Abstract
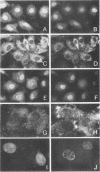
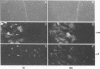
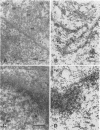
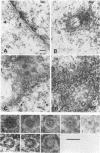
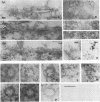
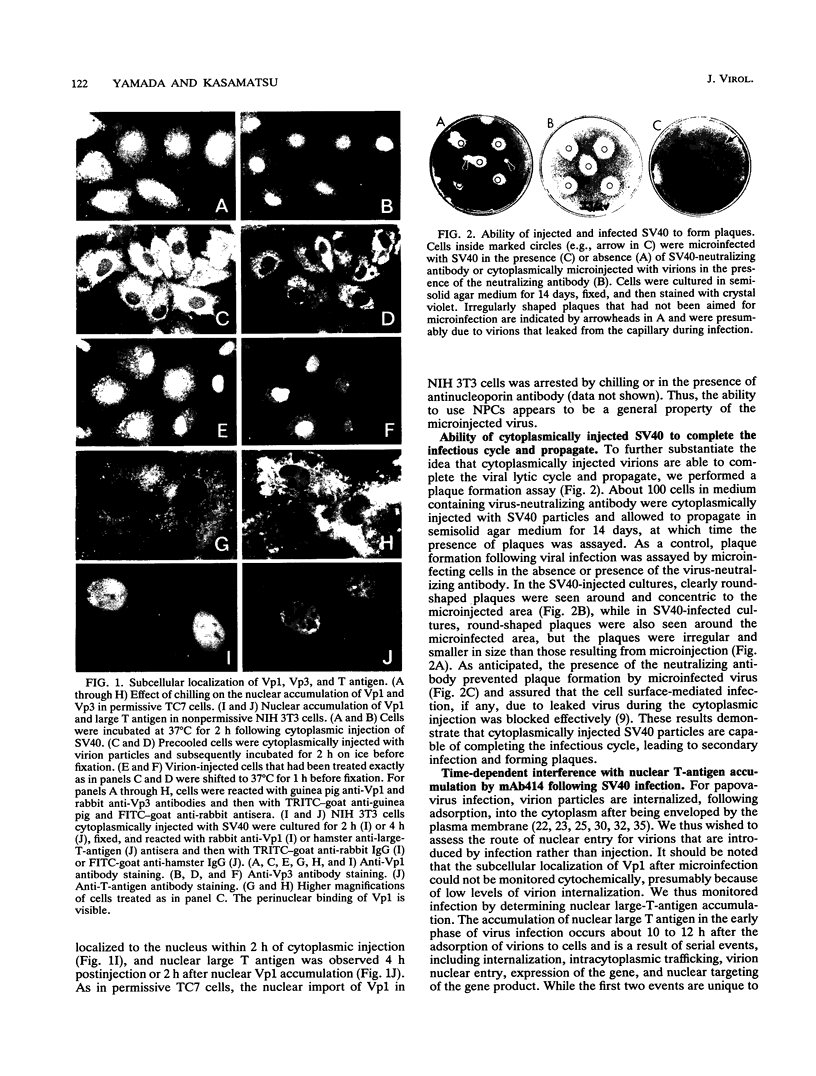
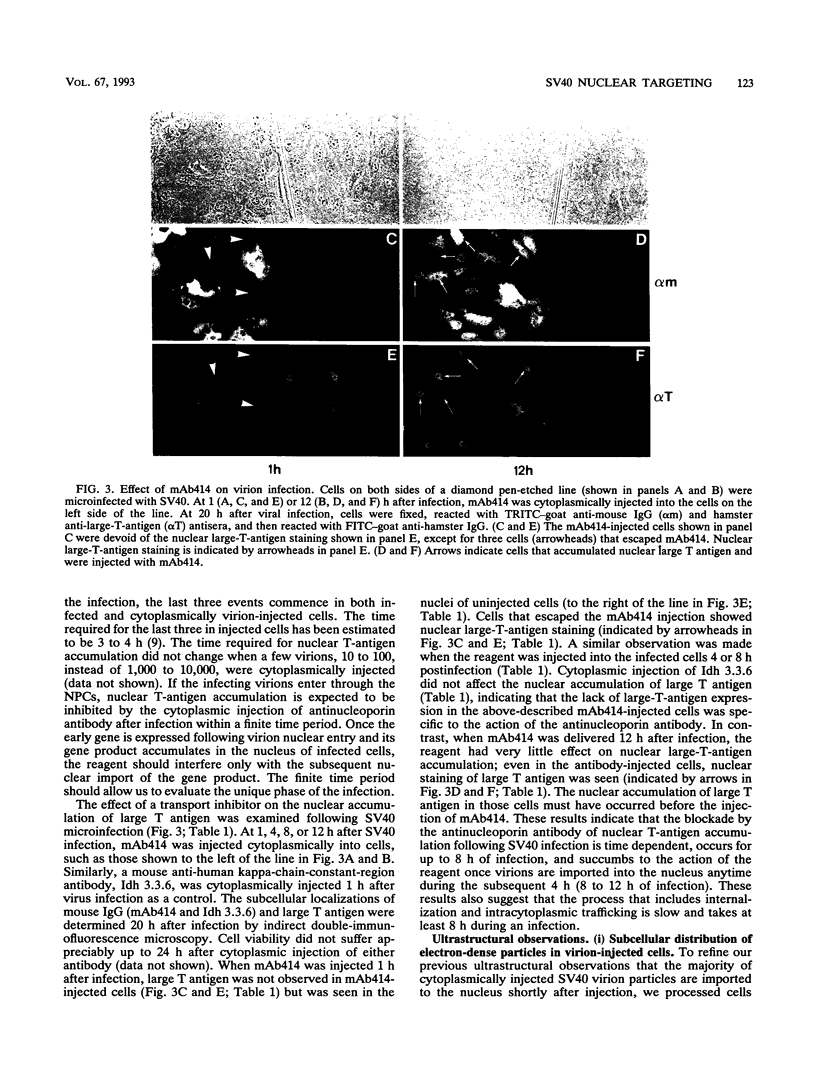
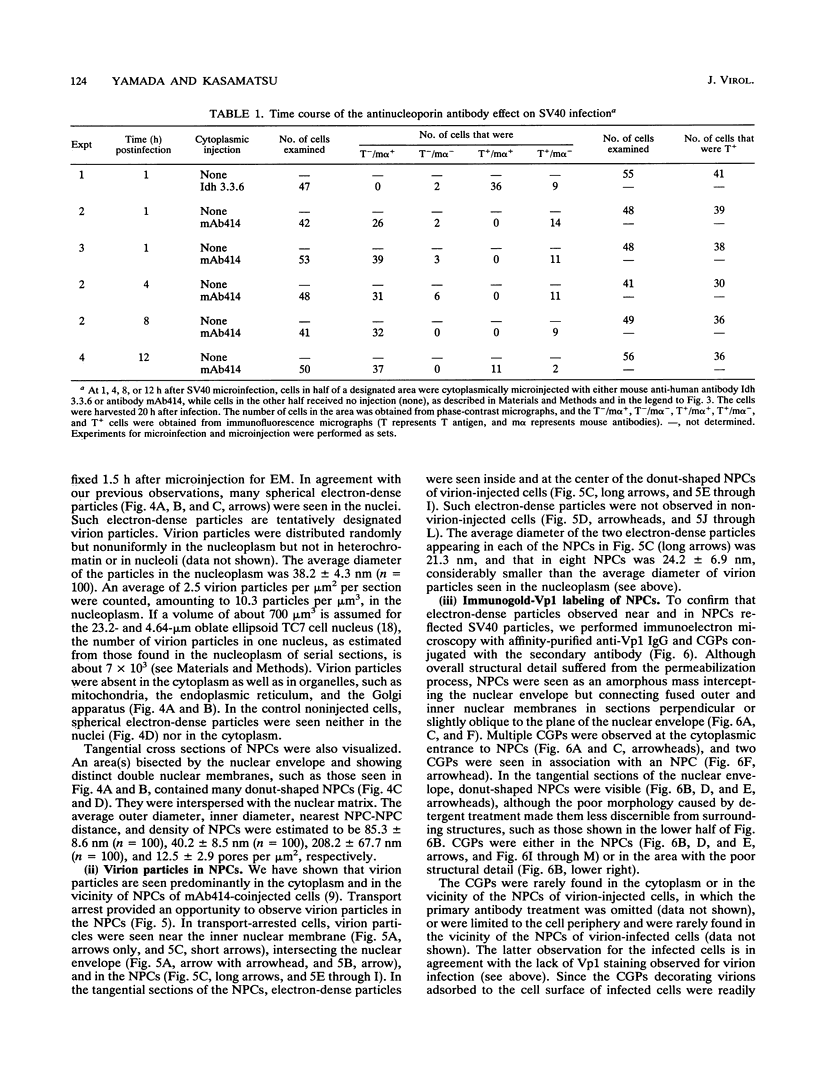
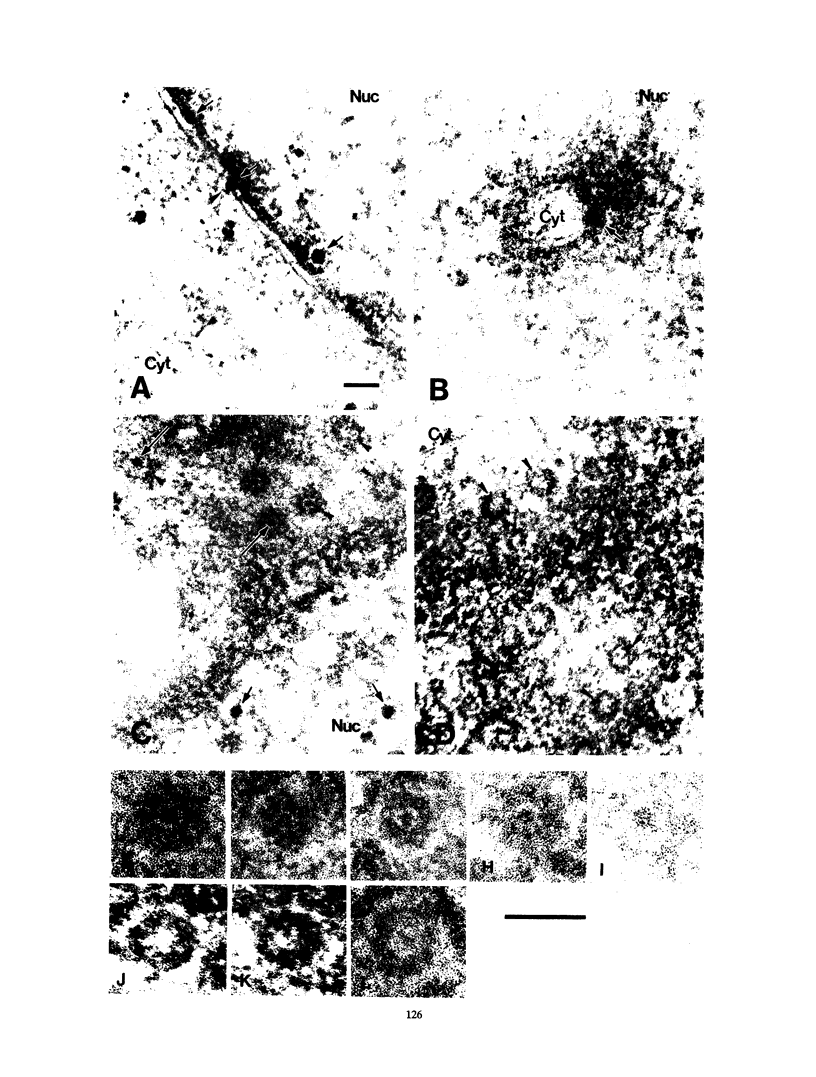
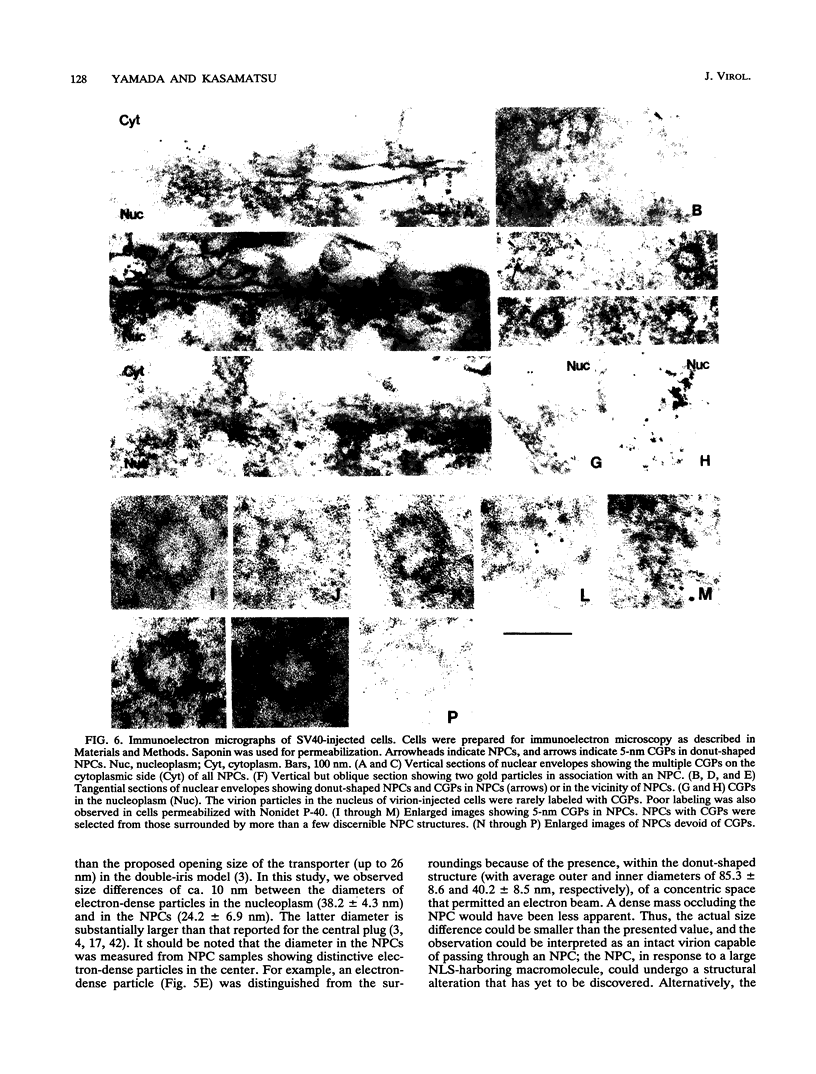
Cytoplasmically injected simian virus 40 (SV40) virions enter the nucleus through nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) and can express large T antigen shortly thereafter (J. Clever, M. Yamada, and H. Kasamatsu, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:7333-7337, 1991). The nuclear import of the protein components of introduced SV40 was reversibly arrested by chilling and energy depletion, corroborating our previous observation that the nuclear entry of injected SV40 is blocked in the presence of wheat germ agglutinin and an antinucleoporin monoclonal antibody (mAb414), general inhibitors of NPC-mediated import. The nuclear accumulation of virion protein components and large T antigen in nonpermissive NIH 3T3 cells was similar to that in the permissive host, indicating that the ability to use NPCs as a route of nuclear entry appears to be a general property of the injected virus. Injected virions were capable of completing their lytic cycle and forming plaques in permissive cells. During the early phase of SV40 infection, the cytoplasmic injection of mAb414 effectively blocked nuclear T-antigen accumulation for up to 8 h of infection but had very little effect after 12 h of infection. The time-dependent interference with nuclear T-antigen accumulation by the antinucleoporin antibody is consistent with the hypothesis that the infecting virions enter the nucleus through NPCs. The interference study also suggests that the early phase of infection consists of at least two steps: a step for virion cell entry and intracytoplasmic trafficking and a step for virion nuclear entry followed by large-T-antigen gene expression and subsequent nuclear localization of the gene product. Virions were visualized as electron-dense particles in ultrathin sections of