Abstract
Mice infected intracerebrally with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCM virus) develop a characteristic central nervous system disease and usually die. If the intravenous or intraperitoneal route is used, the infection leads to less severe clinical signs and the virus is eliminated. Illness and virus clearance are immunological phenomena, which are assumed to be caused exclusively by CD8+ T lymphocytes. In contrast, of the two phases of a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction caused by inoculation of the virus into the mouse's foot, only the first is mediated by CD8+ cells, whereas the second is mediated by CD4+ cells. We have examined LCM virus-specific immune responses in mice devoid of CD8+ T lymphocytes as a result of disruption of the beta 2-microglobulin gene. As expected, the virus persisted but footpad swelling did not occur, although intracerebral infection resulted in CD4+ T-lymphocyte-mediated illness and antiviral antibodies were produced. Different results had been obtained by Fung-Leung et al. (W.-P. Fung-Leung, T. M. Kündig, R. M. Zinkernagel, and T. W. Mak, J. Exp. Med. 174:1425-1429, 1991), who, is essentially identical experiments but with mice lacking CD8+ T lymphocytes as a result of disruption of the Lyt-2-encoding gene, recorded control of the infection and development of a local delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. We consider these differences important, because they provide us with clues that may help to understand the mode of action of the CD8+ T cells in cell-mediated antiviral immunity.
Full text
PDF
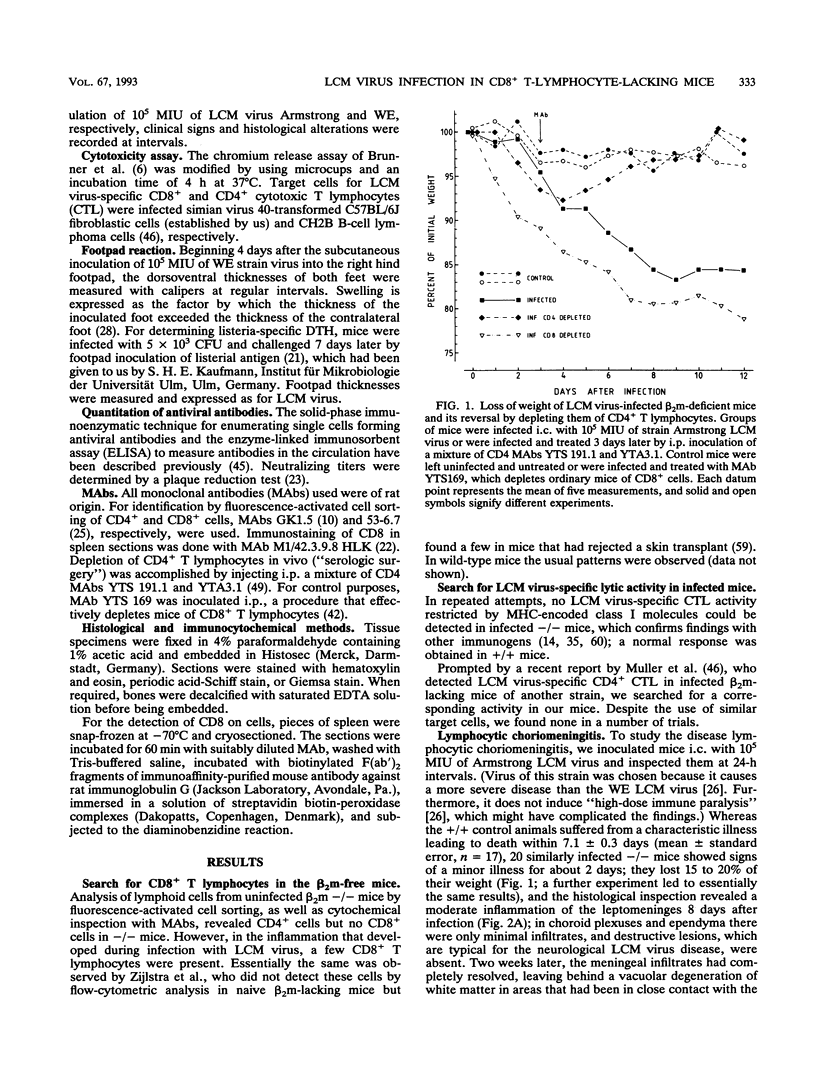
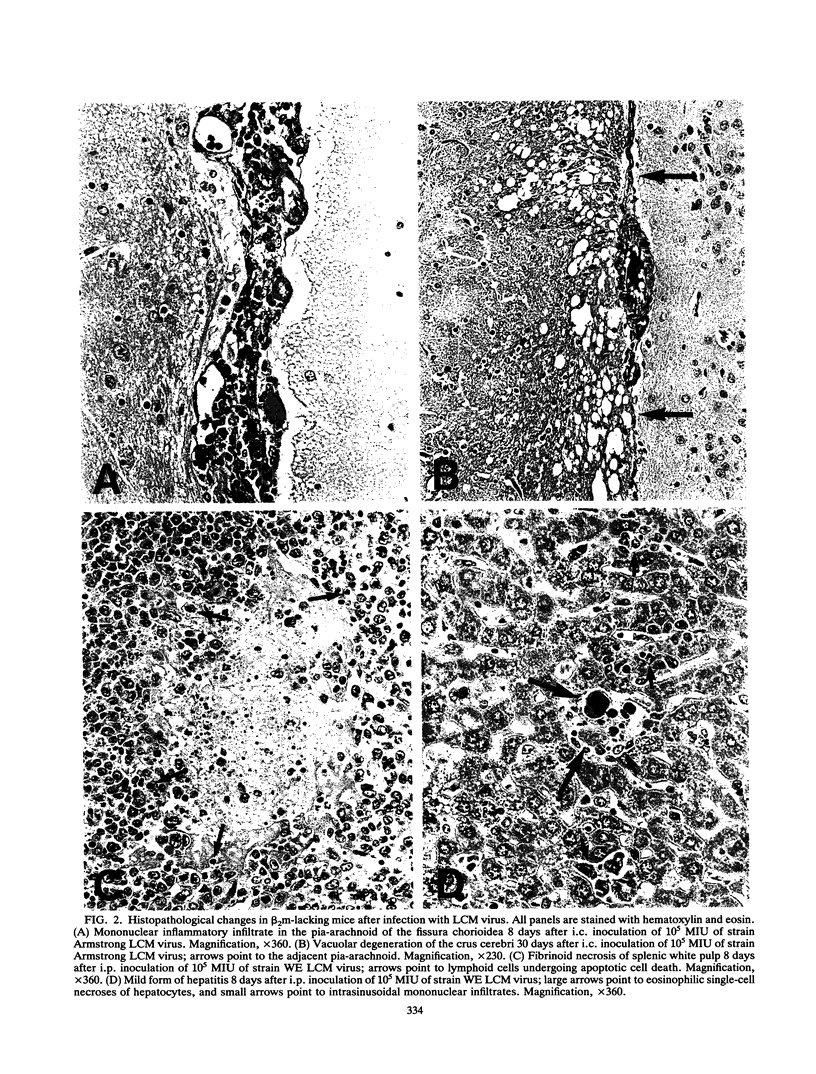
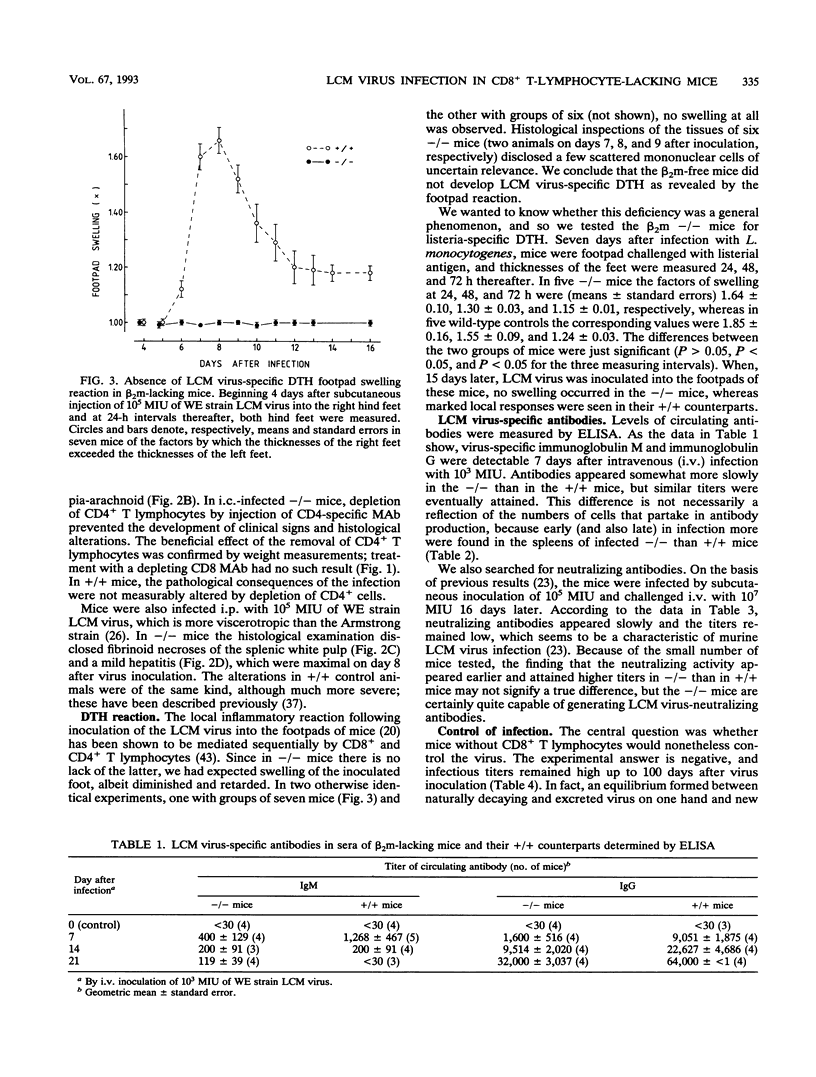


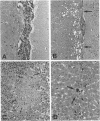
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Butler L. D., Bhatti L. T4+ T helper cell function in vivo: differential requirement for induction of antiviral cytotoxic T-cell and antibody responses. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2102–2106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2102-2106.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen H., Fraser J., Flyer D., Calvin S., Flavell R. Beta 2-microglobulin is not required for cell surface expression of the murine class I histocompatibility antigen H-2Db or of a truncated H-2Db. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender B. S., Croghan T., Zhang L., Small P. A., Jr Transgenic mice lacking class I major histocompatibility complex-restricted T cells have delayed viral clearance and increased mortality after influenza virus challenge. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1143–1145. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Sleckman B. P., Ratnofsky S. E., Burakoff S. J. The biologic roles of CD2, CD4, and CD8 in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:579–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman M., Kappler J., Marrack P. The role of the T cell receptor in positive and negative selection of developing T cells. