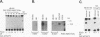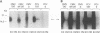Abstract
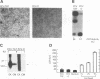
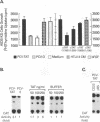
During acute human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection or after transfection of the tat gene, Tat protein is released into the cell culture supernatant. In this extracellular form, Tat stimulates both HIV-1 gene expression and the growth of cells derived from Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) lesions of HIV-1-infected individuals (AIDS-KS cells). Tat protein and its biological activities appear in the cell supernatants at the peak of Tat expression, when the rate of cell death is low (infection) or cell death is undetectable (transfection) and increased levels of cytoplasmic Tat are present. Tat-containing supernatants stimulate maximal AIDS-KS cell growth but only low to moderate levels of HIV-1 gene expression. This is due to the different concentrations of exogenous Tat required for the two effects. The cell growth-promoting effects of Tat peak at between 0.1 and 1 ng of purified recombinant protein per ml in the cell growth medium and do not increase with concentration. In contrast, both the detection of nuclear-localized Tat taken up by cells and the induction of HIV-1 gene expression or replication require higher Tat concentrations (> or = 100 ng/ml), and all increase linearly with increasing amounts of the exogenous protein. These data suggest that Tat can be released by a mechanism(s) other than cell death and that the cell growth-promoting activity and the virus-transactivating effect of extracellular Tat are mediated by different pathways.
Full text
PDF


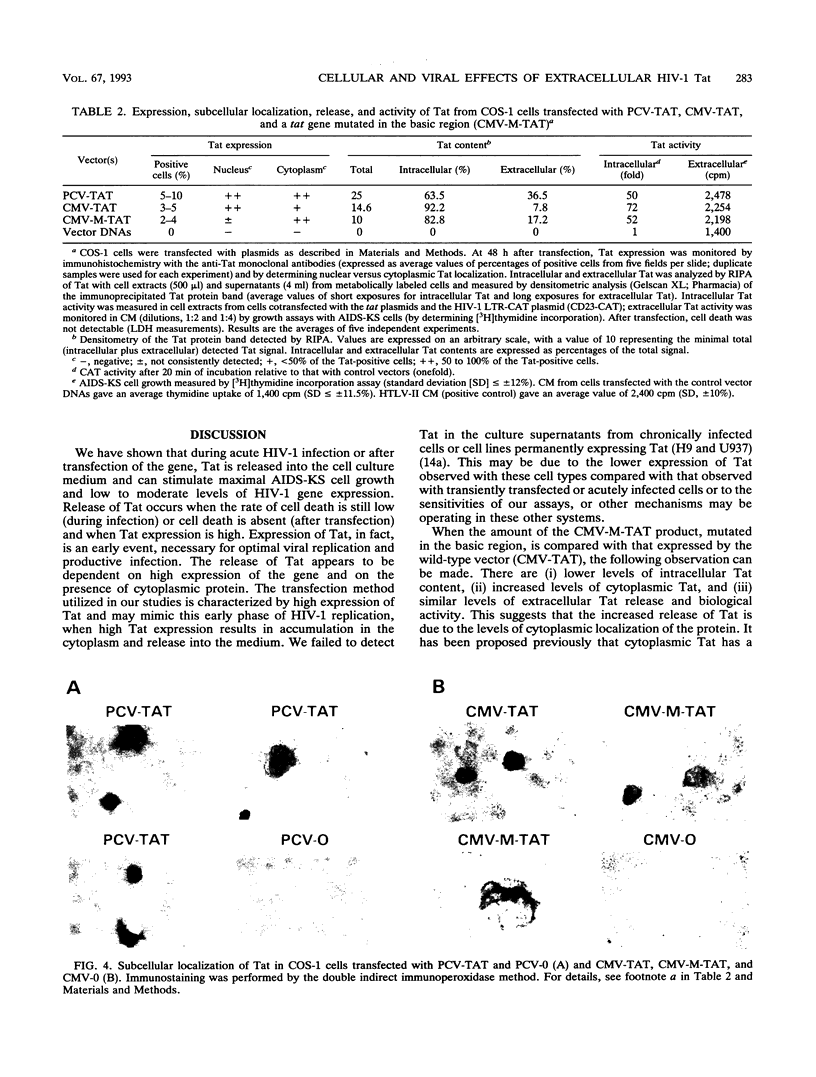
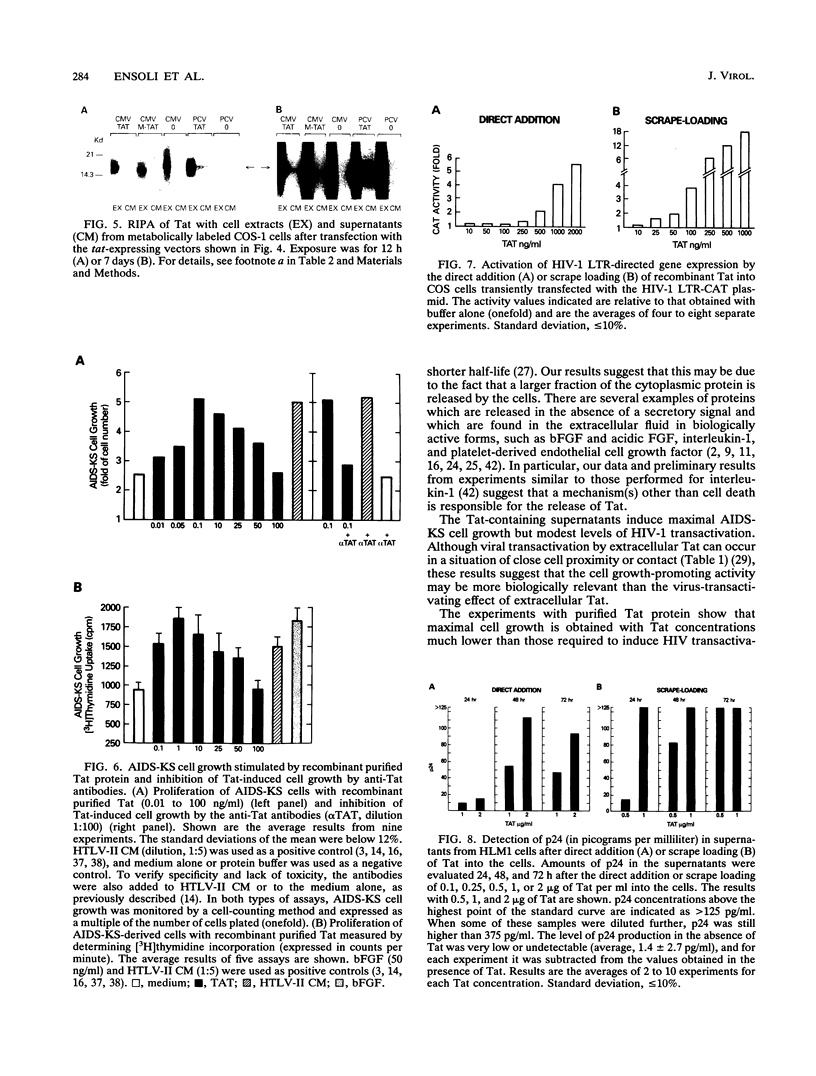
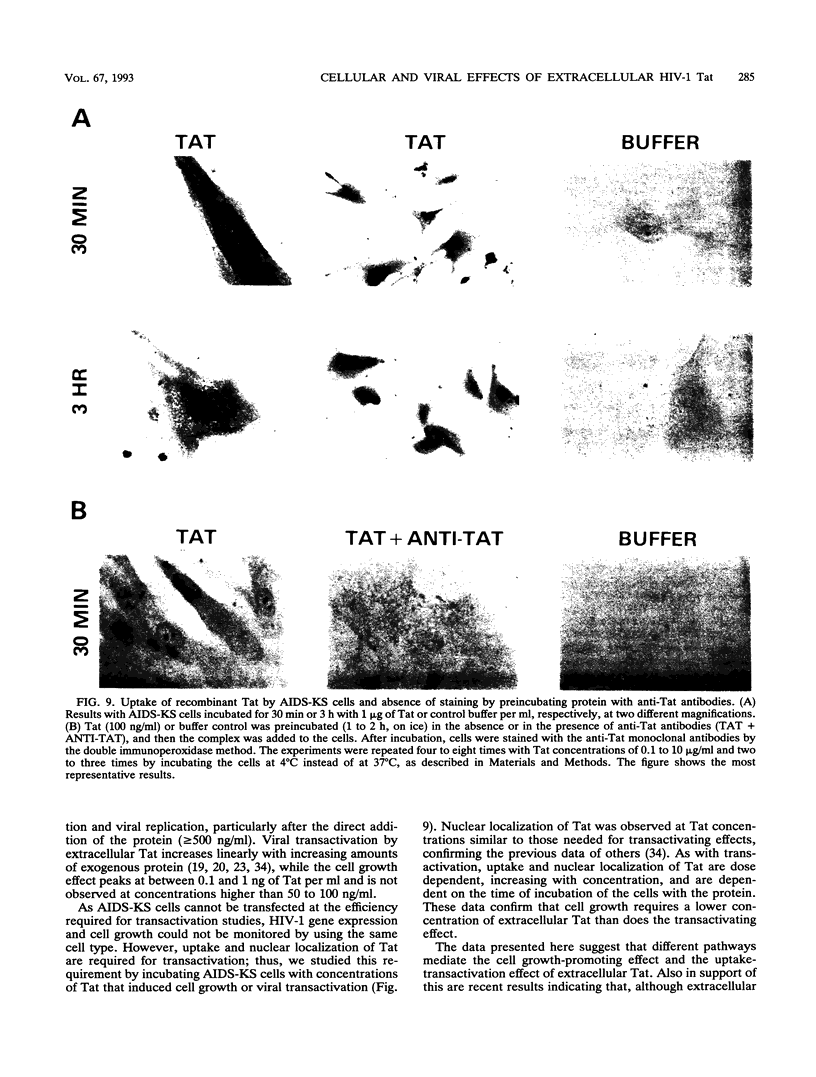


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Guo C., Josephs S. F., Wong-Staal F. Trans-activator gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III). Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):69–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2990040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacle F., Haeffner-Cavaillon N., Laude M., Couturier C., Kazatchkine M. D. Induction of IL-1 release through stimulation of the C3b/C4b complement receptor type one (CR1, CD35) on human monocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):147–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake D. A., Debouck C., Biesecker G. Identification of an Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) cell adhesion site in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transactivation protein, tat. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1275–1281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonaguro L., Barillari G., Chang H. K., Bohan C. A., Kao V., Morgan R., Gallo R. C., Ensoli B. Effects of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein on the expression of inflammatory cytokines. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7159–7167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7159-7167.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore P. A. Modes of FGF release in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Nov;9(3):227–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00046362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Savage N. Interleukin-1 and its receptor. Crit Rev Immunol. 