Abstract
We developed a mouse model of Borna disease to facilitate immunopathogenesis research by adaptation of Borna disease virus to mice through serial passage in mouse brain tissue. Borna disease virus replication, antibody production, inflammation, and Borna disease expression in several different strains of mice were examined.
Full text
PDF
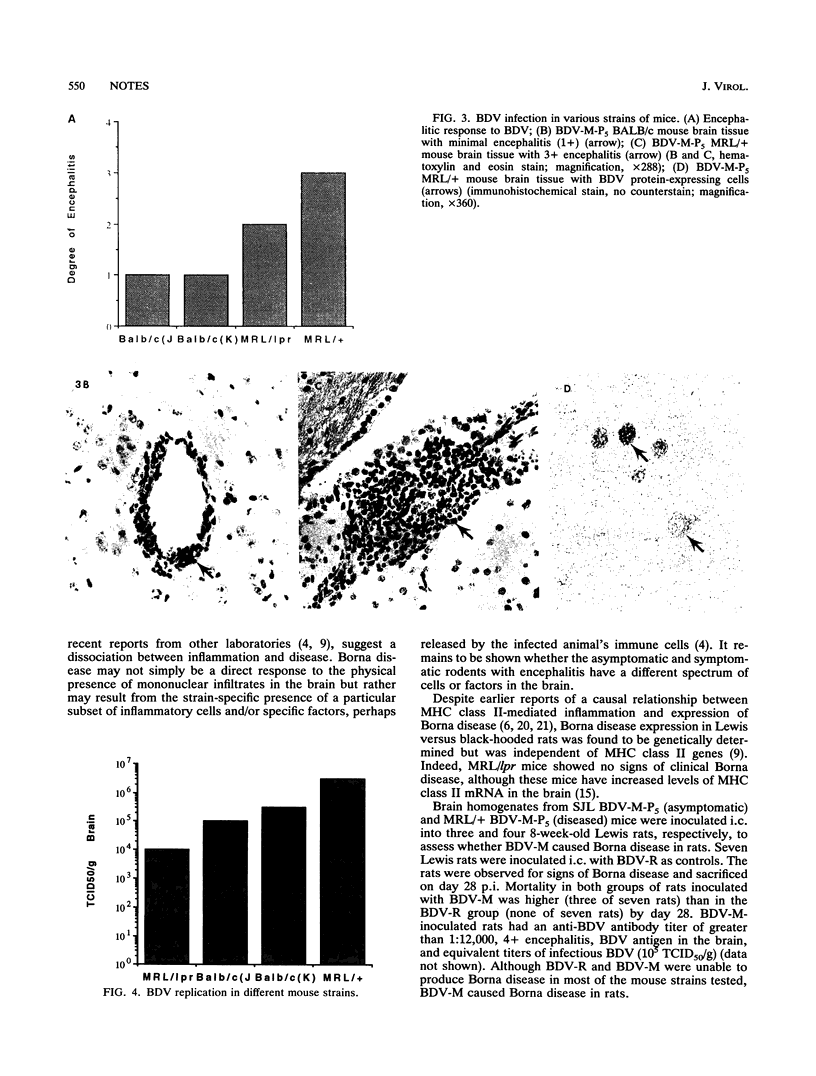

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anzil A. P., Blinzinger K., Mayr A. Persistent Borna virus infection in adult hamsters. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;40(1):52–57. doi: 10.1007/BF01242635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone K. M., Duchala C. S., Griffin J. W., Kincaid A. L., Narayan O. Pathogenesis of Borna disease in rats: evidence that intra-axonal spread is the major route for virus dissemination and the determinant for disease incubation. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3431–3440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3431-3440.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone K. M., Moench T. R., Lipkin W. I. Borna disease virus replicates in astrocytes, Schwann cells and ependymal cells in persistently infected rats: location of viral genomic and messenger RNAs by in situ hybridization. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1991 May;50(3):205–214. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199105000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschl U., Stitz L., Herzog S., Frese K., Rott R. Determination of immune cells and expression of major histocompatibility complex class II antigen in encephalitic lesions of experimental Borna disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;81(1):41–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00662636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz R. B., Skeen M. J., Chou C. H., Zamvil S. S. Localization of an encephalitogenic epitope for the SJL mouse in the N-terminal region of myelin basic protein. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Mar;26(3):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog S., Frese K., Rott R. Studies on the genetic control of resistance of black hooded rats to Borna disease. J Gen Virol. 1991 Mar;72(Pt 3):535–540. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-3-535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Kao M., Ludwig H. Persistent, tolerant or subacute infection in Borna disease virus-infected rats. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1521–1530. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao M., Ludwig H., Gosztonyi G. Adaptation of Borna disease virus to the mouse. J Gen Virol. 1984 Oct;65(Pt 10):1845–1849. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-10-1845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobler R. L., Tunison L. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Selected mutants of mouse hepatitis virus type 4 (JHM strain) induce different CNS diseases. Pathobiology of disease induced by wild type and mutants ts8 and ts15 in BALB/c and SJL/J mice. Am J Pathol. 1982 Nov;109(2):157–168. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legocki R. P., Verma D. P. Multiple immunoreplica Technique: screening for specific proteins with a series of different antibodies using one polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1981 Mar 1;111(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90577-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre K. R., Ayer-LeLièvre C., Persson H. Class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) gene expression in the mouse brain is elevated in the autoimmune MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr strain. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Jun;28(1):39–52. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90039-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Herzog S., Frese K., Scheefers H., Rott R. Pathogenesis of Borna disease in rats: immune-mediated viral ophthalmoencephalopathy causing blindness and behavioral abnormalities. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):305–315. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richt J. A., Stitz L., Wekerle H., Rott R. Borna disease, a progressive meningoencephalomyelitis as a model for CD4+ T cell-mediated immunopathology in the brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):1045–1050. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richt J., Stitz L., Deschl U., Frese K., Rott R. Borna disease virus-induced meningoencephalomyelitis caused by a virus-specific CD4+ T cell-mediated immune reaction. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2565–2573. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R., Herzog S., Richt J., Stitz L. Immune-mediated pathogenesis of Borna disease. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;270(1-2):295–301. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80166-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprankel H., Richarz K., Ludwig H., Rott R. Behavior alterations in tree shrews (Tupaia glis, Diard 1820) induced by Borna disease virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1978 May 26;165(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02121228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckling A. J., Jagelman S., Illavia S. J., Webb H. E. The effect of mouse strain on the pathogenesis of the encephalitis and demyelination induced by avirulent Semliki Forest virus infections. Br J Exp Pathol. 1980 Jun;61(3):281–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelweid C. M., Johnson G. C., Besch-Williford C. L., Basler J., Walker S. E. Inflammatory central nervous system disease in lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice: comparative histologic and immunohistochemical findings. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Dec;35(1-3):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre J. C., Carbone K. M., Lipkin W. I. Molecular characterization of the Borna disease agent. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):853–856. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90154-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]