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1335–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.1972592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner K. T., Mauel J., Cerottini J. C., Chapuis B. Quantitative assay of the lytic action of immune lymphoid cells on 51-Cr-labelled allogeneic target cells in vitro; inhibition by isoantibody and by drugs. Immunology. 1968 Feb;14(2):181–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski J. F., Warner J. F., Dennert G., Welsh R. M. Adoptive transfer studies demonstrating the antiviral effect of natural killer cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):40–52. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. Mulling over mouse models. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):86–86. doi: 10.1038/359086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Allan J. E., Ceredig R. Contributions of host and donor T cells to the inflammatory process in murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis. Cell Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;116(2):475–481. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Allan J. E., Lynch F., Ceredig R. Dissection of an inflammatory process induced by CD8+ T cells. Immunol Today. 1990 Feb;11(2):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Zinkernagel R. M. T-cell-mediated immunopathology in viral infections. Transplant Rev. 1974;19(0):89–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelberger M., Allan W., Zijlstra M., Jaenisch R., Doherty P. C. Clearance of influenza virus respiratory infection in mice lacking class I major histocompatibility complex-restricted CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):875–880. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang L. B., Gessner A., Kühlcke K., Gossmann J., Lehmann-Grube F. Antiviral immune responses of fully allogeneic irradiation bone marrow mouse chimeras. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3133–3138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel T. H., Kubo R. T., Cambier J. C. T-cell development and transmembrane signaling: changing biological responses through an unchanging receptor. Immunol Today. 1991 Feb;12(2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90162-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung-Leung W. P., Kündig T. M., Zinkernagel R. M., Mak T. W. Immune response against lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection in mice without CD8 expression. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1425–1429. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung-Leung W. P., Schilham M. W., Rahemtulla A., Kündig T. M., Vollenweider M., Potter J., van Ewijk W., Mak T. W. CD8 is needed for development of cytotoxic T cells but not helper T cells. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):443–449. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90462-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glas R., Sturmhöfel K., Hämmerling G. J., Kärre K., Ljunggren H. G. Restoration of a tumorigenic phenotype by beta 2-microglobulin transfection to EL-4 mutant cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):843–846. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOTCHIN J. The foot pad reaction of mice to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1962 May;17:214–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Hug E., Väth U., Müller I. Effective protection against Listeria monocytogenes and delayed-type hypersensitivity to listerial antigens depend on cooperation between specific L3T4+ and Lyt 2+ T cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):263–266. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.263-266.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmig B., Lehmann-Grube F. The immune response of the mouse to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. I. Circulating antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1979 Dec;45(3):703–710. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-3-703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Assembly and maturation of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens in vivo. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):979–991. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90210-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F., Ambrassat J. A new method to detect lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific antibody in human sera. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):85–92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F., Krenz I., Krahnert T., Schwachenwald R., Moskophidis D., Löhler J., Villeda Posada C. J. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection. IV. Questionable role of mononuclear phagocytes in the clearance of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus from spleens of mice. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2282–2289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F., Löhler J. Immunopathologic alterations of lymphatic tissues of mice infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. II. Pathogenetic mechanism. Lab Invest. 1981 Mar;44(3):205–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection. VI. Replication of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in and clearance from the foot of the mouse. J Gen Virol. 1988 Aug;69(Pt 8):1883–1891. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-8-1883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F., Moskophidis D., Löhler J. Recovery from acute virus infection. Role of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the elimination of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus from spleens of mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;532:238–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb36343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F. Portraits of viruses: arenaviruses. Intervirology. 