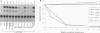Abstract
The bel1 gene of human spumaretrovirus (HSRV) codes for a 300-amino-acid nuclear protein, termed Bel1, that can strongly activate transcription from the cognate long terminal repeat (LTR) by at least 200-fold. Bel1 can also activate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) LTR expression. By using site-directed mutagenesis, we have identified distinct regions of Bel1 essential for HSRV LTR activation. The amino-terminal 55 residues, which comprise a highly acidic region followed by a short basic stretch, were dispensable for activation. The distribution of functionally defective mutants indicates that two distinct regions between residues 56 and 300 cooperate to confer full activator function. The larger, more amino-terminal region between residues 56 and 227 is sufficient to minimally activate the HSRV LTR. It contains a region between residues 88 and 110 that is strongly conserved between the simian and human spumavirus transactivators but otherwise lacks obvious homology to known transcriptional activators except for an Arg-rich nuclear localization sequence (NLS) between residues 211 and 225 that can be functionally substituted for by the NLS of the simian virus 40 large T antigen. The carboxy-terminal 73 residues contain two functionally redundant regions that can independently augment the activity of the more N-terminal minimal activator domain by 30- to 90-fold. Comparative analysis of the effect of Bel1 mutations on HSRV and HIV-1 LTR expression revealed a similar requirement of Bel1 domains for activation of the two LTRs. Bel1 is phosphorylated in vivo, and a nuclear localization-defective mutant lacking residues 211 to 222 was severely defective for phosphorylation, whereas various deletion mutations in residues 228 to 300 resulted in a four- to eightfold reduction in phosphate incorporation. When functionally defective bel1 mutants were examined for a dominant-negative phenotype, only mutants lacking a proline-rich basic region between residues 194 and 200 or the NLS between residues 211 and 222 that were found to occupy predominantly nuclear and cytoplasmic locations, respectively, could suppress wild-type Bel1 function efficiently. In identifying two classes of dominant-negative mutants with distinct subcellular localization phenotypes, the mutational analysis of Bel1 has revealed a feature unusual for known transcriptional activators.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Gene therapy. Intracellular immunization. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):395–396. doi: 10.1038/335395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothe K., Aguzzi A., Lassmann H., Rethwilm A., Horak I. Progressive encephalopathy and myopathy in transgenic mice expressing human foamy virus genes. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):555–557. doi: 10.1126/science.1650034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G. Modulation of HIV-enhancer activity by heterologous agents: a minireview. Gene. 1991 May 30;101(2):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90407-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A., Kramer R., Ruben S., Levine J., Rosen C. A. The human immunodeficiency virus rev protein is a nuclear phosphoprotein. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):264–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90535-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Rethwilm A., Maurer B., Darai G. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the env gene and its flanking regions of the human spumaretrovirus reveals two novel genes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2077–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., MacDonald J. J., Lees-Miller S., Tjian R. GC box binding induces phosphorylation of Sp1 by a DNA-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90296-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A., Partin K. M., Löchelt M., Bannert H., Flügel R. M., Cullen B. R. Characterization of the transcriptional trans activator of human foamy retrovirus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2589–2594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2589-2594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy M., Subramanian T., Srinivasan A., Chinnadurai G. Multiple functional domains of Tat, the trans-activator of HIV-1, defined by mutational analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3551–3561. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Zentgraf H., Flügel R. M. Construction of an infectious DNA clone of the full-length human spumaretrovirus genome and mutagenesis of the bel 1 gene. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90820-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Flügel R. M. The 3'-orf protein of human immunodeficiency virus 2 shows sequence homology with the bel3 gene of the human spumaretrovirus. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):286–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Luciw P. A. Replication and regulation of primate foamy viruses. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):475–482. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90417-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Pratt-Lowe E., Shaw K. E., Renshaw-Gegg L. W., Luciw P. A. cis-acting regulatory regions in the long terminal repeat of simian foamy virus type 1. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):251–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.251-257.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Shaw K. E., Pratt-Lowe E., Barry P. A., Luciw P. A. Identification of the simian foamy virus transcriptional transactivator gene (taf). J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2903–2909. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2903-2909.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Shaw K. E., Pratt-Lowe E., Barry P. A., Luciw P. A. Simian foamy virus type 1 is a retrovirus which encodes a transcriptional transactivator. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3598–3604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3598-3604.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muranyi W., Flügel R. M. Analysis of splicing patterns of human spumaretrovirus by polymerase chain reaction reveals complex RNA structures. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):727–735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.727-735.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Rice S. A., Knipe D. M., Baltimore D. Alternative mechanisms for activation of human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.2830675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Baunach G., Netzer K. O., Maurer B., Borisch B., ter Meulen V. Infectious DNA of the human spumaretrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):733–738. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Erlwein O., Baunach G., Maurer B., ter Meulen V. The transcriptional transactivator of human foamy virus maps to the bel 1 genomic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):941–945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Mori K., Maurer B., ter Meulen V. Transacting transcriptional activation of human spumaretrovirus LTR in infected cells. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):568–571. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90442-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segil N., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Mitotic phosphorylation of the Oct-1 homeodomain and regulation of Oct-1 DNA binding activity. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1814–1816. doi: 10.1126/science.1684878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A. How proteins enter the nucleus. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90233-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Theodorakis P. A., Chinnadurai G. Distinct cis-acting regions in U3 regulate trans-activation of the human spumaretrovirus long terminal repeat by the viral bel1 gene product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3661–3666. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A. Foamy retroviruses. A virus in search of a disease. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):497–498. doi: 10.1038/333497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]