Abstract
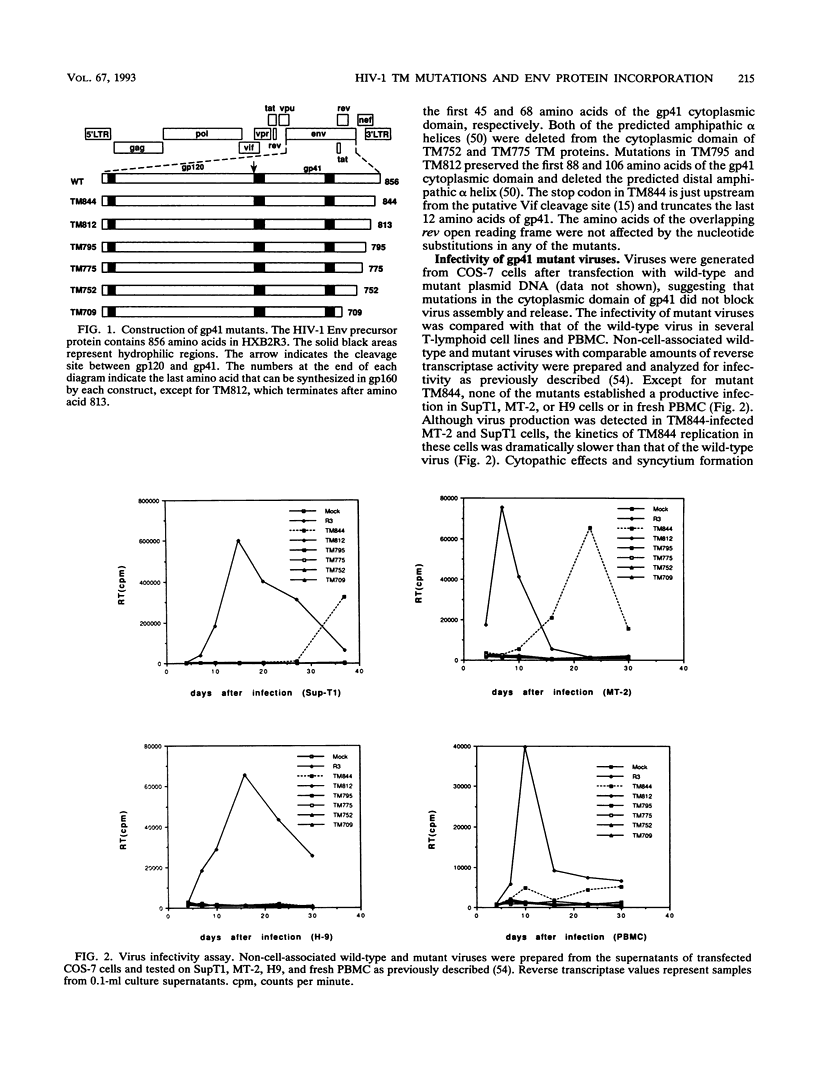
In-frame stop codons were introduced into the coding region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) transmembrane protein (gp41). Truncation of 147 amino acids from the carboxyl terminus of gp41 (TM709) significantly decreased the stability and cell surface expression of the viral Env proteins, while truncation of 104 amino acids (TM752) did not. Truncation of 43 or more amino acids from the carboxyl terminus of gp41 generated mutant viruses which were noninfectious in several human CD4+ T lymphoid cell lines and fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Analysis of the noninfectious mutant virions revealed significantly reduced incorporation of the Env proteins compared with the wild-type virions. Comparable amounts of Env proteins were detected on the surfaces of wild-type- and TM752-transfected cells, suggesting that the structures of gp41 required for efficient incorporation of Env proteins were disrupted in mutant TM752. Truncation of the last 12 amino acids (TM844) from the carboxyl terminus of gp41 did not significantly affect the assembly and release of virions or the incorporation of Env proteins into mature virions. However, the TM844 virus had dramatically decreased infectivity compared with the wild-type virus. This suggests that the cytoplasmic domain of gp41 also plays a role in other steps of virus replication.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brody B. A., Rhee S. S., Sommerfelt M. A., Hunter E. A viral protease-mediated cleavage of the transmembrane glycoprotein of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus can be suppressed by mutations within the matrix protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3443–3447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calafat J., Janssen H., Démant P., Hilgers J., Závada J. Specific selection of host cell glycoproteins during assembly of murine leukaemia virus and vesicular stomatitis virus: presence of Thy-1 glycoprotein and absence of H-2, Pgp-1 and T-200 glycoproteins on the envelopes of these virus particles. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jun;64(Pt 6):1241–1253. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-6-1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Emerman M., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. The cytoplasmic domain of simian immunodeficiency virus transmembrane protein modulates infectivity. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4395–4403. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4395-4403.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier N. C., Knox K., Schlesinger M. J. Inhibition of influenza virus formation by a peptide that corresponds to sequences in the cytoplasmic domain of the hemagglutinin. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):769–772. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford S., Goff S. P. A deletion mutation in the 5' part of the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus blocks proteolytic processing of the gag and pol polyproteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.899-907.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Doms R. W., Moss B. Oligomeric structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Koenig S., Moss B. Biological and immunological properties of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein: analysis of proteins with truncations and deletions expressed by recombinant vaccinia viruses. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):31–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.31-41.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Ratner L., Mitsuya H., Marselle L. M., Harper M. E., Broder S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Infectious mutants of HTLV-III with changes in the 3' region and markedly reduced cytopathic effects. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):655–659. doi: 10.1126/science.3014663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa M., Miura T., Hasegawa A., Morikawa S., Tsujimoto H., Miki K., Kitamura T., Hayami M. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from African green monkey, a new member of the HIV/SIV group. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):457–461. doi: 10.1038/333457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D. H., Lever A., Terwilliger E., Sodroski J. Effects of deletions in the cytoplasmic domain on biological functions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoproteins. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3306–3315. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3306-3315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R., Ball J. M., Garry R. F., Griffin M. C., Montelaro R. C. A general model for the transmembrane proteins of HIV and other retroviruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):431–440. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt A., Bosch J. V., Ziemiecki A., Friis R. R. Rous sarcoma virus p19 and gp35 can be chemically crosslinked to high molecular weight complexes. An insight into virus assembly. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 5;174(2):297–317. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90340-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granowitz C., Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Analysis of mutations in the envelope gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus: separation of infectivity from superinfection resistance. