Abstract
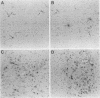
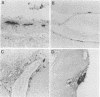
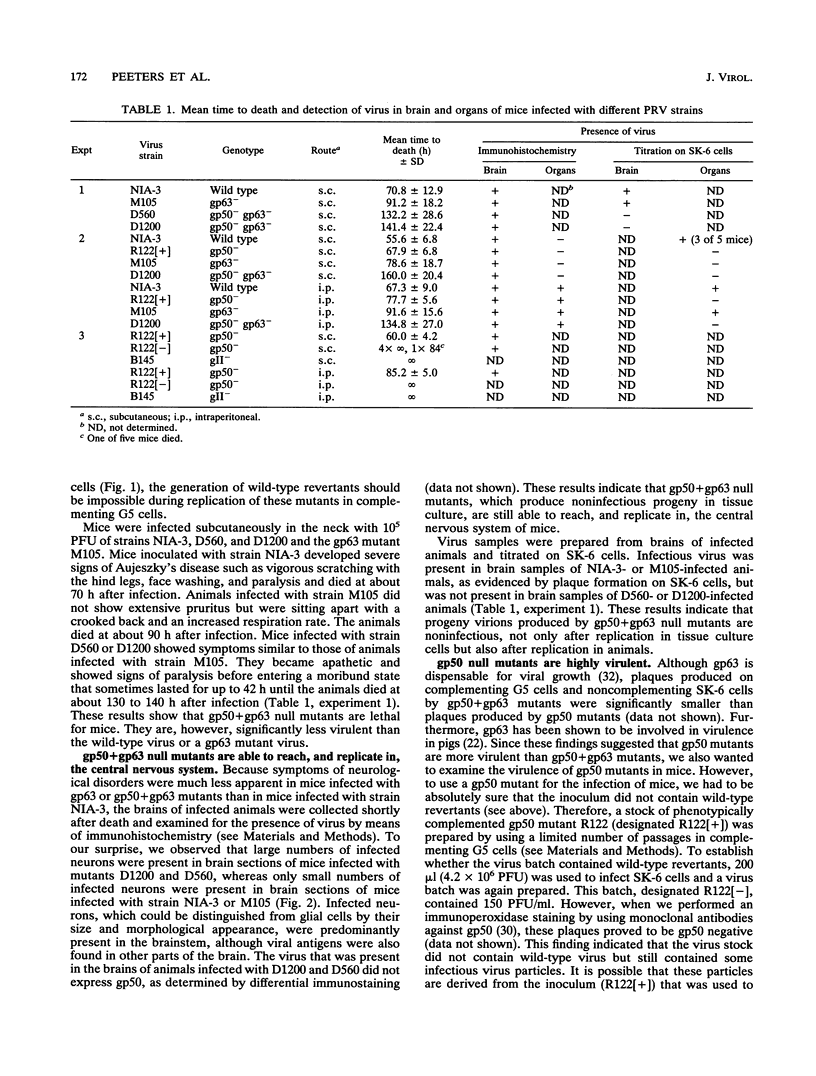
Phenotypically complemented pseudorabies virus gp50 null mutants are able to produce plaques on noncomplementing cell lines despite the fact that progeny virions are noninfectious. To determine whether gp50 null mutants and gp50+gp63 null mutants are also able to replicate and spread in animals, mice were infected subcutaneously or intraperitoneally. Surprisingly, both gp50 mutants and gp50+gp63 double mutants proved to be lethal for mice. In comparison with the wild-type virus, gp50 mutants were still highly virulent, whereas the virulence of gp50+gp63 mutants was significantly reduced. Severe signs of neurological disorders, notably pruritus, were apparent in animals infected with the wild-type virus or a gp50 mutant but were much less pronounced in animals infected with a gp50+gp63 or gp63 mutant. Immunohistochemical examination of infected animals showed that all viruses were able to reach, and replicate in, the brain. Examination of visceral organs of intraperitoneally infected animals showed that viral antigen was predominantly present in peripheral nerves, suggesting that the viruses reached the central nervous system by means of retrograde axonal transport. Infectious virus could not be recovered from the brains and organs of animals infected with gp50 or gp50+gp63 mutants, indicating that progeny virions produced in vivo are noninfectious. Virions that lacked gp50 in their envelopes, and a phenotypically complemented pseudorabies virus gII mutant (which is unable to produce plaques in tissue culture cells), proved to be nonvirulent for mice. Together, these results show that gp50 is required for the primary infection but not for subsequent replication and viral spread in vivo. These results furthermore indicate that transsynaptic transport of the virus is independent of gp50. Since progeny virions produced by gp50 mutants are noninfectious, they are unable to spread from one animal to another. Therefore, such mutants may be used for the development of a new generation of safer (carrier) vaccines.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cai W. H., Gu B., Person S. Role of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1 in viral entry and cell fusion. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2596–2604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2596-2604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Arsenakis M., Farabegoli F., Roizman B. Entry of herpes simplex virus 1 in BJ cells that constitutively express viral glycoprotein D is by endocytosis and results in degradation of the virus. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):159–167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.159-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card J. P., Rinaman L., Schwaber J. S., Miselis R. R., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Neurotropic properties of pseudorabies virus: uptake and transneuronal passage in the rat central nervous system. J Neurosci. 1990 Jun;10(6):1974–1994. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-06-01974.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus envelope glycoprotein gI influences both neurotropism and virulence during infection of the rat visual system. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3032–3041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3032-3041.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Moore R. Y., Enquist L. W. Two alpha-herpesvirus strains are transported differentially in the rodent visual system. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):957–969. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90236-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Pathogenesis of herpetic neuritis and ganglionitis in mice: evidence for intra-axonal transport of infection. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):272–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.272-288.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix R. D., McKendall R. R., Baringer J. R. Comparative neurovirulence of herpes simplex virus type 1 strains after peripheral or intracerebral inoculation of BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):103–112. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.103-112.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Hill T. J. The pathogenesis of pseudorabies in mice following peripheral inoculation. J Gen Virol. 1974 May;23(2):145–157. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-23-2-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Hill T. J. The pathogenesis of pseudorabies in mice: virus replication at the inoculation site and axonal uptake. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jan;26(1):145–148. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-1-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester A., Farrell H., Wilkinson G., Kaye J., Davis-Poynter N., Minson T. Construction and properties of a mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1 with glycoprotein H coding sequences deleted. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):341–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.341-348.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser G., Ramachandran S. P. Studies on the virus of Aujeszky's disease. I. Pathogenicity for rats and mice. J Comp Pathol. 1969 Oct;79(4):435–444. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(69)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gompels U. A., Minson A. C. Antigenic properties and cellular localization of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein H synthesized in a mammalian cell expression system. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4744–4755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4744-4755.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. L., Engel J. P. Altered pathogenesis in herpes simplex virus type 1 infection due to a syncytial mutation mapping to the carboxy terminus of glycoprotein B. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1770–1778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1770-1778.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highlander S. L., Sutherland S. L., Gage P. J., Johnson D. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies specific for herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D inhibit virus penetration. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3356–3364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3356-3364.