1984;22(3):121–145. doi: 10.1159/000149543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist T. P., Eppler M., Zinkernagel R. M. Enhanced virus replication and inhibition of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus disease in anti-gamma interferon-treated mice. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2813–2819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2813-2819.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao N. S., Bix M., Zijlstra M., Jaenisch R., Raulet D. MHC class I deficiency: susceptibility to natural killer (NK) cells and impaired NK activity. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):199–202. doi: 10.1126/science.1853205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacher A. E., Braciale V. L., Braciale T. J. In vivo effector function of influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones is highly specific. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):814–826. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löhler J., Lehmann-Grube F. Immunopathologic alterations of lymphatic tissues of mice infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. I. Histopathologic findings. Lab Invest. 1981 Mar;44(3):193–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. L., Pala P., Cerottini J. C., MacDonald H. R. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted cytolytic T lymphocytes: inhibition of cytolysis by anti-CD8 monoclonal antibodies depends upon both concentration and primary sequence of peptide antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1863–1866. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre K. W., Bukowski J. F., Welsh R. M. Exquisite specificity of adoptive immunization in arenavirus-infected mice. Antiviral Res. 1985 Oct;5(5):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(85)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis D., Cobbold S. P., Waldmann H., Lehmann-Grube F. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection: treatment of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-infected mice with monoclonal antibodies reveals that Lyt-2+ T lymphocytes mediate clearance of virus and regulate the antiviral antibody response. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1867–1874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1867-1874.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis D., Fang L., Gossmann J., Drjupin R., Löhler J., Bruns M., Lehmann-Grube F. Virus-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH). Cells mediating lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific DTH reaction in mice. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1926–1934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis D., Fang L., Gossmann J., Lehmann-Grube F. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection. IX. Clearance of lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) virus from the feet of mice undergoing LCM virus-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3305–3316. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