1989;9(1):1–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Gallo R. C. Pathogenesis of AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1991 Apr;5(2):281–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Tat protein of HIV-1 stimulates growth of cells derived from Kaposi's sarcoma lesions of AIDS patients. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):84–86. doi: 10.1038/345084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Lusso P., Schachter F., Josephs S. F., Rappaport J., Negro F., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Human herpes virus-6 increases HIV-1 expression in co-infected T cells via nuclear factors binding to the HIV-1 enhancer. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3019–3027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Nakamura S., Salahuddin S. Z., Biberfeld P., Larsson L., Beaver B., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells express cytokines with autocrine and paracrine growth effects. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.2643161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D., Frankel A. D. The role of Tat in the human immunodeficiency virus life cycle indicates a primary effect on transcriptional elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Feinberg M. B., Josephs S. F., Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Reyes G., Gonda M. A., Aldovini A., Debouk C., Gallo R. C. The trans-activator gene of HTLV-III is essential for virus replication. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):367–371. doi: 10.1038/320367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Biancalana S., Hudson D. Activity of synthetic peptides from the Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7397–7401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Pabo C. O. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1189–1193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman-Kien A. E. Disseminated Kaposi's sarcoma syndrome in young homosexual men. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981 Oct;5(4):468–471. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(81)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Bioassay for trans-activation using purified human immunodeficiency virus tat-encoded protein: trans-activation requires mRNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):821–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Globus R. K., Plouet J., Gospodarowicz D. Cultured bovine bone cells synthesize basic fibroblast growth factor and store it in their extracellular matrix. Endocrinology. 1989 Mar;124(3):1539–1547. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-3-1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh K., Furusawa S., Kawa Y., Negishi-Okitsu S., Mizoguchi M. Production of interleukin-1-alpha and -beta by human peripheral polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;88(3):297–303. doi: 10.1159/000234815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. Mutational analysis of the conserved basic domain of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1181–1187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1181-1187.