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasza L., Shadduck J. A., Christofinis G. J. Establishment, viral susceptibility and biological characteristics of a swine kidney cell line SK-6. Res Vet Sci. 1972 Jan;13(1):46–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimman T. G., de Wind N., Oei-Lie N., Pol J. M., Berns A. J., Gielkens A. L. Contribution of single genes within the unique short region of Aujeszky's disease virus (suid herpesvirus type 1) to virulence, pathogenesis and immunogenicity. J Gen Virol. 1992 Feb;73(Pt 2):243–251. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligas M. W., Johnson D. C. A herpes simplex virus mutant in which glycoprotein D sequences are replaced by beta-galactosidase sequences binds to but is unable to penetrate into cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1486–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1486-1494.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke E., Kristensson K., Svennerholm B., Vahlne A., Ziegler R. Uptake and transport of herpes simplex virus in neurites of rat dorsal root ganglia cells in culture. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):55–64. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken R. M., McFerran J. B., Dow C. The neural spread of pseudorabies virus in calves. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jul;20(1):17–28. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C. Molecular biology of pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) virus. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991;14(2):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(91)90128-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minson A. C., Hodgman T. C., Digard P., Hancock D. C., Bell S. E., Buckmaster E. A. An analysis of the biological properties of monoclonal antibodies against glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus and identification of amino acid substitutions that confer resistance to neutralization. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1001–1013. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B., de Wind N., Broer R., Gielkens A., Moormann R. Glycoprotein H of pseudorabies virus is essential for entry and cell-to-cell spread of the virus. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3888–3892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3888-3892.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B., de Wind N., Hooisma M., Wagenaar F., Gielkens A., Moormann R. Pseudorabies virus envelope glycoproteins gp50 and gII are essential for virus penetration, but only gII is involved in membrane fusion. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):894–905. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.894-905.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Gierman T. M., Post L. E. Deletions in vaccine strains of pseudorabies virus and their effect on synthesis of glycoprotein gp63. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1166–1169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1166-1169.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt K. B., Maré C. J., Hinz P. N. Differentiation of vaccine strains and field isolates of pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) virus: trypsin sensitivity and mouse virulence markers. Arch Virol. 1980;63(2):107–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01320767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pol J. M., Gielkens A. L., van Oirschot J. T. Comparative pathogenesis of three strains of pseudorabies virus in pigs. Microb Pathog. 1989 Nov;7(5):361–371. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pol J. M., Quint W. G., Kok G. L., Broekhuysen-Davies J. M. Pseudorabies virus infections in explants of porcine nasal mucosa. Res Vet Sci. 1991 Jan;50(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0034-5288(91)90052-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauh I., Mettenleiter T. C. Pseudorabies virus glycoproteins gII and gp50 are essential for virus penetration. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5348–5356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5348-5356.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rziha H. J., Mettenleiter T. C., Ohlinger V., Wittmann G. Herpesvirus (pseudorabies virus) latency in swine: occurrence and physical state of viral DNA in neural tissues. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):600–613. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90220-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strack A. M., Loewy A. D. Pseudorabies virus: a highly specific transneuronal cell body marker in the sympathetic nervous system. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2139–2147. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02139.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weise K., Kaerner H. C., Glorioso J., Schröder C. H. Replacement of glycoprotein B gene sequences in herpes simplex virus type 1 strain ANG by corresponding sequences of the strain KOS causes changes of plaque morphology and neuropathogenicity. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):1909–1919. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-1909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsak L., Zuckermann F., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Glycoprotein gI of pseudorabies virus promotes cell fusion and virus spread via direct cell-to-cell transmission. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2316–2325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2316-2325.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann F. A., Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Complex between glycoproteins gI and gp63 of pseudorabies virus: its effect on virus replication. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4622–4626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4622-4626.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wind N., Zijderveld A., Glazenburg K., Gielkens A., Berns A. Linker insertion mutagenesis of herpesviruses: inactivation of single genes within the Us region of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4691–4696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4691-4696.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zijl M., Quint W., Briaire J., de Rover T., Gielkens A., Berns A. Regeneration of herpesviruses from molecularly cloned subgenomic fragments. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2191–2195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2191-2195.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]