Abstract
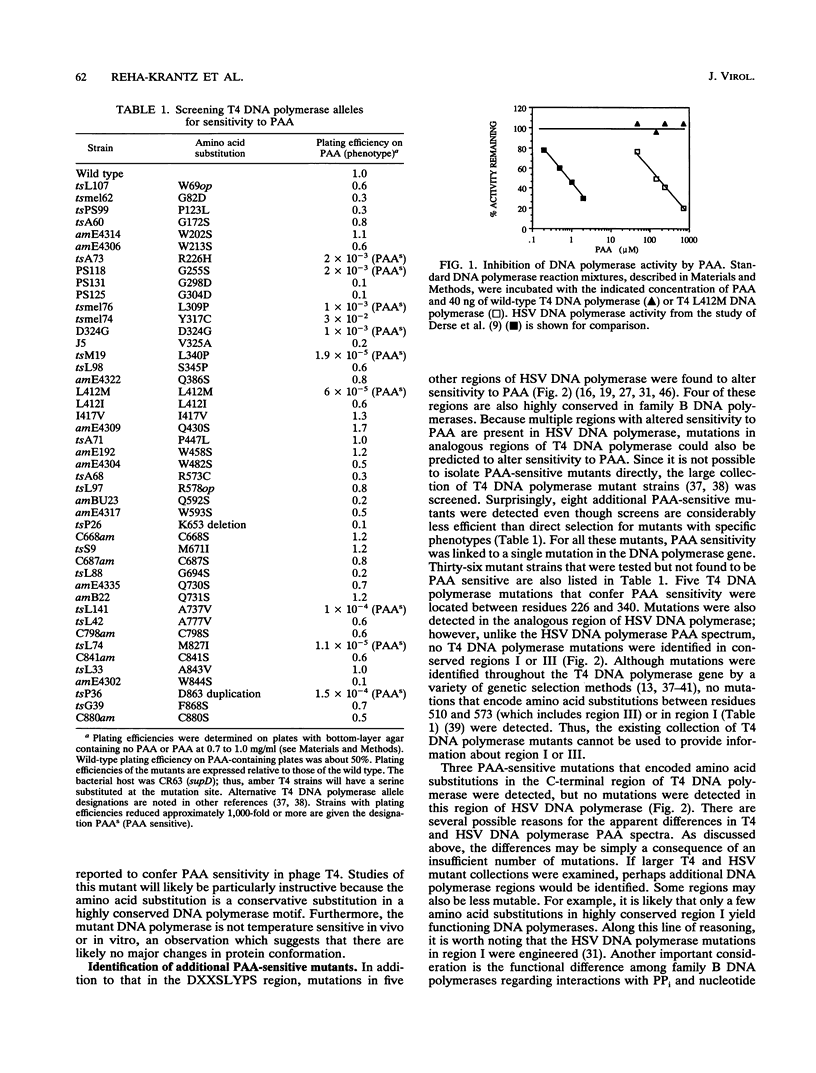
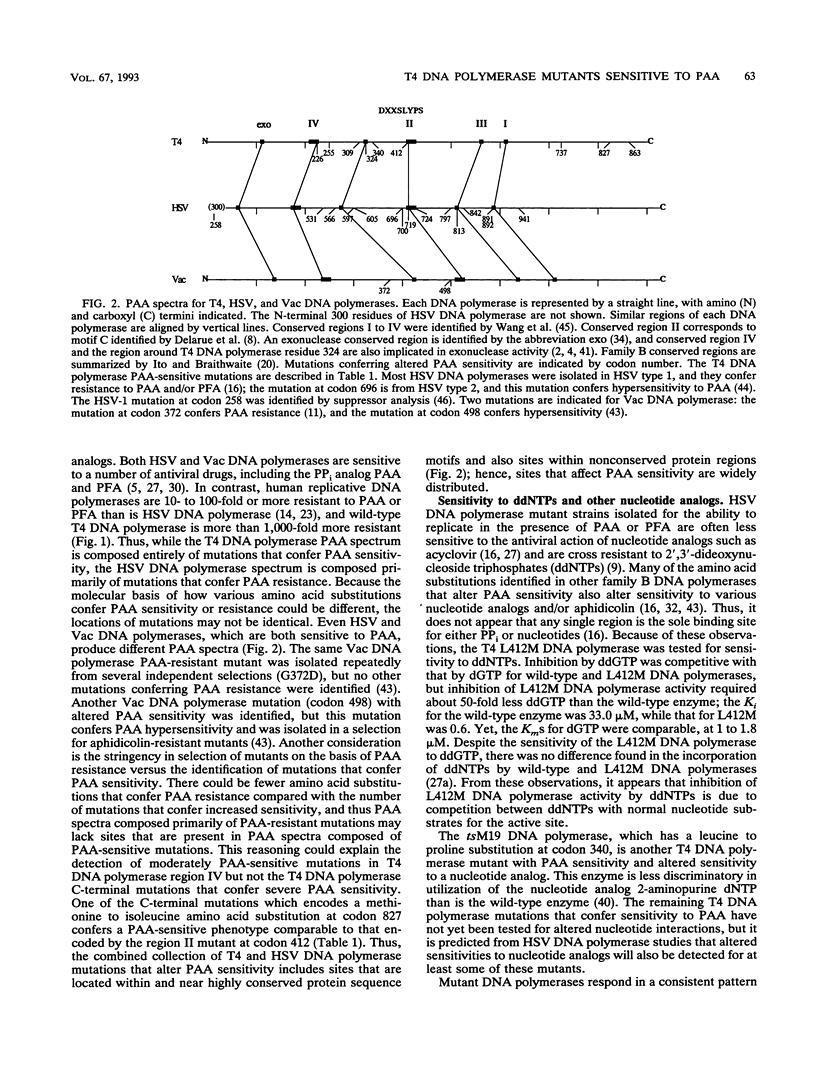
Mutations that conferred sensitivity to the pyrophosphate analog phosphonoacetic acid in bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase were identified. The mutations were loosely clustered in four regions of the gene. As found for herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase, T4 mutations that altered sensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid also altered sensitivity to nucleotide analogs. Some of the T4 DNA polymerase mutations also altered the ability of the enzyme to translocate from one template position to the next and affected DNA replication fidelity. Kornberg (A. Kornberg, Science 163:1410-1418, 1969) envisioned a DNA polymerase active center which accommodates primer terminus and template DNAs and the incoming nucleotide. Some mutations identified on the basis of sensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid may be part of such an active center because single amino acid substitutions simultaneously alter several DNA polymerase functions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beauchamp B. B., Richardson C. C. A unique deoxyguanosine triphosphatase is responsible for the optA1 phenotype of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2563–2567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernad A., Blanco L., Lázaro J. M., Martín G., Salas M. A conserved 3'----5' exonuclease active site in prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90883-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernad A., Lázaro J. M., Salas M., Blanco L. The highly conserved amino acid sequence motif Tyr-Gly-Asp-Thr-Asp-Ser in alpha-like DNA polymerases is required by phage phi 29 DNA polymerase for protein-primed initiation and polymerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4610–4614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco L., Bernad A., Blasco M. A., Salas M. A general structure for DNA-dependent DNA polymerases. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:27–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90346-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolden A., Aucker J., Weissbach A. Synthesis of herpes simplex virus, vaccinia virus, and adenovirus DNA in isolated HeLa cell nuclei. I. Effect of viral-specific antisera and phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1584–1592. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1584-1592.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase M, Doermann A H. High Negative Interference over Short Segments of the Genetic Structure of Bacteriophage T4. Genetics. 1958 May;43(3):332–353. doi: 10.1093/genetics/43.3.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg M. E., Benkovic S. J. Kinetic mechanism of DNA polymerase I (Klenow fragment): identification of a second conformational change and evaluation of the internal equilibrium constant. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):4835–4843. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delarue M., Poch O., Tordo N., Moras D., Argos P. An attempt to unify the structure of polymerases. Protein Eng. 1990 May;3(6):461–467. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.6.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S. Site-specific mutagenesis of a highly conserved region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase gene. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1394–1397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1394-1397.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Jones E. V., Moss B. Homology between DNA polymerases of poxviruses, herpesviruses, and adenoviruses: nucleotide sequence of the vaccinia virus DNA polymerase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund P. T., Huberman J. A., Jovin T. M., Kornberg A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXX. Binding of triphosphates to deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):3038–3044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B., Oberg B., Wahren B. Pyrophosphate analogues as inhibitors of DNA polymerases of cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus and cellular origin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 26;696(2):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss P., Doherty D. H., Gold L. Bacterial and phage mutations that reveal helix-unwinding activities required for bacteriophage T4 DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1669–1673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Chiou H. C., Bastow K. F., Cheng Y. C., Coen D. M. Identification of amino acids in herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase involved in substrate and drug recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6672–6676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Nossal N. G. Control of mutation frequency by bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. I. The CB120 antimutator DNA polymerase is defective in strand displacement. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5219–5224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulian M., Lucas Z. J., Kornberg A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXV. Purification and properties of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase induced by infection with phage T4. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):627–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang C. B., Ruffner K. L., Coen D. M. A point mutation within a distinct conserved region of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene confers drug resistance. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1774–1776. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1774-1776.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito J., Braithwaite D. K. Compilation and alignment of DNA polymerase sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4045–4057. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik J., Botstein D. Conditional-lethal mutations that suppress genetic defects in morphogenesis by altering structural proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2738–2742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung G. H., Leavitt M. C., Schultz M., Ito J. Site-specific mutagenesis of PRD1 DNA polymerase: mutations in highly conserved regions of the family B DNA polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 16;170(3):1294–1300. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90534-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallin B., Sternås L., Saemundssen A. K., Luka J., Jörnvall H., Eriksson B., Tao P. Z., Nilsson M. T., Klein G. Purification of Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase from P3HR-1 cells. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):561–568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.561-568.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf C. W. Nucleotide sequence of the DNA polymerase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 strain Angelotti. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8225–8226. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Wang J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1377403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A. Active center of DNA polymerase. Science. 1969 Mar 28;163(3874):1410–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3874.1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D., Darby G. Related functional domains in virus DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):169–175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04735.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Reno J. M., Lee L. F., Isbell A. F., Boezi J. A. Mechanism of phosphonoacetate inhibition of herpesvirus-induced DNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):426–430. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. C., Rush J., Spicer E. K., Konigsberg W. H. Cloning and expression of T4 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7000–7004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E., Overby L. R. Inhibition of DNA polymerase from herpes simplex virus-infected wi-38 cells by phosphonoacetic Acid. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1281–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1281-1283.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcy A. I., Hwang C. B., Ruffner K. L., Coen D. M. Engineered herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase point mutants: the most highly conserved region shared among alpha-like DNA polymerases is involved in substrate recognition. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5883–5890. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5883-5890.