Abstract
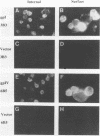
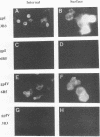
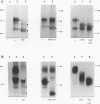
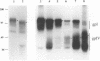
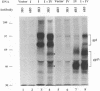
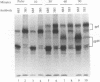
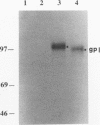
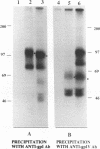
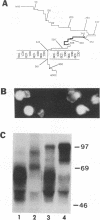
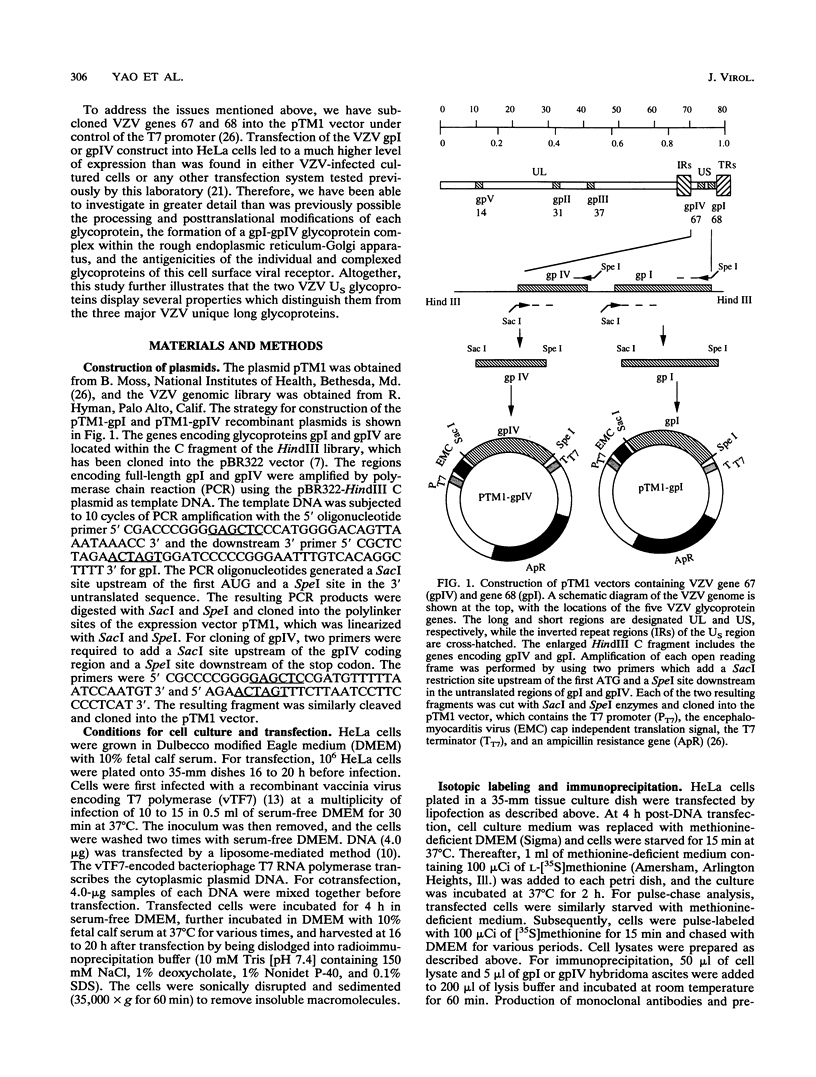
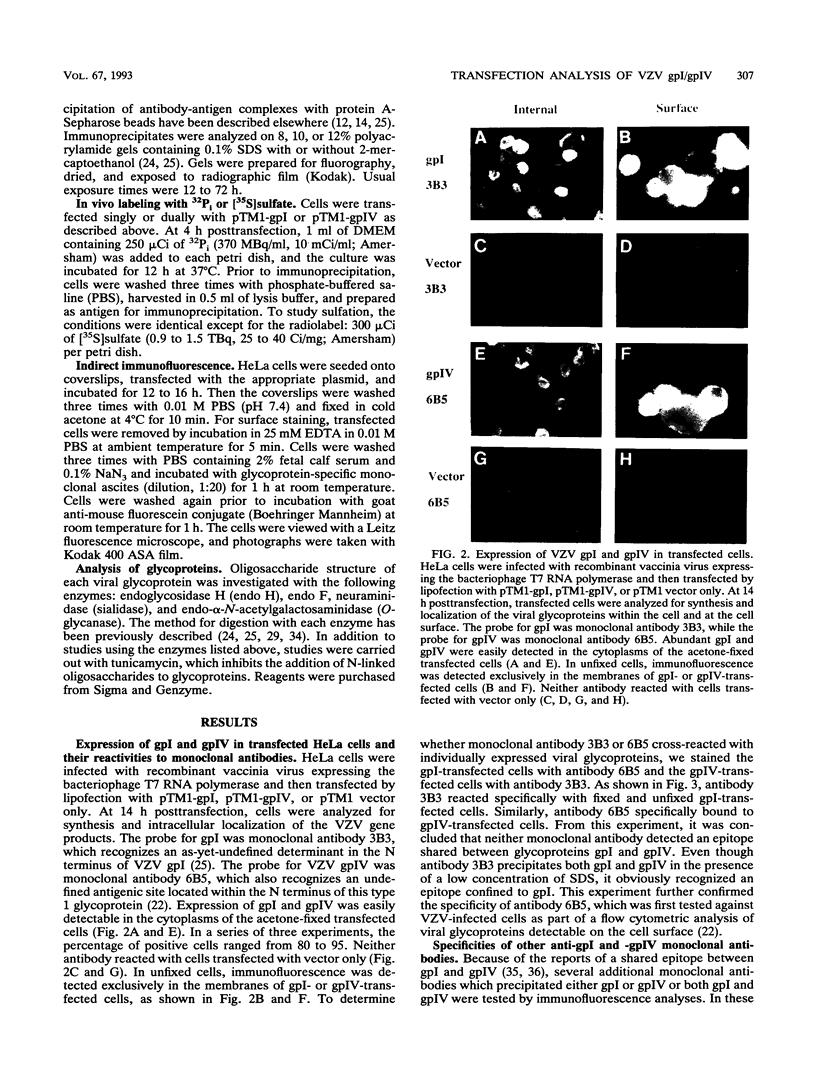
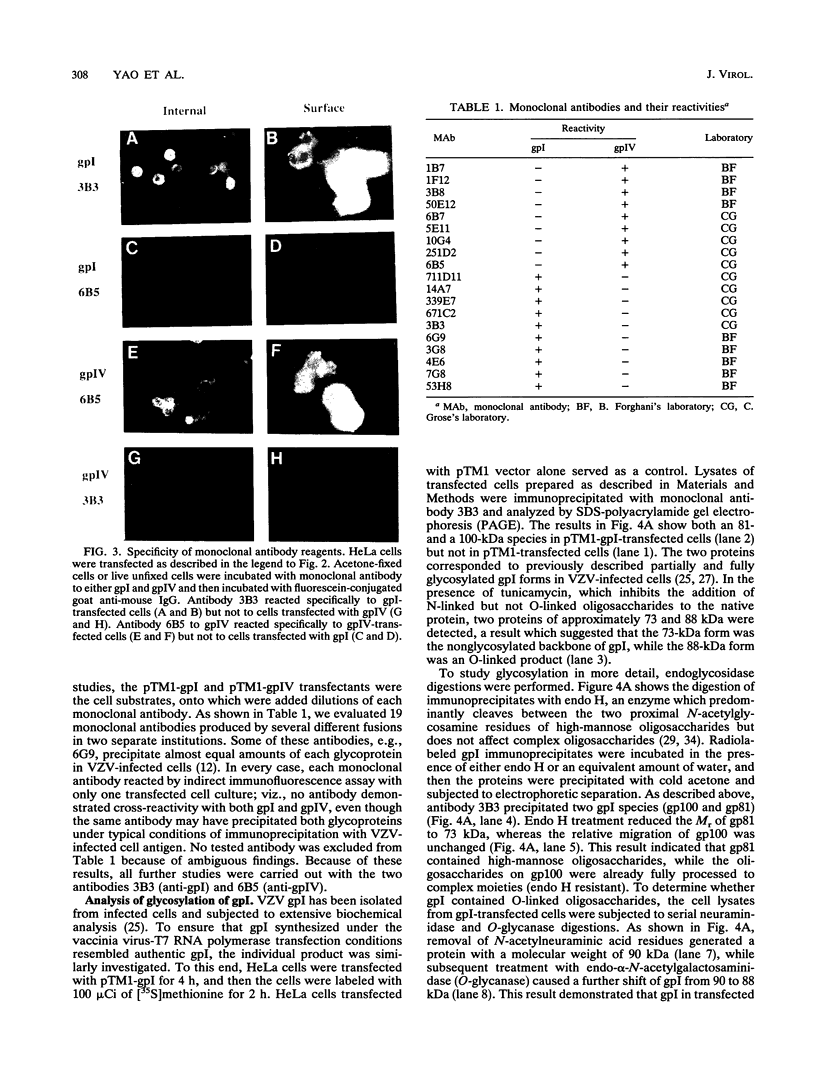
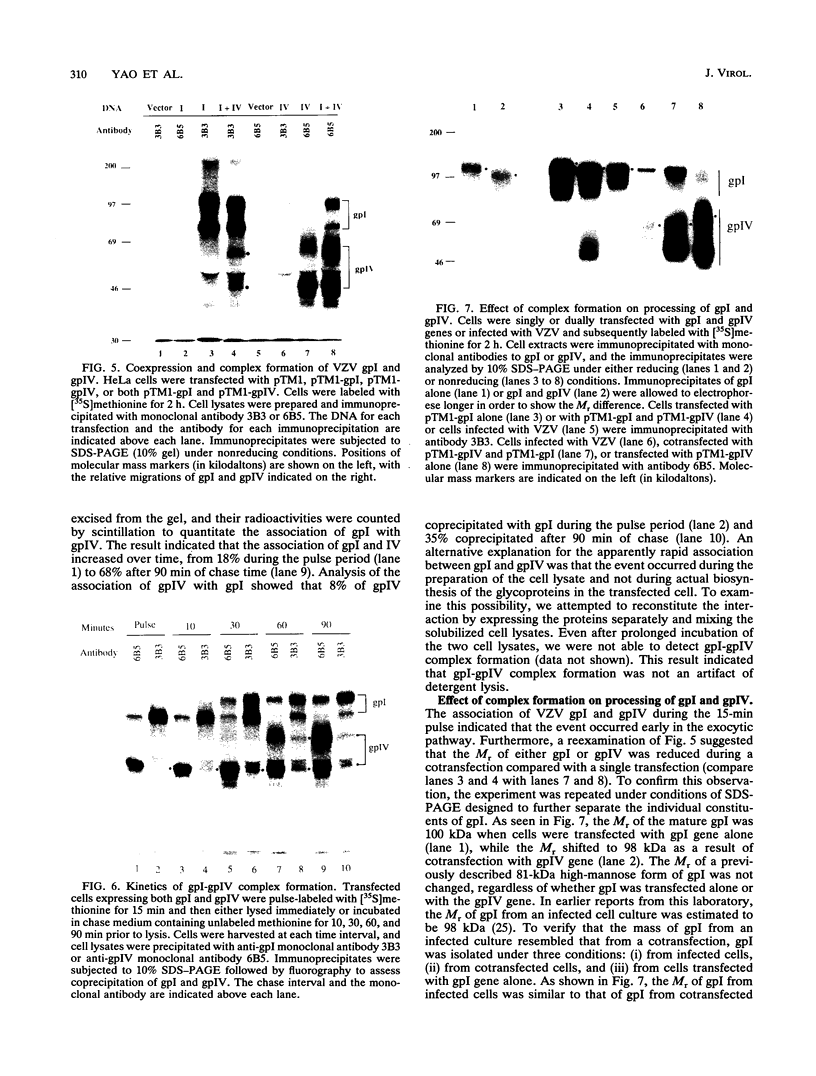
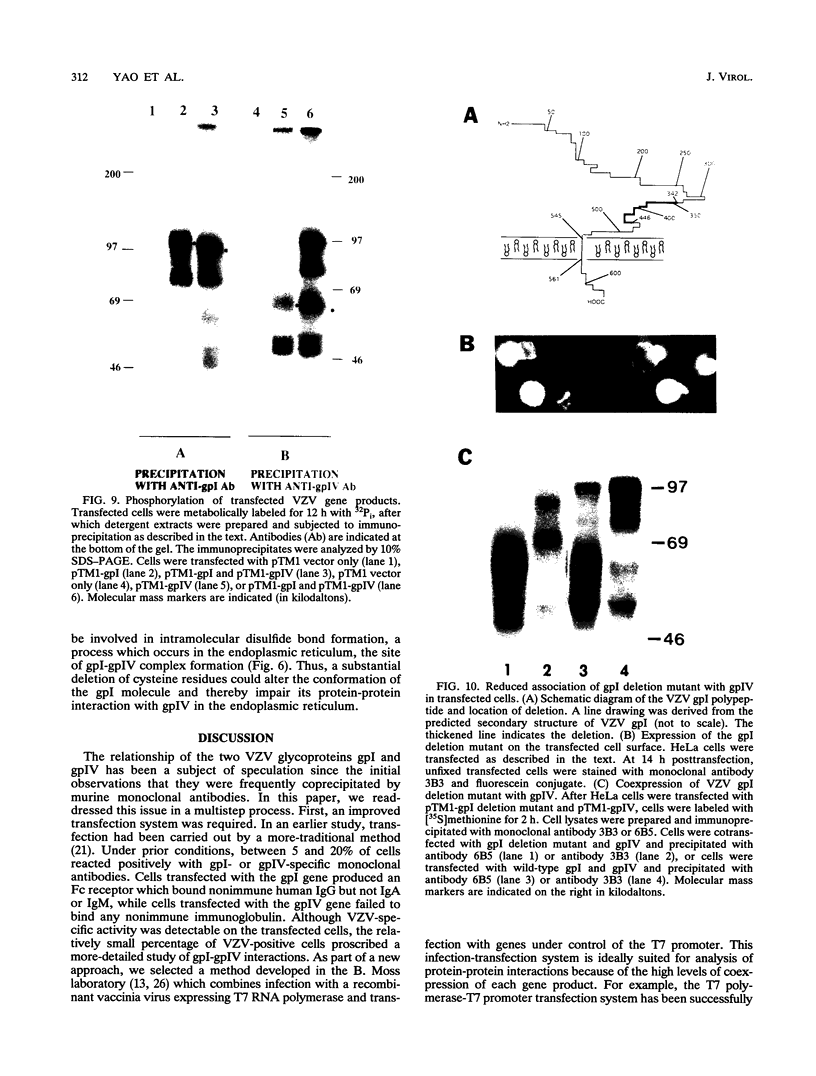
The unique short region of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) genome contains two open reading frames which encode glycoproteins designated gpI and gpIV (herpes simplex virus homologs gE and gI, respectively). Like its herpesviral counterpart gE, the VZV gpI gene product functions as a cell surface receptor (V. Litwin, W. Jackson, and C. Grose, J. Virol. 66:3643-3651, 1992). To evaluate the biosynthesis of the two VZV glycoproteins and further explore their relationship to one another, the two glycoprotein genes were individually cloned into a pTM1 vector under control of the T7 promoter. Transfection of the cloned gpI or gpIV construct into HeLa cells previously infected with vaccinia recombinant virus expressing bacteriophage T7 polymerase resulted in a much higher level expression of each VZV glycoprotein than previously achieved. Synthesis of both gpI and gpIV included intermediary partially glycosylated forms and mature N- and O-linked final product. Transfections in the presence of 32Pi demonstrated that the mature forms of both gpI and gpIV were phosphorylated, while similar experiments with [35S]sulfate showed that only the mature gpI was sulfated. When gpI and gpIV were coexpressed in the same cell, the two glycoproteins were complexed to each other, as both proteins could be immunoprecipitated by antibodies against either gpI or gpIV. Coprecipitation did not occur as a result of a shared epitope, because gpI expressed alone was not precipitated by antibody to gpIV, and gpIV expressed alone was not precipitated by antibody to gpI. Pulse-chase analysis demonstrated that the gpI-gpIV association occurred early in processing; furthermore, this complex formation interfered with