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Perkins A., Heimer E. P., Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression is mediated by nuclear events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6364–6368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helland D. E., Welles J. L., Caputo A., Haseltine W. A. Transcellular transactivation by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tat protein. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4547–4549. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4547-4549.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Susin M., Pahwa S. G., Fetten J., Allen S. L., Lichtman S., Sarngadharan M. G., Gallo R. C. Neoplastic complications of HTLV-III infection. Lymphomas and solid tumors. Am J Med. 1987 Mar;82(3):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeuwenberg J. F., von Asmuth E. J., Jeunhomme T. M., Buurman W. A. IFN-gamma regulates the expression of the adhesion molecule ELAM-1 and IL-6 production by human endothelial cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2110–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Hoffman A. D., Kramer S. M., Landis J. A., Shimabukuro J. M., Oshiro L. S. Isolation of lymphocytopathic retroviruses from San Francisco patients with AIDS. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):840–842. doi: 10.1126/science.6206563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm P. F., Marriott S. J., Gitlin S. D., Bohan C. A., Brady J. N. Induction of nuclear NF-kappa B DNA binding activity after exposure of lymphoid cells to soluble tax1 protein. New Biol. 1990 Nov;2(11):1034–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. A., Frankel A. D. Endocytosis and targeting of exogenous HIV-1 Tat protein. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1733–1739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07697.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott S. J., Lindholm P. F., Reid R. L., Brady J. N. Soluble HTLV-I Tax1 protein stimulates proliferation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. New Biol. 1991 Jul;3(7):678–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles S. A., Martínez-Maza O., Rezai A., Magpantay L., Kishimoto T., Nakamura S., Radka S. F., Linsley P. S. Oncostatin M as a potent mitogen for AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1432–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.1542793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair B. C., DeVico A. L., Nakamura S., Copeland T. D., Chen Y., Patel A., O'Neil T., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Identification of a major growth factor for AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma cells as oncostatin M. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1430–1432. doi: 10.1126/science.1542792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Salahuddin S. Z., Biberfeld P., Ensoli B., Markham P. D., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Kaposi's sarcoma cells: long-term culture with growth factor from retrovirus-infected CD4+ T cells. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):426–430. doi: 10.1126/science.3262925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Delling U., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Sonenberg N. A bulge structure in HIV-1 TAR RNA is required for Tat binding and Tat-mediated trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1365–1373. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubartelli A., Cozzolino F., Talio M., Sitia R. A novel secretory pathway for interleukin-1 beta, a protein lacking a signal sequence. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1503–1510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08268.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S., Perkins A., Purcell R., Joung K., Sia R., Burghoff R., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. Structural and functional characterization of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.1-8.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadaie M. R., Mukhopadhyaya R., Benaissa Z. N., Pavlakis G. N., Wong-Staal F. Conservative mutations in the putative metal-binding region of human immunodeficiency virus tat disrupt virus replication. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Nov;6(11):1257–1263. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadaie M. R., Tschachler E., Valerie K., Rosenberg M., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N., Klotman M. E., Wong-Staal F. Activation of tat-defective human immunodeficiency virus by ultraviolet light. New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):479–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Nakamura S., Biberfeld P., Kaplan M. H., Markham P. D., Larsson L., Gallo R. C. Angiogenic properties of Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells after long-term culture in vitro. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):430–433. doi: 10.1126/science.2459779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Feinberg M. B., Holbrook N., Wong-Staal F., Greene W. C. Activation of interleukin 2 and interleukin 2 receptor (Tac) promoter expression by the trans-activator (tat) gene product of human T-cell leukemia virus, type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5389–5393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R. P., Mayur K., Lederman H. M., Frankel A. D. Inhibition of antigen-induced lymphocyte proliferation by Tat protein from HIV-1. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1606–1608. doi: 10.1126/science.2556795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel J., Hinrichs S. H., Reynolds R. K., Luciw P. A., Jay G. The HIV tat gene induces dermal lesions resembling Kaposi's sarcoma in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):606–611. doi: 10.1038/335606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. M., Felber B. K., Paskalis H., Pavlakis G. N. Expression and characterization of the trans-activator of HTLV-III/LAV virus. Science. 1986 Nov 21;234(4779):988–992. doi: 10.1126/science.3490693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yohn J. J., Critelli M., Lyons M. B., Norris D. A. Modulation of melanocyte intercellular adhesion molecule-1 by immune cytokines. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Aug;95(2):233–237. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12478093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]