samples in which transport was permitted or arrested. In the former cells, electron-dense particles were predominantly observed in the nucleus. The virions were distributed randomly and nonuniformly in the nucleoplasm but were not observed in heterochromatin or in nucleoli. In the latter cells, the electron-dense particles were seen intersecting the nuclear envelope, near the inner nuclear membrane, and in NPCs. In tangential cross sections of NPCs, which appeared as donut-shaped structures, a spherical electron-dense particle was observed in the center of the structure. Immunoelectron microscopy revealed that NPCs were selectively decorated with 5-nm colloidal gold particles-anti-Vp1 immunoglobulin G at the cytoplasmic entrance to and in NPCs, confirming that the morphologically observed electron-dense particles in NPCs contain the viral structural protein. These results support the hypothesis that the nuclear import of SV40 is catalyzed through NPCs by an active transport mechanism that is similar to that of other karyophiles.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Lobl T. J., Mitchell M. A., Gerace L. Identification of specific binding proteins for a nuclear location sequence. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):276–279. doi: 10.1038/337276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W., Goldfarb D. S. Protein import through the nuclear pore complex is a multistep process. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):971–982. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W. Interactions and structure of the nuclear pore complex revealed by cryo-electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):955–970. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W. Visualization of transport-related configurations of the nuclear pore transporter. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):341–355. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82381-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benavente R., Scheer U., Chaly N. Nucleocytoplasmic sorting of macromolecules following mitosis: fate of nuclear constituents after inhibition of pore complex function. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;50(1):209–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M. Protein migration into nuclei. I. Frog oocyte nuclei in vivo accumulate microinjected histones, allow entry to small proteins, and exclude large proteins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):421–430. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeuwer M., Goldfarb D. S. Facilitated nuclear transport of histone H1 and other small nucleophilic proteins. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):999–1008. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90348-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clever J., Kasamatsu H. Simian virus 40 Vp2/3 small structural proteins harbor their own nuclear transport signal. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):78–90. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90472-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clever J., Yamada M., Kasamatsu H. Import of simian virus 40 virions through nuclear pore complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7333–7337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworetzky S. I., Lanford R. E., Feldherr C. M. The effects of variations in the number and sequence of targeting signals on nuclear uptake. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1279–1287. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Darby M. K., Gerace L. A monoclonal antibody against the nuclear pore complex inhibits nucleocytoplasmic transport of protein and RNA in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1289–1297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldherr C. M., Akin D. The permeability of the nuclear envelope in dividing and nondividing cell cultures. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):1–8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldherr C. M., Kallenbach E., Schultz N. Movement of a karyophilic protein through the nuclear pores of oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2216–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendrick J. L., Hallick L. M. Optimal conditions for titration of SV40 by the plaque assay method. J Virol Methods. 1983 Aug;7(2):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(83)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay D. R., Newmeyer D. D., Price T. M., Forbes D. J. Inhibition of in vitro nuclear transport by a lectin that binds to nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):189–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W. Structure, biochemistry, and functions of the nuclear envelope. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;Suppl 4:71–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. P., Kasamatsu H. Immuno-electron-microscopic localization of a centriole-related antigen in ciliated cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;239(1):43–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00214901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershey E. L., Diacumakos E. G. Simian virus 40 production after viral uncoating in the CV-1 cell nucleus. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):415–416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.415-416.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb D. S., Gariépy J., Schoolnik G., Kornberg R. D. Synthetic peptides as nuclear localization signals. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):641–644. doi: 10.1038/322641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith G. R., Marriott S. J., Rintoul D. A., Consigli R. A. Early events in polyomavirus infection: fusion of monopinocytotic vesicles containing virions with mouse kidney cell nuclei. Virus Res. 1988 Apr;10(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummeler K., Tomassini N., Sokol F. Morphological aspects of the uptake of simian virus 40 by permissive cells. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):87–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.87-93.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamoto-Sonobe N., Yoneda Y., Iwamoto R., Sugawa H., Uchida T. ATP-dependent association of nuclear proteins with isolated rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3426–3430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartenbeck J., Stukenbrok H., Helenius A. Endocytosis of simian virus 40 into the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2721–2729. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamatsu H., Wu M. Protein-SV40 DNA complex stable in high salt and sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):927–936. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Induction of nuclear transport with a synthetic peptide homologous to the SV40 T antigen transport signal. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang I., Scholz M., Peters R. Molecular mobility and nucleocytoplasmic flux in hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1183–1190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Hata T., Kasamatsu H. Subcellular distribution of viral structural proteins during simian virus 40 infection. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):363–371. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.363-371.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. L., Consigli R. A. Early events in polyoma virus infection: attachment, penetration, and nuclear entry. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):620–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.620-636.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G., Price J. W., Lieberman M. W. Formation and distribution of nuclear pore complexes in interphase. J Cell Biol. 1971 Nov;51(21):405–418. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G., Rovera G., Vorbrodt A., Abramczuk J. Membrane fusion as a mechanism of simian virus 40 entry into different cellular compartments. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):936–944. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.936-944.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Forbes D. J. Nuclear import can be separated into distinct steps in vitro: nuclear pore binding and translocation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):641–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Lucocq J. M., Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. Assembly in vitro of nuclei active in nuclear protein transport: ATP is required for nucleoplasmin accumulation. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):501–510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura T., Kawai N., Kawai M., Notake K., Ichihara I. Fusion of SV40-induced endocytotic vacuoles with the nuclear membrane. Cell Struct Funct. 