Abstract
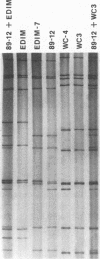
Natural infection by very similar strains of rotavirus during the 1988-1989 rotavirus season in Cincinnati, Ohio, provided complete protection of young children against subsequent rotavirus illnesses for a period of at least 2 years. Using this limited strain variability, we characterized the association between the titers of antibody to either the VP4 or the VP7 neutralization protein and protection against subsequent rotavirus disease. This was done by using reassortants that contained only one of the two rotavirus neutralization proteins of 89-12, a culture-adapted isolate representative of the protective rotavirus strains. The other neutralization protein in these reassortants was derived from a heterologous rotavirus (WC3 or EDIM) to which the infected subjects made little or no neutralizing antibody (titers, < or = 20). The geometric mean titer (GMT) of antibody to 89-12 in convalescent-phase sera from the 21 subjects analyzed was 2,323. The GMT of antibody to a reassortant (strain WC-4) that contained the VP7 protein of 89-12 and VP4 of WC3 was 387. In contrast, the GMT of antibody to a reassortant (strain EDIM-7) that contained the VP4 protein of 89-12 and the VP7 protein of EDIM was 1,078. Thus, the major neutralization response was directed against VP4 rather than VP7, a finding that has important implications for development of appropriate rotavirus vaccines.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein D. I., Sander D. S., Smith V. E., Schiff G. M., Ward R. L. Protection from rotavirus reinfection: 2-year prospective study. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):277–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein D. I., Smith V. E., Sander D. S., Pax K. A., Schiff G. M., Ward R. L. Evaluation of WC3 rotavirus vaccine and correlates of protection in healthy infants. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1055–1062. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. Y., Estes M. K., Ramig R. F. Specific interactions between rotavirus outer capsid proteins VP4 and VP7 determine expression of a cross-reactive, neutralizing VP4-specific epitope. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):432–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.432-439.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D., Burns J. W., Estes M. K., Ramig R. F. Phenotypes of rotavirus reassortants depend upon the recipient genetic background. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3743–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Borian F. E., Plotkin S. A. Immune protection of infants against rotavirus gastroenteritis by a serotype 1 reassortant of bovine rotavirus WC3. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1099–1104. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S., Kirkwood C. Relation of VP7 amino acid sequence to monoclonal antibody neutralization of rotavirus and rotavirus monotype. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5968–5974. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5968-5974.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Sarasini A., Parea M., Arista S., Miranda P., Brüssow H., Hoshino Y., Flores J. Isolation and characterization of two distinct human rotavirus strains with G6 specificity. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.9-16.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Larralde G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Antigenic relationships among human rotaviruses as determined by outer capsid protein VP4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7155–7159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Kapikian A. Z. Identification of VP7 epitopes associated with protection against human rotavirus illness or shedding in volunteers. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):548–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.548-553.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Valdesuso J., van Wyke K., Midthun K., Walsh M., McAuliffe V., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Hoshino Y. Production and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed at two surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):267–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.267-275.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Independent segregation of two antigenic specificities (VP3 and VP7) involved in neutralization of rotavirus infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8701–8704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Sereno M. M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genes of human (strain Wa) and bovine (strain UK) rotaviruses that code for neutralization and subgroup antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton D. R., Spector D. M., Ward R. L. Development of an improved method for measuring neutralizing antibody to rotavirus. J Virol Methods. 1991 Jun;33(1-2):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90013-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S. M., Mackow E. R., Greenberg H. B. Molecular determinant of rotavirus neutralization and protection. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:181–214. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60585-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Blavat G. Identification of the two rotavirus genes determining neutralization specificities. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):376–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.376-378.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padilla-Noriega L., Arias C. F., López S., Puerto F., Snodgrass D. R., Taniguchi K., Greenberg H. B. Diversity of rotavirus serotypes in Mexican infants with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1114–1119. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1114-1119.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Schael I., Blanco M., Vilar M., Garcia D., White L., Gonzalez R., Kapikian A. Z., Flores J. Clinical studies of a quadrivalent rotavirus vaccine in Venezuelan infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):553–558. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.553-558.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad B. V., Wang G. J., Clerx J. P., Chiu W. Three-dimensional structure of rotavirus. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Stoner-Ma D. L., Estes M. K., Greenberg H. B. Specific enzyme-linked immunoassay for rotavirus serotypes 1 and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.286-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urasawa S., Urasawa T., Wakasugi F., Kobayashi N., Taniguchi K., Lintag I. C., Saniel M. C., Goto H. Presumptive seventh serotype of human rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1990;113(3-4):279–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01316680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Knowlton D. R., Greenberg H. B., Schiff G. M., Bernstein D. I. Serum-neutralizing antibody to VP4 and VP7 proteins in infants following vaccination with WC3 bovine rotavirus. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2687–2691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2687-2691.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Knowlton D. R., Pierce M. J. Efficiency of human rotavirus propagation in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):748–753. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.748-753.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Knowlton D. R., Schiff G. M., Hoshino Y., Greenberg H. B. Relative concentrations of serum neutralizing antibody to VP3 and VP7 proteins in adults infected with a human rotavirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1543–1549. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1543-1549.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., McNeal M. M., Clemens J. D., Sack D. A., Rao M., Huda N., Green K. Y., Kapikian A. Z., Coulson B. S., Bishop R. F. Reactivities of serotyping monoclonal antibodies with culture-adapted human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):449–456. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.449-456.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., McNeal M. M., Sheridan J. F. Development of an adult mouse model for studies on protection against rotavirus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5070–5075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5070-5075.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., McNeal M. M., Sheridan J. F. Evidence that active protection following oral immunization of mice with live rotavirus is not dependent on neutralizing antibody. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90734-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Sander D. S., Schiff G. M., Bernstein D. I. Effect of vaccination on serotype-specific antibody responses in infants administered WC3 bovine rotavirus before or after a natural rotavirus infection. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1298–1303. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]