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90983-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy B., Geist M., Dott K., Spehner D., Kieny M. P., Lecocq J. P. A specific inhibitor of cysteine proteases impairs a Vif-dependent modification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Env protein. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1325–1331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1325-1331.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Dowbenko D. J., Berman P. W. The cytoplasmic tail of HIV-1 gp160 contains regions that associate with cellular membranes. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):439–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90054-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Nakamura G. R., Berman P. W. The carboxy terminus of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp160 limits its proteolytic processing and transport in transfected cell lines. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3100–3103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3100-3103.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Sowder R., Copeland T. D., Smythers G., Oroszlan S. Quantitative separation of murine leukemia virus proteins by reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography reveals newly described gag and env cleavage products. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):492–500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.492-500.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V. M., Edmondson P., Murphey-Corb M., Arbeille B., Johnson P. R., Mullins J. I. SIV adaptation to human cells. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):573–574. doi: 10.1038/341573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V., Riedel N., Mullins J. I. The genome organization of STLV-3 is similar to that of the AIDS virus except for a truncated transmembrane protein. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90283-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E., Swanstrom R. Retrovirus envelope glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:187–253. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kail M., Hollinshead M., Ansorge W., Pepperkok R., Frank R., Griffiths G., Vaux D. The cytoplasmic domain of alphavirus E2 glycoprotein contains a short linear recognition signal required for viral budding. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2343–2351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07773.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karshin W. L., Arcement L. J., Naso R. B., Arlinghaus R. B. Common precursor for Rauscher leukemia virus gp69/71, p15(E), and p12(E). J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):787–798. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.787-798.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Yoshinaka Y., Rein A., Shibuya M., Odaka T., Oroszlan S. Murine leukemia virus maturation: protease region required for conversion from "immature" to "mature" core form and for virus infectivity. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):280–292. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90161-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Wooley D. P., Naidu Y. M., Kestler H. W., 3rd, Daniel M. D., Li Y., Desrosiers R. C. Significance of premature stop codons in env of simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4709–4714. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4709-4714.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. J., Hu W., Fisher A. G., Looney D. J., Kao V. F., Mitsuya H., Ratner L., Wong-Staal F. Role of the carboxy-terminal portion of the HIV-1 transmembrane protein in viral transmission and cytopathogenicity. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):441–449. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Porter M. Specific incorporation of host cell surface proteins into budding vesicular stomatitis virus particles. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metsikkö K., Garoff H. Oligomers of the cytoplasmic domain of the p62/E2 membrane protein of Semliki Forest virus bind to the nucleocapsid in vitro. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4678–4683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4678-4683.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelaro R. C., Sullivan S. J., Bolognesi D. P. An analysis of type-C retrovirus polypeptides and their associations in the virion. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. J., Yamshchikov G. V., Ritter G. D., Jr, Gao F., Jin M. J., Nail C. D., Spies C. P., Hahn B. H., Compans R. W. Cytoplasmic domain truncation enhances fusion activity by the exterior glycoprotein complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 in selected cell types. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3971–3975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3971-3975.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. J., Compans R. W. Expression of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein is restricted to basolateral surfaces of polarized epithelial cells. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):978–982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.978-982.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. J., Dubay J. W., Hunter E., Compans R. W. Human immunodeficiency virus envelope protein determines the site of virus release in polarized epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3987–3991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez L. G., Davis G. L., Hunter E. Mutants of the Rous sarcoma virus envelope glycoprotein that lack the transmembrane anchor and cytoplasmic domains: analysis of intracellular transport and assembly into virions. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2981–2988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2981-2988.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puddington L., Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. Cytoplasmic domains of cellular and viral integral membrane proteins substitute for the cytoplasmic domain of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein in transport to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2147–2157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Bhat B. M., Wold W. S., Peterson P. A. A short sequence in the COOH-terminus makes an adenovirus membrane glycoprotein a resident of the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90226-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racevskis J., Sarkar N. H. Murine mammary tumor virus structural protein interactions: formation of oligomeric complexes with cleavable cross-linking agents. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):937–948. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.937-948.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviprakash K., Rasile L., Ghosh K., Ghosh H. P. Shortened cytoplasmic domain affects intracellular transport but not nuclear localization of a viral glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1777–1782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Henderson L. E., Sowder R. C., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Edwards J. F. Synthesis and processing of the transmembrane envelope protein of equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3770–3778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3770-3778.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Altered cytoplasmic domains affect intracellular transport of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RusS G., Poláková K., Závada J. Assembly of xenotropic murine leukaemia virus-related antigens from the surface of mouse L cells by vesicular stomatitis virus. Acta Virol. 1983 Mar;27(2):105–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Luftig R. B. Comparative immunofluorescence of murine leukemia virus-derived membrane-associated antigens. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):259–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J. Formation of an infectious virus-antibody complex with Rous sarcoma virus and antibodies directed against the major virus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):1063–1067. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.1063-1067.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Hasebe F., Tsuchie H., Morikawa S., Ushijima H., Kitamura T. Analysis of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate carrying a truncated transmembrane glycoprotein. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):534–546. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90577-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen M., Garoff H. Alphavirus spike-nucleocapsid interaction and network antibodies. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5106–5109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5106-5109.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger E., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A. Effects of mutations within the 3' orf open reading frame region of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) on replication and cytopathogenicity. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):754–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.754-760.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. J., Helenius A., Mellman I. Spike--nucleocapsid interaction in Semliki Forest virus reconstructed using network antibodies. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):36–42. doi: 10.1038/336036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venable R. M., Pastor R. W., Brooks B. R., Carson F. W. Theoretically determined three-dimensional structures for amphipathic segments of the HIV-1 gp41 envelope protein. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Feb;5(1):7–22. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitt M. A., Chong L., Rose J. K. Glycoprotein cytoplasmic domain sequences required for rescue of a vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein mutant. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3569–3578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3569-3578.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk T., Pfeiffer T., Bosch V. Retained in vitro infectivity and cytopathogenicity of HIV-1 despite truncation of the C-terminal tail of the env gene product. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):167–177. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90692-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. A., Bates P., Willert K., Varmus H. E. Efficient incorporation of human CD4 protein into avian leukosis virus particles. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2175047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X., Yuan X., Matsuda Z., Lee T. H., Essex M. The matrix protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is required for incorporation of viral envelope protein into mature virions. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4966–4971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4966-4971.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