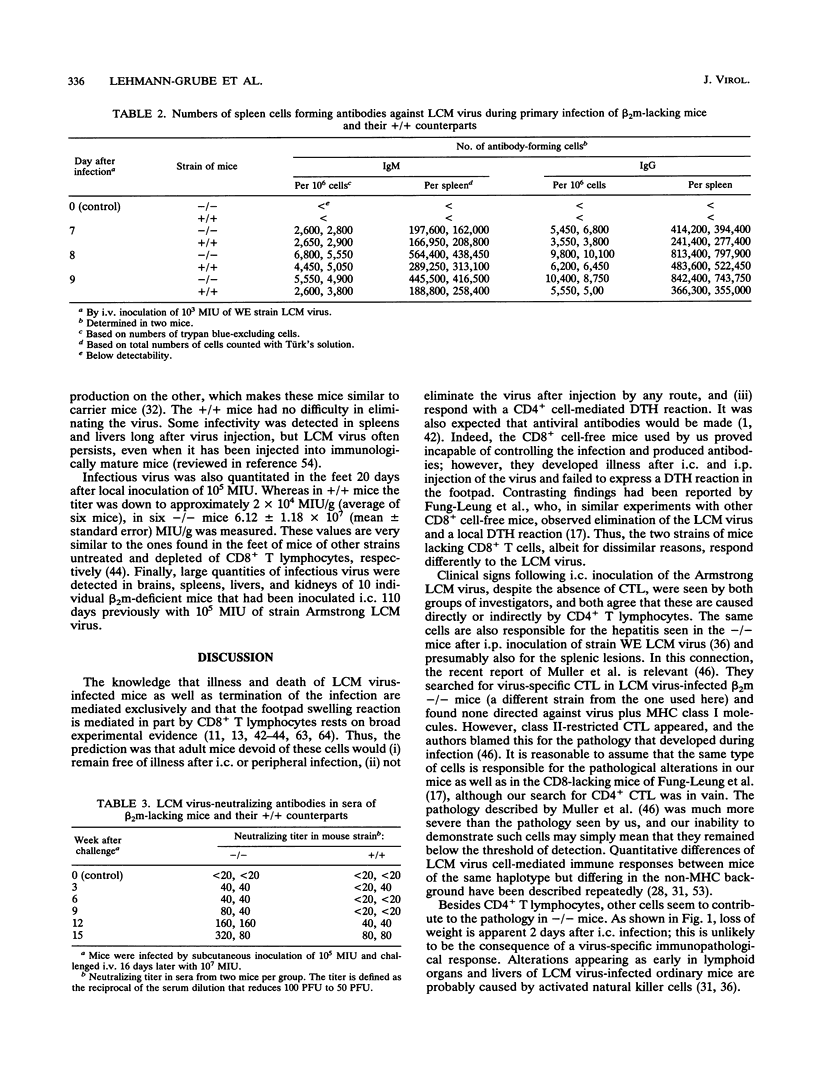
- Moskophidis D., Lehmann-Grube F. The immune response of the mouse to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. IV. Enumeration of antibody-producing cells in spleens during acute and persistent infection. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3366–3370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
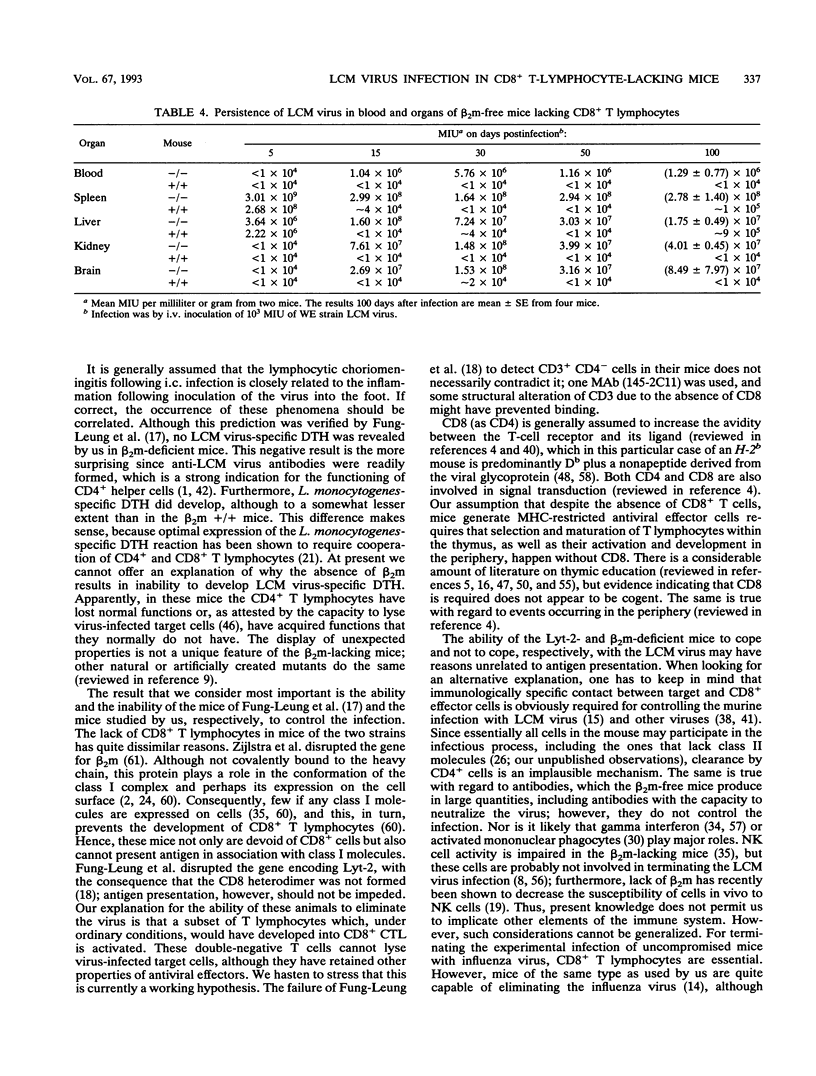
- Muller D., Koller B. H., Whitton J. L., LaPan K. E., Brigman K. K., Frelinger J. A. LCMV-specific, class II-restricted cytotoxic T cells in beta 2-microglobulin-deficient mice. Science. 1992 Mar 20;255(5051):1576–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.1347959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolić-Zugić J. Phenotypic and functional stages in the intrathymic development of alpha beta T cells. Immunol Today. 1991 Feb;12(2):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90160-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Whitton J. L., Lewicki H., Tishon A. Fine dissection of a nine amino acid glycoprotein epitope, a major determinant recognized by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific class I-restricted H-2Db cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):559–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin S., Cobbold S., Tighe H., Benjamin R., Waldmann H. CD4 monoclonal antibody pairs for immunosuppression and tolerance induction. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Aug;17(8):1159–1165. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivers T. M., McNair Scott T. F. MENINGITIS IN MAN CAUSED BY A FILTERABLE VIRUS. Science. 1935 May 3;81(2105):439–440. doi: 10.1126/science.81.2105.439-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Koller B. H., Sato T., Morrissey P. J., Fanslow W. C., Smithies O., Voice R. F., Widmer M. B., Maliszewski C. R. Beta 2-microglobulin-, CD8+ T-cell-deficient mice survive inoculation with high doses of vaccinia virus and exhibit altered IgG responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6070–6074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen A. R., Marker O. MHC and non-MHC genes regulate elimination of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus and antiviral cytotoxic T lymphocyte and delayed-type hypersensitivity mediating T lymphocyte activity in parallel. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1333–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M., Larsen J. H. Immunological tolerance to viruses. Prog Med Virol. 