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3684–3694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3684-3694.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E. Studies on the sequential development of acute interstitial pneumonia caused by Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.81-86.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Wolfinbarger J. Evidence of restricted viral replication in adult mink infected with Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1495–1507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1495-1507.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Wolfinbarger J., Race R. E. In situ molecular hybridization for detection of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus DNA by using strand-specific probes: identification of target cells for viral replication in cell cultures and in mink kits with virus-induced interstitial pneumonia. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2407–2419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2407-2419.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Carpenter S. Characterization of variable regions in the envelope and S3 open reading frame of equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4255–4262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4255-4262.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Larsen S., Cohn A., Uttenthal A., Race R. E., Aasted B., Hansen M., Bloom M. E. Passive transfer of antiviral antibodies restricts replication of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):9–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.9-17.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S., Zack J. A., Chen I. S. Characterization and expression of novel singly spliced RNA species of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4585–4588. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4585-4588.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballaun C., Farrington G. K., Dobrovnik M., Rusche J., Hauber J., Böhnlein E. Functional analysis of human T-cell leukemia virus type I rex-response element: direct RNA binding of Rex protein correlates with in vivo activity. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4408–4413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4408-4413.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becerra S. P., Koczot F., Fabisch P., Rose J. A. Synthesis of adeno-associated virus structural proteins requires both alternative mRNA splicing and alternative initiations from a single transcript. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2745–2754. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2745-2754.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becerra S. P., Rose J. A., Hardy M., Baroudy B. M., Anderson C. W. Direct mapping of adeno-associated virus capsid proteins B and C: a possible ACG initiation codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7919–7923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Rozenblatt S., Arnheiter H., Richardson C. D. Measles virus P gene codes for two proteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):908–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.908-919.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benko D. M., Schwartz S., Pavlakis G. N., Felber B. K. A novel human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protein, tev, shares sequences with tat, env, and rev proteins. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2505–2518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2505-2518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Alexandersen S., Garon C. F., Mori S., Wei W., Perryman S., Wolfinbarger J. B. Nucleotide sequence of the 5'-terminal palindrome of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus and construction of an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3551–3556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3551-3556.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Alexandersen S., Perryman S., Lechner D., Wolfinbarger J. B. Nucleotide sequence and genomic organization of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (ADV): sequence comparisons between a nonpathogenic and a pathogenic strain of ADV. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2903–2915. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2903-2915.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeck R., Curran J., Matsuoka Y., Compans R., Kolakofsky D. The parainfluenza virus type 1 P/C gene uses a very efficient GUG codon to start its C' protein. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1765–1768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1765-1768.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselut R., Lim F., Romond P. C., Frampton J., Brady J., Ghysdael J. Myb protein binds to multiple sites in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 long terminal repeat and transactivates LTR-mediated expression. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):764–769. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90044-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burny A., Cleuter Y., Kettmann R., Mammerickx M., Marbaix G., Portetelle D., van den Broeke A., Willems L., Thomas R. Bovine leukaemia: facts and hypotheses derived from the study of an infectious cancer. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Jul;17(3):197–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Baker B. S. Drosophila doublesex gene controls somatic sexual differentiation by producing alternatively spliced mRNAs encoding related sex-specific polypeptides. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):997–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90633-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein S., Pirker F. P., Hofer L., Zimmermann K., Bachmayer H., Böhnlein E., Hauber J. Transdominant repressors for human T-cell leukemia virus type I rex and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 rev function. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.81-88.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S., Alexandersen S., Long M. J., Perryman S., Chesebro B. Identification of a hypervariable region in the long terminal repeat of equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1605–1610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1605-1610.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S., Evans L. H., Sevoian M., Chesebro B. Role of the host immune response in selection of equine infectious anemia virus variants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3783–3789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3783-3789.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S., Miller L. D., Alexandersen S., Whetstone C. A., VanDerMaaten M. J., Viuff B., Wannemuehler Y., Miller J. M., Roth J. A. Characterization of early pathogenic effects after experimental infection of calves with bovine immunodeficiency-like virus. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1074–1083. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1074-1083.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciminale V., Pavlakis G. N., Derse D., Cunningham C. P., Felber B. K. Complex splicing in the human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) family of retroviruses: novel mRNAs and proteins produced by HTLV type I. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1737–1745. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1737-1745.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. A., Terwilliger E. F., Jalinoos Y., Proulx J., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Identification of HIV-1 vpr product and function. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(1):11–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. L., Dougherty G., Harn H. J., Jackson S., Baptist E. W., Byers J., Datta A., Phillips G., Isola N. R. The complex CD44 transcriptional unit; alternative splicing of three internal exons generates the epithelial form of CD44. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):569–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91770-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornil I., Levy D. In vivo inhibition of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) expression. Leukemia. 1989 Feb;3(2):159–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandell R. A., Fabricant C. G., Nelson-Rees W. A. Development, characterization, and viral susceptibility of a feline (Felis catus) renal cell line (CRFK). In Vitro. 1973 Nov-Dec;9(3):176–185. doi: 10.1007/BF02618435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta P., Reddy C. D., Saikumar P., Reddy E. P. The cellular proto-oncogene product Myb acts as transcriptional activator of the long terminal repeat of human T-lymphotropic virus type I. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):270–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.270-276.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta P., Saikumar P., Reddy C. D., Reddy E. P. Myb protein binds to human immunodeficiency virus 1 long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences and transactivates LTR-mediated transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8090–8094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depelchin A., Letesson J. J., Lostrie-Trussart N., Mammerickx M., Portetelle D., Burny A. Bovine leukemia virus (BLV)-infected B-cells express a marker similar to the CD5 T cell marker. Immunol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;20(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(89)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D. Bovine leukemia virus transcription is controlled by a virus-encoded trans-acting factor and by cis-acting response elements. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2462–2471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2462-2471.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Caradonna S. J., Casey J. W. Bovine leukemia virus long terminal repeat: a cell type-specific promoter. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):317–320. doi: 10.1126/science.2981431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D. trans-acting regulation of bovine leukemia virus mRNA processing. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1115–1119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1115-1119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn P., DaSilva L., Martarano L., Derse D. Equine infectious anemia virus tat: insights into the structure, function, and evolution of lentivirus trans-activator proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1616–1624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1616-1624.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum C., Burny A., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Morein B. Detection of B and T cells, with lectins or antibodies, in healthy and bovine leukemia virus-infected cattle. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Apr;18(3):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furtado M. R., Balachandran R., Gupta P., Wolinsky S. M. Analysis of alternatively spliced human immunodeficiency virus type-1 mRNA species, one of which encodes a novel tat-env fusion protein. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):258–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90773-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Furukawa K., Shiku H. Alternatively spliced mRNA of the pX region of human T lymphotropic virus type I proviral genome. FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 16;295(1-3):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81404-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Nerurkar L. S. Human retroviruses: their role in neoplasia and immunodeficiency. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;567:82–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb16461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessain A., Louie A., Gout O., Gallo R. C., Franchini G. Human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus type I (HTLV-I) expression in fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1628–1633. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1628-1633.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalck E., Alexandersen S., Cohn A., Poulsen L. A., Bloom M. E., Aasted B. Nucleotide sequence analysis of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus shows that multiple virus types are present in infected mink. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4378–4386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4378-4386.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. L., Chen I. S. Regulation of human T cell leukemia virus expression. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):169–175. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2404818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Böhnlein E., Ballard D. W. HIV-1, HTLV-1 and normal T-cell growth: transcriptional strategies and surprises. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guatelli J. C., Gingeras T. R., Richman D. D. Alternative splice acceptor utilization during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of cultured cells. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4093–4098. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4093-4098.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Chatterjee R., Cai Q. Prevalence of the plasma bovine leukaemia virus blocking factor in cattle from a commercial dairy herd. Vet Rec. 1989 Jul 1;125(1):5–6. doi: 10.1136/vr.125.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Kashmiri S. V., Ferrer J. F. Transcriptional control of the bovine leukemia virus genome: role and characterization of a non-immunoglobulin plasma protein from bovine leukemia virus-infected cattle. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):267–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.267-270.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly S. M., Rimsky L. T., Malim M. H., Kim J. H., Hauber J., Duc Dodon M., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Comparative analysis of the HTLV-I Rex and HIV-1 Rev trans-regulatory proteins and their RNA response elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1534–1544. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer L., Weichselbraun I., Quick S., Farrington G. K., Böhnlein E., Hauber J. Mutational analysis of the human T-cell leukemia virus type I trans-acting rex gene product. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3379–3383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3379-3383.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope T. J., McDonald D., Huang X. J., Low J., Parslow T. G. Mutational analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev transactivator: essential residues near the amino terminus. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5360–5366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5360-5366.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen W. A., Rovnak J., Cockerell G. L. In vivo transcription of the bovine leukemia virus tax/rex region in normal and neoplastic lymphocytes of cattle and sheep. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2484–2490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2484-2490.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwagi S., Kajiyama W., Hayashi J., Noguchi A., Nakashima K., Nomura H., Ikematsu H., Sawada T., Kida S., Koide A. Antibody to p40tax protein of human T cell leukemia virus 1 and infectivity. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):426–429. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen A. L., Kornberg T. B., Bishop J. M. Isolation of the proto-oncogene c-myb from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):449–456. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Cleuter Y., Gregoire D., Burny A. Role of the 3' long open reading frame region of bovine leukemia virus in the maintenance of cell transformation. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):899–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.899-901.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Deschamps J., Cleuter Y., Couez D., Burny A., Marbaix G. Leukemogenesis by bovine leukemia virus: proviral DNA integration and lack of RNA expression of viral long terminal repeat and 3' proximate cellular sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2465–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Marbaix G., Cleuter Y., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Burny A. Genomic integration of bovine leukemia provirus and lack of viral RNA expression in the target cells of cattle with different responses to BLV infection. Leuk Res. 1980;4(6):509–519. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(80)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. R., Kennedy B. S., Engel J. D. Two chicken erythrocyte band 3 mRNAs are generated by alternative transcriptional initiation and differential RNA splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5198–5206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Shimoyama M., Tobinai K., Ito M., Ito S., Ikeda S., Tajima K., Shimotohno K., Sugimura T. Detection of mRNA for the tax1/rex1 gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells of adult T-cell leukemia patients and viral carriers by using the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5620–5624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. Leucine zippers of fos, jun and GCN4 dictate dimerization specificity and thereby control DNA binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):568–571. doi: 10.1038/340568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota S., Siomi H., Satoh T., Endo S., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Functional similarity of HIV-I rev and HTLV-I rex proteins: identification of a new nucleolar-targeting signal in rev protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90767-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagarias D. M., Radke K. Transcriptional activation of bovine leukemia virus in blood cells from experimentally infected, asymptomatic sheep with latent infections. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2099–2107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2099-2107.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part II. Myb. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2235–2241. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi H., Ono E., Gupta K. C. Initiation of translation at CUG, GUG, and ACG codons in mammalian cells. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N. L., Morrow P., Mosca J., Vahey M., Burke D. S., Redfield R. R. Induction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression in chronically infected cells is associated primarily with a shift in RNA splicing patterns. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1291–1303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1291-1303.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Miller L. D., Olson C., Gillette K. G. Virus-like particles in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocyte cultures with reference to bovine lymphosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Dec;43(6):1297–1305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumberg D., Lucibello F. C., Schuermann M., Müller R. Alternative splicing of fosB transcripts results in differentially expressed mRNAs encoding functionally antagonistic proteins. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1212–1223. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muranyi W., Flügel R. M. Analysis of splicing patterns of human spumaretrovirus by polymerase chain reaction reveals complex RNA structures. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):727–735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.727-735.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa M., Kataoka K., Goto N., Fujiwara K. T., Kawai S. v-maf, a viral oncogene that encodes a "leucine zipper" motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7711–7715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama A., Chen Y. M., Tachibana N., Shioiri S., Lee T. H., Tsuda K., Essex M. High incidence of antibodies to HTLV-I tax in blood relatives of adult T cell leukemia patients. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):47–52. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita S., Saiga A., Takagi S., Tanaka T., Okumura K., Aono Y., Hinuma Y., Igarashi H. A novel alternatively spliced viral mRNA transcribed in cells infected with human T cell leukemia virus type 1 is mainly responsible for expressing p21X protein. FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 16;295(1-3):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81402-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers M. A., Grossman D., Kidd L. C., Radke K. Episodic occurrence of antibodies against the bovine leukemia virus Rex protein during the course of infection in sheep. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4959–4965. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4959-4965.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., De Billy G., Wang P., Darlix J. L. CUG initiation codon used for the synthesis of a cell surface antigen coded by the murine leukemia virus. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Simek S. L., Dubois G. C., Showalter S. D., Gilden R. V., Stephens R. M. Expression of the bovine leukemia virus X region in virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1577–1585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1577-1585.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Stephens R. M., Couez D., Deschamps J., Kettmann R., Burny A., Gilden R. V. The nucleotide sequence of the env gene and post-env region of bovine leukemia virus. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):82–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsky L., Dodon M. D., Dixon E. P., Greene W. C. Trans-dominant inactivation of HTLV-I and HIV-1 gene expression by mutation of the HTLV-I Rex transactivator. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):453–456. doi: 10.1038/341453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Guroff M., Popovic M., Gartner S., Markham P., Gallo R. C., Reitz M. S. Structure and expression of tat-, rev-, and nef-specific transcripts of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in infected lymphocytes and macrophages. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3391–3398. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3391-3398.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Willems L., Kettmann R., Campbell K., Zaya R., Burny A., Haseltine W. A. The 3' region of bovine leukemia virus genome encodes a trans-activator protein. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2585–2589. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04538.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. A., Kaeberle M. L., Griffith R. W. Effects of bovine viral diarrhea virus infection on bovine polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Feb;42(2):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Nagayoshi-Aida M., Shimizu F., Imagawa K., Ikawa Y. Identification and some biochemical properties of the major XBL gene product of bovine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7879–7883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Yasunaga T., Ikawa Y. Two distinct polypeptides may be translated from a single spliced mRNA of the X genes of human T-cell leukemia and bovine leukemia viruses. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel K. P., Hodge D. R., Chen Y. M., Papas T. S. Nef proteins of the human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV-1 and HIV-2) and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) are structurally similar to leucine zipper transcriptional activation factors. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Aug;7(8):697–706. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz R. L., Shih D. S., Rasty S., Montelaro R. C., Rushlow K. E. Equine infectious anemia virus gene expression: characterization of the RNA splicing pattern and the protein products encoded by open reading frames S1 and S2. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3455–3465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3455-3465.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Benko D. M., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Cloning and functional analysis of multiply spliced mRNA species of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2519–2529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2519-2529.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Env and Vpu proteins of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 are produced from multiple bicistronic mRNAs. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5448–5456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5448-5456.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Mechanism of translation of monocistronic and multicistronic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):207–219. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L. The myb oncogene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 1;1032(1):39–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(90)90011-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. P., Ehrlich G. D., Ferrer J. F., Sninsky J. J., Zandomeni R., Dock N. L., Poiesz B. Amplification and analysis of specific DNA and RNA sequences of bovine leukemia virus from infected cows by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):185–191. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.185-191.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Takahashi Y., Shimizu N., Gojobori T., Golde D. W., Chen I. S., Miwa M., Sugimura T. Complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of human T-cell leukemia virus type II: an open reading frame for the protease gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3101–3105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu G., Wurster A. L., Lipsick J. S., Hedrick S. M. Expression of the CD4 gene requires a Myb transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1592–1604. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Greene W. C. Characterization of a novel nuclear localization signal in the HTLV-I tax transactivator protein. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):316–320. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90320-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Greene W. C. Molecular biology of the type I human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I) and adult T-cell leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):761–766. doi: 10.1172/JCI115078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tochikura T., Iwahashi M., Matsumoto T., Koyanagi Y., Hinuma Y., Yamamoto N. Effect of human serum anti-HTLV antibodies on viral antigen induction in vitro cultured peripheral lymphocytes from adult T-cell leukemia patients and healthy virus carriers. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jul 15;36(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttenthal A., Larsen S., Lund E., Bloom M. E., Storgård T., Alexandersen S. Analysis of experimental mink enteritis virus infection in mink: in situ hybridization, serology, and histopathology. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2768–2779. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2768-2779.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetstone C. A., VanDerMaaten M. J., Miller J. M. A western blot assay for the detection of antibodies to bovine immunodeficiency-like virus in experimentally inoculated cattle, sheep, and goats. Arch Virol. 1991;116(1-4):119–131. doi: 10.1007/BF01319236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Bruck C., Portetelle D., Burny A., Kettmann R. Expression of a cDNA clone corresponding to the long open reading frame (XBL-I) of the bovine leukemia virus. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Gegonne A., Chen G., Burny A., Kettmann R., Ghysdael J. The bovine leukemia virus p34 is a transactivator protein. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3385–3389. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip M. T., Chen I. S. Modes of transformation by the human T-cell leukemia viruses. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Feb;7(1):33–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Seiki M. Recent advances in the molecular biology of HTLV-1: trans-activation of viral and cellular genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:541–559. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M. Multiple cDNA clones encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobel A., Kalkbrenner F., Guehmann S., Nawrath M., Vorbrueggen G., Moelling K. Interaction of the v-and c-Myb proteins with regulatory sequences of the human c-myc gene. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1397–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]