Abstract
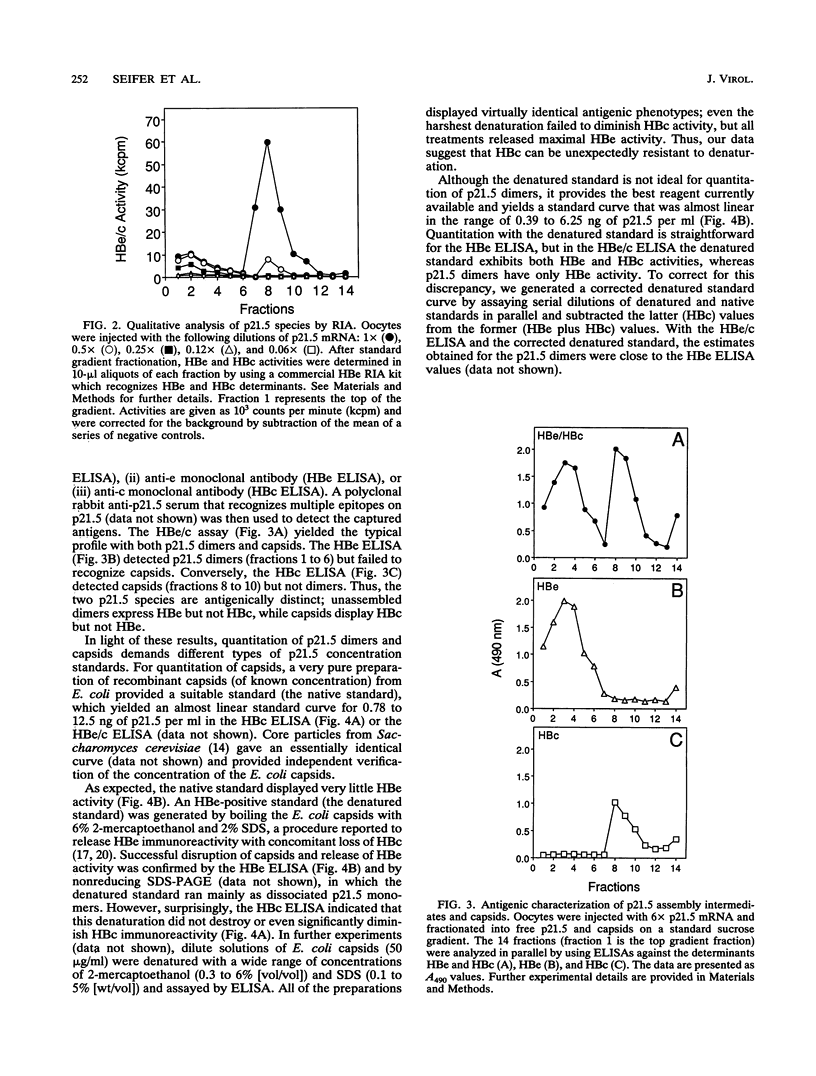
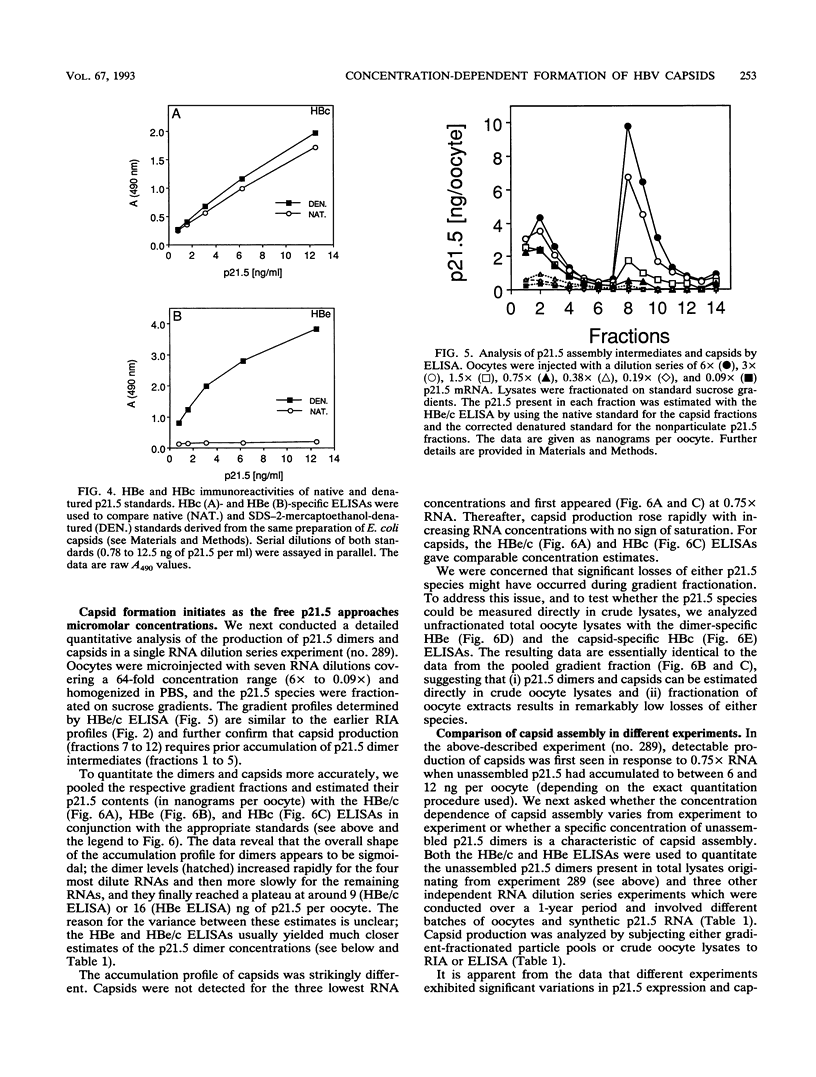
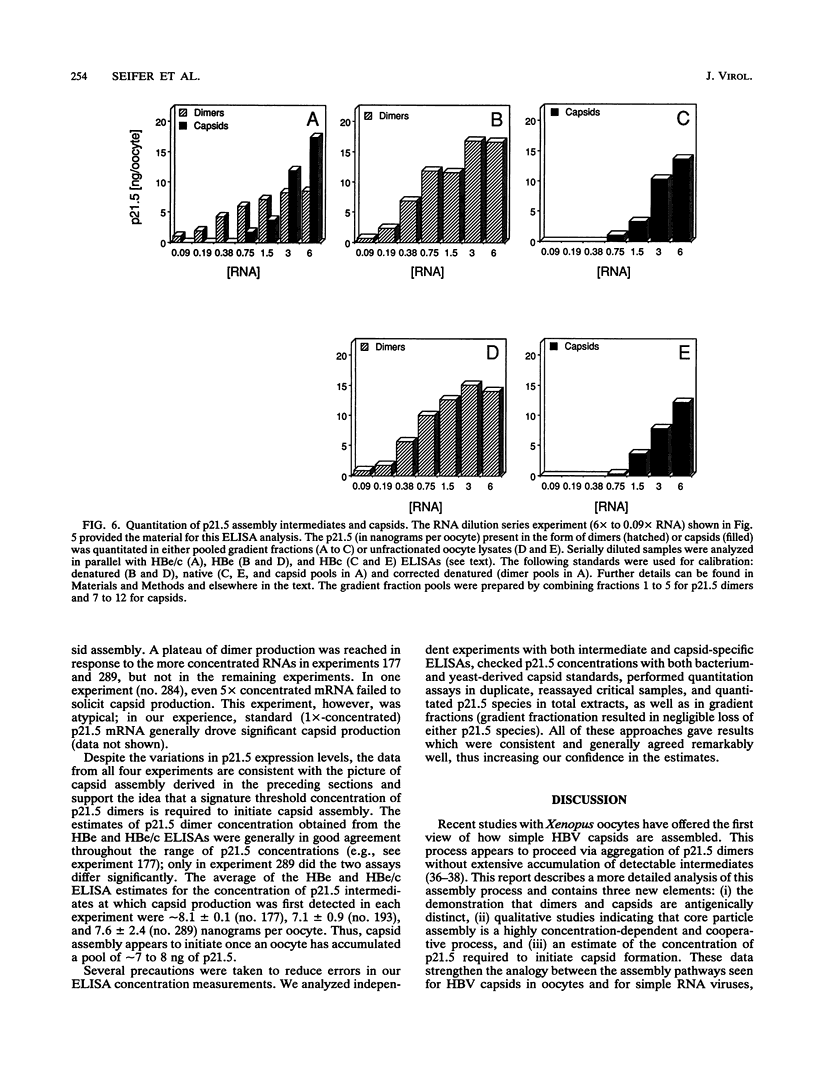
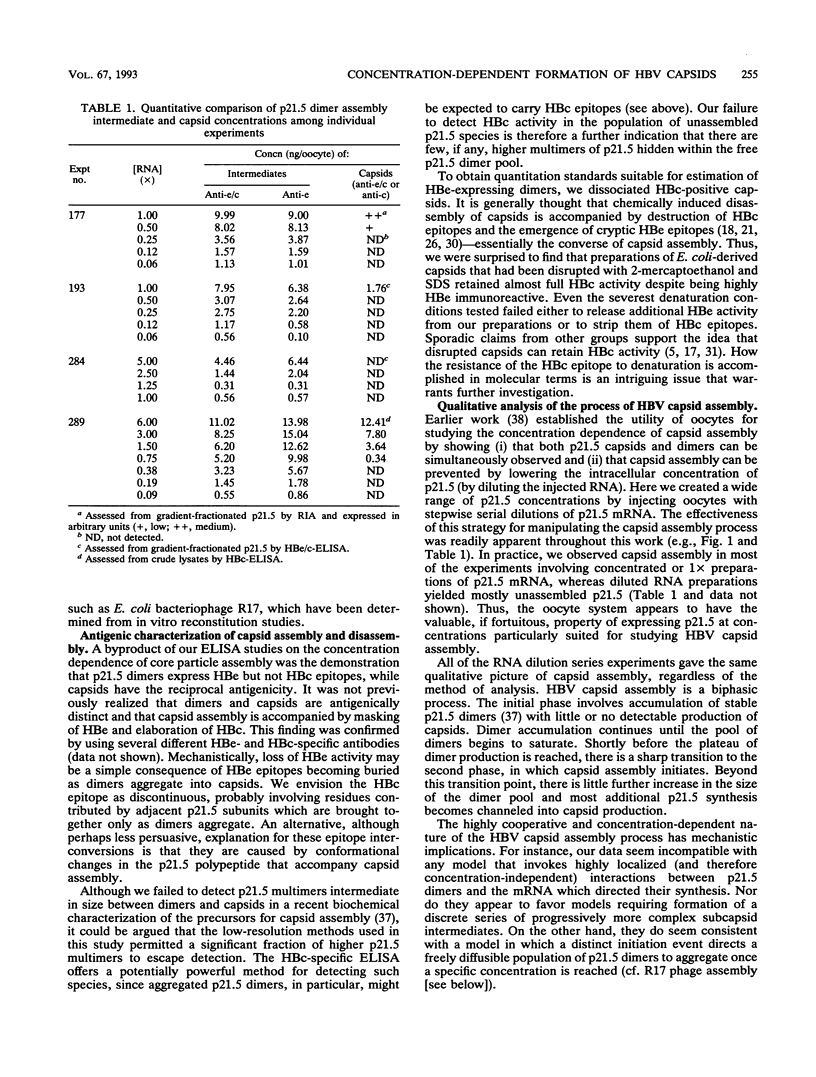
Assembly of hepatitis B virus capsid-like (core) particles occurs efficiently in a variety of heterologous systems via aggregation of approximately 180 molecules of a single 21.5-kDa core protein (p21.5), resulting in an icosahedral capsid structure with T = 3 symmetry. Recent studies on the assembly of hepatitis B virus core particles in Xenopus oocytes suggested that dimers of p21.5 represent the major building block from which capsids are generated. Here we determined the concentration dependence of this assembly process. By injecting serially diluted synthetic p21.5 mRNA into Xenopus oocytes, we expressed different levels of intracellular p21.5 and monitored the production of p21.5 dimers and capsids by radiolabeling and immunoprecipitation, by radioimmunoassay, or by quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis. The data revealed that (i) p21.5 dimers and capsids are antigenically distinct, (ii) capsid assembly is a highly cooperative and concentration-dependent process, and (iii) p21.5 must accumulate to a signature concentration of approximately 0.7 to 0.8 microM before capsid assembly initiates. This assembly process is strikingly similar to the assembly of RNA bacteriophage R17 as defined by in vitro studies.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Rubenstein D., Stott E. J. New antigen-antibody system in Australia-antigen-positive hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1225–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckett D., Uhlenbeck O. C. Ribonucleoprotein complexes of R17 coat protein and a translational operator analog. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):927–938. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckett D., Wu H. N., Uhlenbeck O. C. Roles of operator and non-operator RNA sequences in bacteriophage R17 capsid assembly. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum F., Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid assembly: primary structure requirements in the core protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3319–3330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3319-3330.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Hallewell R. A., Valenzuela P., Goodman H. M., Rutter W. J. Synthesis of hepatitis B surface and core antigens in E. coli. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):503–506. doi: 10.1038/291503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallina A., Bonelli F., Zentilin L., Rindi G., Muttini M., Milanesi G. A recombinant hepatitis B core antigen polypeptide with the protamine-like domain deleted self-assembles into capsid particles but fails to bind nucleic acids. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4645–4652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4645-4652.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D. Assembly of hepadnaviral virions and subviral particles. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;168:61–83. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76015-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Wickens M. P. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:370–386. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton T., Zhou S., Standring D. N. RNA- and DNA-binding activities in hepatitis B virus capsid protein: a model for their roles in viral replication. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5232–5241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5232-5241.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kniskern P. J., Hagopian A., Montgomery D. L., Burke P., Dunn N. R., Hofmann K. J., Miller W. J., Ellis R. W. Unusually high-level expression of a foreign gene (hepatitis B virus core antigen) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1986;46(1):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Notvall L. Expression of hepatitis B virus core and precore antigens in insect cells and characterization of a core-associated kinase activity. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):222–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90247-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Vriend G., Kamer G., Minor I., Arnold E., Rossmann M. G., Boege U., Scraba D. G., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. The atomic structure of Mengo virus at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):182–191. doi: 10.1126/science.3026048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay P., Lees J., Murray K. The conversion of hepatitis B core antigen synthesized in E coli into e antigen. J Med Virol. 1981;8(4):237–243. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890080404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida A., Ohnuma H., Takai E., Tsuda F., Tanaka T., Naito M., Munekata E., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Antigenic sites on the arginine-rich carboxyl-terminal domain of the capsid protein of hepatitis B virus distinct from hepatitis B core or e antigen. Mol Immunol. 