posttranslational modifications and thereby reduced the M(r)s of the mature forms of both gpI and gpIV. Similarly, the molecular masses of the cotransfected gene products corresponded with those of the infected cell glycoproteins, a result which suggested that authentic gpI and gpIV were ordinarily found within a complex. Thus, the adjacent open reading frames 67 and 68 code for two glycoproteins which in turn form a distinctive sulfated and phosphorylated cell surface complex with receptor properties.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S., Cranage M., Borysiewicz L., Minson T. Induction of immunoglobulin G Fc receptors by recombinant vaccinia viruses expressing glycoproteins E and I of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2181–2186. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2181-2186.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns A., van den Ouweland A., Quint W., van Oirschot J., Gielkens A. Presence of markers for virulence in the unique short region or repeat region or both of pseudorabies hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):89–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.89-93.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus envelope glycoprotein gI influences both neurotropism and virulence during infection of the rat visual system. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3032–3041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3032-3041.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crise B., Buonocore L., Rose J. K. CD4 is retained in the endoplasmic reticulum by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 glycoprotein precursor. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5585–5593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5585-5593.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Waters D. J., Edson C. M. Identification of the products of a varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein gene. J Gen Virol. 1985 Oct;66(Pt 10):2237–2242. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-10-2237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker J. R., Hyman R. W. Varicella zoster virus DNA exists as two isomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson C. M., Hosler B. A., Poodry C. A., Schooley R. T., Waters D. J., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Varicella-zoster virus envelope glycoproteins: biochemical characterization and identification in clinical material. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):62–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson C. M., Hosler B. A., Waters D. J. Varicella-zoster virus gpI and herpes simplex virus gE: phosphorylation and Fc binding. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):599–602. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiete D., Srivastava V., Hindsgaul O., Baenziger J. U. A hepatic reticuloendothelial cell receptor specific for SO4-4GalNAc beta 1,4GlcNAc beta 1,2Man alpha that mediates rapid clearance of lutropin. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1103–1110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Dupuis K. W., Schmidt N. J. Epitopes functional in neutralization of varicella-zoster virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2500–2506. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2500-2506.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C. Glycoproteins encoded by varicella-zoster virus: biosynthesis, phosphorylation, and intracellular trafficking. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:59–80. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.000423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Jackson W., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein gpI by mammalian casein kinase II and casein kinase I. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3912–3918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3912-3918.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper D. R., Kangro H. O. Lipoproteins of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1990 Feb;71(Pt 2):459–463. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-2-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope R. G., Palfreyman J., Suh M., Marsden H. S. Sulphated glycoproteins induced by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Feb;58(Pt 2):399–415. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-58-2-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabbar M. A., Nayak D. P. Intracellular interaction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (ARV-2) envelope glycoprotein gp160 with CD4 blocks the movement and maturation of CD4 to the plasma membrane. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6297–6304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6297-6304.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Feenstra V. Identification of a novel herpes simplex virus type 1-induced glycoprotein which complexes with gE and binds immunoglobulin. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2208–2216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2208-2216.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Frame M. C., Ligas M. W., Cross A. M., Stow N. D. Herpes simplex virus immunoglobulin G Fc receptor activity depends on a complex of two viral glycoproteins, gE and gI. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1347–1354. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1347-1354.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin V., Jackson W., Grose C. Receptor properties of two varicella-zoster virus glycoproteins, gpI and gpIV, homologous to herpes simplex virus gE and gI. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3643–3651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3643-3651.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin V., Sandor M., Grose C. Cell surface expression of the varicella-zoster virus glycoproteins and Fc receptor. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90402-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B., Watanabe S., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Genetic basis of the neurovirulence of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):198–205. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.198-205.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montalvo E. A., Grose C. Neutralization epitope of varicella zoster virus on native viral glycoprotein gp118 (VZV glycoprotein gpIII). Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):230–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montalvo E. A., Parmley R. T., Grose C. Structural analysis of the varicella-zoster virus gp98-gp62 complex: posttranslational addition of N-linked and O-linked oligosaccharide moieties. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):761–770. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.761-770.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Elroy-Stein O., Mizukami T., Alexander W. A., Fuerst T. R. Product review. New mammalian expression vectors. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):91–92. doi: 10.1038/348091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno T., Yamanishi K., Shiraki K., Takahashi M. Synthesis and processing of glycoproteins of Varicella-Zoster virus (VZV) as studied with monoclonal antibodies to VZV antigens. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Post L. E. Use of lambda gt11 to isolate genes for two pseudorabies virus glycoproteins with homology to herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):185–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.185-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Hubbard S. C., Turco S. J., Wirth D. F. Proposal for a common oligosaccharide intermediate in the synthesis of membrane glycoproteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):893–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. S., Amrein K. E., Hammond C., Stern D. F., Sefton B. M., Rose J. K. The lck tyrosine protein kinase interacts with the cytoplasmic tail of the CD4 glycoprotein through its unique amino-terminal domain. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Maley F. The release of intact oligosaccharides from specific glycoproteins by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):818–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vafai A., Jensen K., Kubo R. Existence of similar antigenic-sites on varicella-zoster virus gpI and gpIV. Virus Res. 1989 Aug;13(4):319–336. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vafai A., Wroblewska Z., Mahalingam R., Cabirac G., Wellish M., Cisco M., Gilden D. Recognition of similar epitopes on varicella-zoster virus gpI and gpIV by monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2544–2551. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2544-2551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Z., Jones D. H., Grose C. Site-directed mutagenesis of herpesvirus glycoprotein phosphorylation sites by recombination polymerase chain reaction. PCR Methods Appl. 1992 Feb;1(3):205–207. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.3.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]