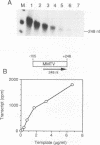
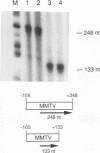
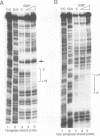
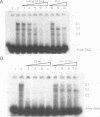
Abstract
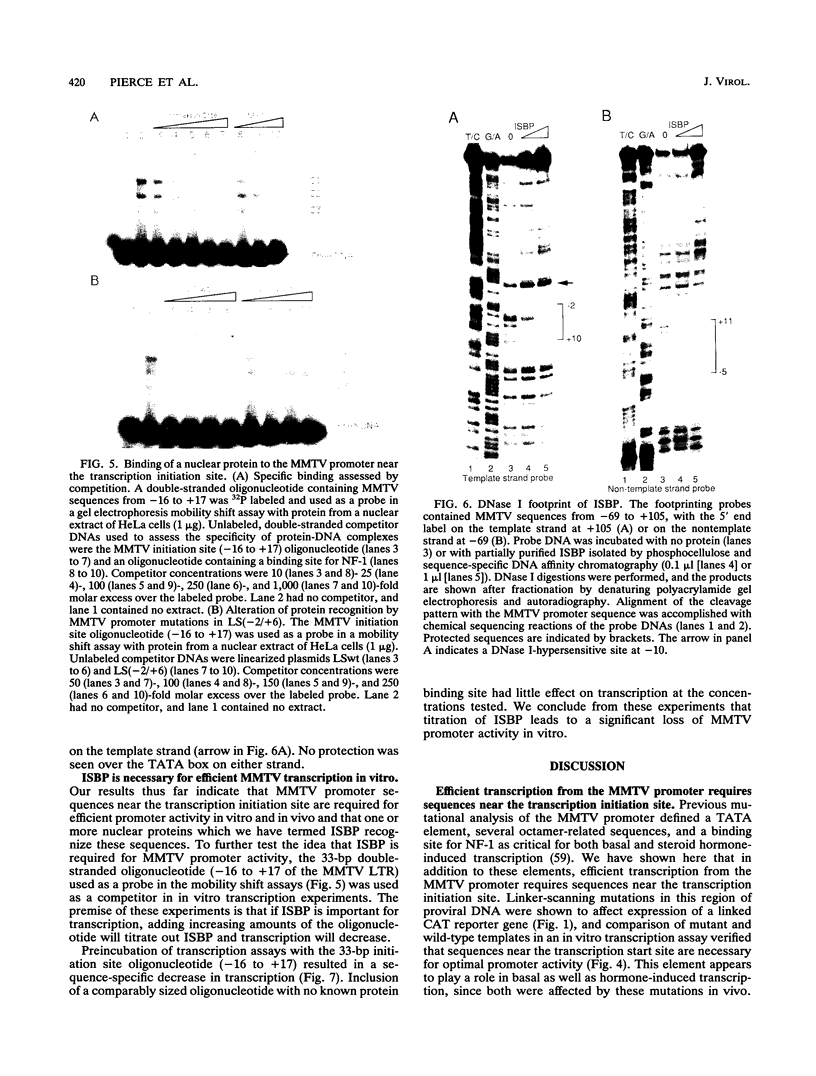
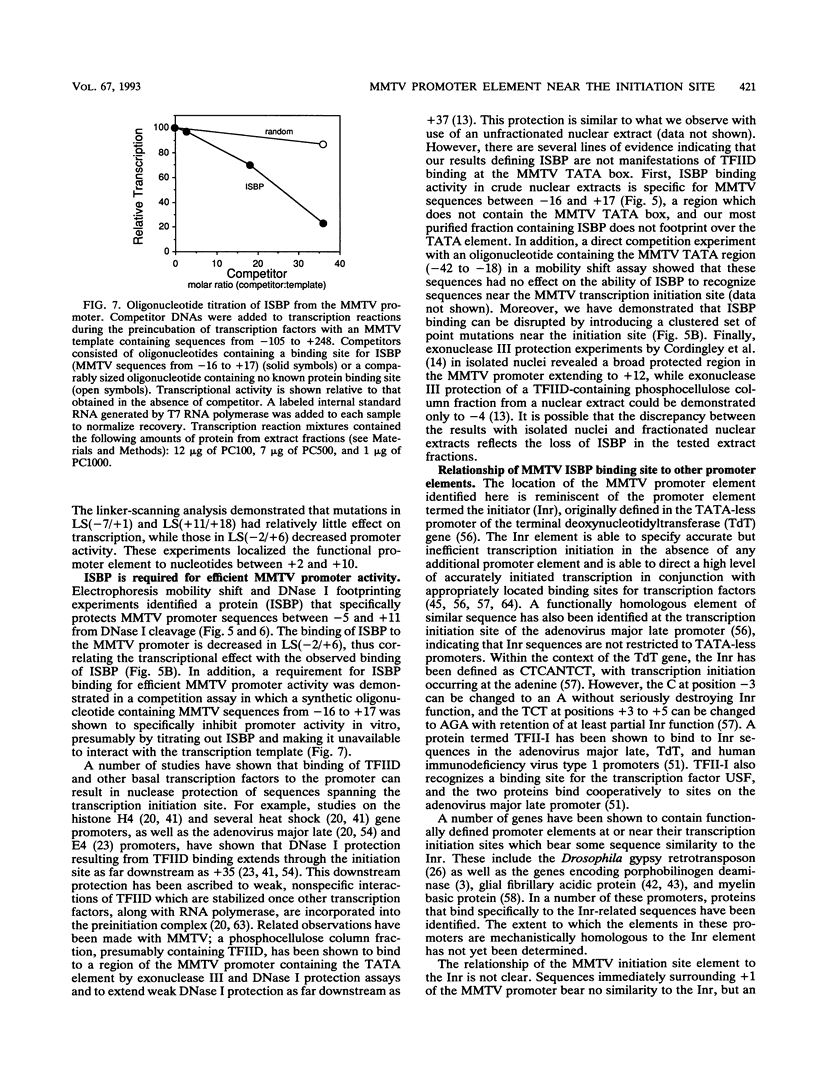
Transcription from the promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus is subject to both positive and negative control by cellular factors, and proviral promoter elements that mediate a basal level of transcription must in some way respond to these cellular regulatory signals. Several such elements, including a TATA box, a region containing three octamer-related sequences, and a binding site for nuclear factor 1, have been previously defined. Additional promoter mutations have allowed a fourth basal promoter element to be identified near the transcription initiation site between +2 and +10. Sequence alterations within this element affect transcription both in vivo and in vitro. Gel electrophoresis mobility shift and DNase I footprinting assays define a nuclear protein, termed initiation site-binding protein, that specifically recognizes this region of the promoter. Optimal levels of transcription from the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter require initiation site-binding protein, as demonstrated by a correlation between protein affinity and transcriptional activity and by specific inhibition of transcription in vitro by an oligonucleotide capable of titrating the protein from transcriptionally active fractions.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt-Jovin D. J., Jovin T. M., Bähr W., Frischauf A. M., Marquardt M. Covalent attachment of DNA to agarose. Improved synthesis and use in affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):411–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Dynan W. S. Simian virus 40 major late promoter: a novel tripartite structure that includes intragenic sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2021–2033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaupain D., Eléouët J. F., Roméo P. H. Initiation of transcription of the erythroid promoter of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene is regulated by a cis-acting sequence around the cap site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6509–6515. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Azizkhan J. C. Transcription factor E2F is required for efficient expression of the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4994–5002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Jambou R. C., Swick A. G., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Transcriptional initiation is controlled by upstream GC-box interactions in a TATAA-less promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6632–6641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Lobos S., Merino A., Buckbinder L., Weinmann R., Natarajan V., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Role of factors IID and MLTF in transcription from the adenovirus major late and IVa2 promoters. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7704–7714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Henderson D., Ponta H. The hormone response element of the mouse mammary tumour virus DNA mediates the progestin and androgen induction of transcription in the proviral long terminal repeat region. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):363–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Miksicek R., Schütz G., Arnemann J., Beato M. The hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumour virus mediates progesterone induction. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2237–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. B., Yang L., Thompson J. A., Safer B. Identification of a downstream sequence and binding protein that regulate adenovirus major late promoter transcription in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10377–10385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Hager G. L. Binding of multiple factors to the MMTV promoter in crude and fractionated nuclear extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):609–628. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel S., Thompson J. A., Jacob W. F., Cohen R., Safer B. Identification and characterization of an adenovirus 2 major late promoter CAP sequence DNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10309–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Dietz T. J., Elgin S. C. TATA box-dependent protein-DNA interactions are detected on heat shock and histone gene promoters in nuclear extracts derived from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3204–3214. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., Roeder R. G. Functional steps in transcription initiation and reinitiation from the major late promoter in a HeLa nuclear extract. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3452–3461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., Roeder R. G. Separation and partial characterization of three functional steps in transcription initiation by human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8163–8172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. L., Fabritius C., Dudley J. Mouse mammary tumor virus proviruses in T-cell lymphomas lack a negative regulatory element in the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4644–4652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4644-4652.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N., van Ooyen A. J., Kennedy N., Herrlich P., Ponta H., Groner B. Subfragments of the large terminal repeat cause glucocorticoid-responsive expression of mouse mammary tumor virus and of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. A., Meselson M. Drosophila retrotransposon promoter includes an essential sequence at the initiation site and requires a downstream sequence for full activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):102–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Luciw P. A., Duchange N. Structural arrangements of transcription control domains within the 5'-untranslated leader regions of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 promoters. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1101–1114. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Repression of HIV-1 transcription by a cellular protein. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1476–1479. doi: 10.1126/science.2006421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo W. L., Vilander L. R., Huang M., Peterson D. O. A transcriptionally defective long terminal repeat within an endogenous copy of mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2394–2402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2394-2402.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Hall C. V., Ringold G. M., Dobson D. E., Luh J., Jacob P. E. Functional analysis of the steroid hormone control region of mouse mammary tumor virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4191–4206. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. W., Moffitt P. G., Morley K. L., Peterson D. O. Multipartite structure of a negative regulatory element associated with a steroid hormone-inducible promoter. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24101–24108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J., Varmus H. E. A small region of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat confers glucocorticoid hormone regulation on a linked heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5866–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., Wagenaar E., Weijers P. Rearrangements in the long terminal repeat of extra mouse mammary tumor proviruses in T-cell leukemias of mouse strain GR result in a novel enhancer-like structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):823–830. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley K. L., Toohey M. G., Peterson D. O. Transcriptional repression of a hormone-responsive promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6973–6989. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani Y., Brenner M., Freese E. An RNA polymerase II promoter containing sequences upstream and downstream from the RNA startpoint that direct initiation of transcription from the same site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4289–4293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani Y., Horikoshi M., Brenner M., Yamamoto T., Besnard F., Roeder R. G., Freese E. A downstream initiation element required for efficient TATA box binding and in vitro function of TFIID. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):86–88. doi: 10.1038/348086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowock J., Borgmeyer U., Püschel A. W., Rupp R. A., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA protein binds to the MMTV-LTR, the adenovirus origin of replication, and the BK virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2045–2061. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea-Greenfield A., Smale S. T. Roles of TATA and initiator elements in determining the start site location and direction of RNA polymerase II transcription. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1391–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Tomkins G. M., Bishop M., Varmus H. E. Dexamethasone-mediated induction of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA: a system for studying glucocorticoid action. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Reinberg D., Jacob W. F., Maldonado E., Carcamo J., Garfinkel S., Cohen R. Interaction of CAP sequence site binding factor and transcription factor IID preceding and following binding to the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10989–10994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman A. G., Weinmann R. Promoter specificity and modulation of RNA polymerase II transcription. FASEB J. 1989 Apr;3(6):1723–1733. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.6.2649403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J., Baltimore D. Transcriptional activation by Sp1 as directed through TATA or initiator: specific requirement for mammalian transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Sumita K., Hirose S., Mikoshiba K. Core promoter of the mouse myelin basic protein gene governs brain-specific transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3101–3108. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toohey M. G., Lee J. W., Huang M., Peterson D. O. Functional elements of the steroid hormone-responsive promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4477–4488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4477-4488.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toohey M. G., Morley K. L., Peterson D. O. Multiple hormone-inducible enhancers as mediators of differential transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4526–4538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Sagami I., Wang H., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Interactions between a DNA-binding transcription factor (COUP) and a non-DNA binding factor (S300-II). Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Yamamoto K. R. Early events in the stimulation of mammary tumor virus RNA synthesis by glucocorticoids. Novel assays of transcription rates. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7416–7420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G., Sawadogo M. Physical analysis of transcription preinitiation complex assembly on a class II gene promoter. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.3413495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu L. C., Thali M., Schaffner W. Upstream box/TATA box order is the major determinant of the direction of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6699–6704. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]