1989 Apr;26(4):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnius L. O., Espmark J. A. New specificities in Australia antigen positive sera distinct from the Le Bouvier determinants. J Immunol. 1972 Nov;109(5):1017–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohori H., Shimizu N., Yamada E., Onodera S., Ishida N. Immunological and morphological properties of HBeAg subtypes (HBeAg/1 and HBeAg/2) in hepatitis B virus core particles. J Gen Virol. 1984 Feb;65(Pt 2):405–414. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohori H., Yamaki M., Onodera S., Yamada E., Ishida N. Antigenic conversion from HBcAg to HBeAg by degradation of hepatitis B core particles. Intervirology. 1980;13(2):74–82. doi: 10.1159/000149110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera S., Ohori H., Yamaki M., Ishida N. Electron microscopy of human hepatitis B virus cores by negative staining-carbon film technique. J Med Virol. 1982;10(2):147–155. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890100209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Laub O., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B virus gene function: the precore region targets the core antigen to cellular membranes and causes the secretion of the e antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1578–1582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Johnson J. E. Icosahedral RNA virus structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:533–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl S. J., Murray K. Immunogenicity of peptide fusions to hepatitis B virus core antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6283–6287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Masiarz F. R., Rutter W. J. A signal peptide encoded within the precore region of hepatitis B virus directs the secretion of a heterogeneous population of e antigens in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8405–8409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Rutter W. J. Assembly of viral particles in Xenopus oocytes: pre-surface-antigens regulate secretion of the hepatitis B viral surface envelope particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9338–9342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Imai M., Gotanda T., Sano T., Oinuma A., Mishiro S., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Hepatitis B e antigen polypeptides isolated from sera of individuals infected with hepatitis B virus: comparison with HBeAg polypeptide derived from Dane particles. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):49–57. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Machida A., Funatsu G., Nomura M., Usuda S., Aoyagi S., Tachibana K., Miyamoto H., Imai M., Nakamura T. Immunochemical structure of hepatitis B e antigen in the serum. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2903–2907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uy A., Bruss V., Gerlich W. H., Köchel H. G., Thomssen R. Precore sequence of hepatitis B virus inducing e antigen and membrane association of the viral core protein. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witherell G. W., Gott J. M., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific interaction between RNA phage coat proteins and RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;40:185–220. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60842-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Hirano T., Hirokawa H., Sugahara K., Mizokami H., Matsubara K. Cryo-electron microscopy of hepatitis B virus core particles produced by transformed yeast: comparison with negative staining and ultrathin sectioning. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1988;37(6):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. Q., Walter M., Standring D. N. Hepatitis B virus p25 precore protein accumulates in Xenopus oocytes as an untranslocated phosphoprotein with an uncleaved signal peptide. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):37–45. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.37-45.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou S. L., Standring D. N. Production of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsidlike core particles in Xenopus oocytes: assembly occurs mainly in the cytoplasm and does not require the nucleus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5457–5464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5457-5464.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou S., Standring D. N. Hepatitis B virus capsid particles are assembled from core-protein dimer precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10046–10050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou S., Yang S. Q., Standring D. N. Characterization of hepatitis B virus capsid particle assembly in Xenopus oocytes. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3086–3092. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3086-3092.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]