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Kim C. I., Kobayashi H., Kanehiro H., Hirokawa H. Aphidicolin-resistant DNA polymerase of bacteriophage phi 29 APHr71 mutant is hypersensitive to phosphonoacetic acid and butylphenyldeoxyguanosine 5'-triphosphate. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):337–339. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90416-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. F., Hama-Inaba H., Mace D., Sinha N. K., Alberts B. Purification of the gene 43, 44, 45, and 62 proteins of the bacteriophage T4 DNA replication apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6787–6796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Bell J. B., Kunkel T. A., Sugino A. Eukaryotic DNA polymerase amino acid sequence required for 3'----5' exonuclease activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9473–9477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzyczka N., Poland R. L., Bessman M. J. Studies on the biochemical basis of spontaneous mutation. I. A comparison of the deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of mutator, antimutator, and wild type strains of bacteriophage T4. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7116–7122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollis D. L., Brick P., Hamlin R., Xuong N. G., Steitz T. A. Structure of large fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I complexed with dTMP. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):762–766. doi: 10.1038/313762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reha-Krantz L. J. Amino acid changes coded by bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase mutator mutants. Relating structure to function. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):711–724. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90552-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reha-Krantz L. J., Bessman M. J. Studies on the biochemical basis of mutation VI. Selection and characterization of a new bacteriophage T4 mutator DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):677–695. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90309-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reha-Krantz L. J. Locations of amino acid substitutions in bacteriophage T4 tsL56 DNA polymerase predict an N-terminal exonuclease domain. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4762–4766. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4762-4766.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reha-Krantz L. J., Stocki S., Nonay R. L., Dimayuga E., Goodrich L. D., Konigsberg W. H., Spicer E. K. DNA polymerization in the absence of exonucleolytic proofreading: in vivo and in vitro studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2417–2421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Rush J., Fung C., Reha-Krantz L. J., Karam J. D., Konigsberg W. H. Primary structure of T4 DNA polymerase. Evolutionary relatedness to eucaryotic and other procaryotic DNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7478–7486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taddie J. A., Traktman P. Genetic characterization of the vaccinia virus DNA polymerase: identification of point mutations conferring altered drug sensitivities and reduced fidelity. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):869–879. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.869-879.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi T., Maeno K., Nishiyama Y. A single-base change within the DNA polymerase locus of herpes simplex virus type 2 can confer resistance to aphidicolin. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):388–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.388-394.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Wong S. W., Korn D. Human DNA polymerase alpha: predicted functional domains and relationships with viral DNA polymerases. FASEB J. 1989 Jan;3(1):14–21. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.1.2642867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. S., Woodward S., Hall J. D. Use of suppressor analysis to identify DNA polymerase mutations in herpes simplex virus which affect deoxynucleoside triphosphate substrate specificity. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1814–1816. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1814-1816.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