1965;7:160–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Brubaker J. O., Vargas-Cortes M., O'Donnell C. L. Natural killer (NK) cell response to virus infections in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. The stimulation of NK cells and the NK cell-dependent control of virus infections occur independently of T and B cell function. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1053–1063. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille A., Gessner A., Lother H., Lehmann-Grube F. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection. VIII. Treatment of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-infected mice with anti-interferon-gamma monoclonal antibody blocks generation of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes and virus elimination. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1283–1288. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi Y., Tishon A., Lewicki H., Cubitt B. A., Oldstone M. B. Diversity of T-cell receptors in virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognizing three distinct viral epitopes restricted by a single major histocompatibility complex molecule. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2527–2531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2527-2531.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., Auchincloss H., Jr, Loring J. M., Chase C. M., Russell P. S., Jaenisch R. Skin graft rejection by beta 2-microglobulin-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):885–893. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., Bix M., Simister N. E., Loring J. M., Raulet D. H., Jaenisch R. Beta 2-microglobulin deficient mice lack CD4-8+ cytolytic T cells. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):742–746. doi: 10.1038/344742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., Li E., Sajjadi F., Subramani S., Jaenisch R. Germ-line transmission of a disrupted beta 2-microglobulin gene produced by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):435–438. doi: 10.1038/342435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Haenseler E., Leist T., Cerny A., Hengartner H., Althage A. T cell-mediated hepatitis in mice infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Liver cell destruction by H-2 class I-restricted virus-specific cytotoxic T cells as a physiological correlate of the 51Cr-release assay? J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1075–1092. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Welsh R. M. H-2 compatibility requirement for virus-specific T cell-mediated effector functions in vivo. I. Specificity of T cells conferring antiviral protection against lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus is associated with H-2K and H-2D. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1495–1502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H., Kisielow P. Self-nonself discrimination by T cells. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1369–1373. doi: 10.1126/science.1972594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]