1986 Jun;11(2):135–141. doi: 10.1247/csf.11.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L., Moore L. C., Horowitz S. B. Nuclear envelope permeability. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):109–114. doi: 10.1038/254109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt R., Holzenburg A., Buhle E. L., Jr, Jarnik M., Engel A., Aebi U. Correlation between structure and mass distribution of the nuclear pore complex and of distinct pore complex components. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):883–894. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Mills A. D., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Nuclear protein migration involves two steps: rapid binding at the nuclear envelope followed by slower translocation through nuclear pores. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P., Sadler I., Osborne M. A. Yeast proteins that recognize nuclear localization sequences. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):983–989. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Milligan R. A. A large particle associated with the perimeter of the nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):63–75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki L., Kanda P., Lanford R. E. Identification of four nuclear transport signal-binding proteins that interact with diverse transport signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3028–3036. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda Y., Arioka T., Imamoto-Sonobe N., Sugawa H., Shimonishi Y., Uchida T. Synthetic peptides containing a region of SV 40 large T-antigen involved in nuclear localization direct the transport of proteins into the nucleus. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jun;170(2):439–452. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda Y., Imamoto-Sonobe N., Matsuoka Y., Iwamoto R., Kiho Y., Uchida T. Antibodies to Asp-Asp-Glu-Asp can inhibit transport of nuclear proteins into the nucleus. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):275–278. doi: 10.1126/science.3051382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]