Abstract
Hox proteins are transcriptional regulators that bind consensus DNA sequences. The DNA-binding specificity of many of these Hox proteins is modulated by the heterodimerization with partners, such as the Pbx proteins. This cooperative heterodimerization is accomplished through a conserved hexapeptide motif found N-terminal to the Hox DNA-binding homeodomain. Several human leukemias have been associated with a chromosomal translocation involving either the Hox gene (i.e., NUP98/HOXA9) or the gene encoding Pbx1 (E2A/PBX1). The transforming ability of these fusion oncoproteins relies at least partially on the ability to interact with one another through this hexapeptide motif. Herein we describe NMR structural calculations of the hexapeptide of HoxB1 (Nα-acetyl-Thr-Phe-Asp-Trp-Met-Lys-amide) that has been shown to mediate binding between HoxB1 and Pbx1 and a hexapeptide consensus sequence (Nα-acetyl-Leu-Phe-Pro-Trp-Met-Arg-amide). The consensus peptide exists in two conformations caused by cis–trans isomerization of the Phe–Pro peptide bond. The structures of the HoxB1 peptide and the trans form of the consensus peptide reveal a turn very similar to that found as part of the HoxB1/Pbx1/DNA complex in the X-ray crystal structure. This observation implies that this region is at least partially ′preformed' and thus ready to interact with Pbx1 and stabilize binding of Pbx1 and HoxB1 to DNA. The structural results presented here provide a starting point for synthesizing potential nonpeptide or cyclical peptide antagonists that mimic the interaction of these transcriptional cofactors resulting in a potential chemotherapeutic for certain types of leukemias.
Keywords: Hox, Pbx, DNA, transcription, inhibitor, NMR, peptide
The Homeobox genes are a family of developmental regulatory genes that encode nuclear homeoproteins that act as transcription factors (Gehring et al. 1994). These proteins contain a highly conserved common 60-63-residue DNA-binding homeodomain (HD) that is capable of binding DNA as a monomer (Laughon 1991). Although the homeobox genes were initially described as crucial to the correct anteroposterior patterning of the embryo in vertebrates, Drosophila, and Caenorhabditis elegans (for review, see McGinnis and Krumlauf 1992), the homeobox has subsequently been identified in a wide range of ∼100 mammalian proteins (Stein et al. 1996).
The class-I homeobox genes are defined by homology with the Drosophila Antennapeida (Antp) homeodomain (Akam 1987). The 40 mammalian class-I genes (Hox genes) have attracted the most attention because of their clustered organization on four chromosomes (Scott et al. 1989). The Hox proteins are very specific regulators of transcription, and yet, as monomers in vitro, they exhibit similar DNA-binding specificities (Laughon 1991). However, although the monomeric Hox proteins show little discrimination among different DNA sequences, their specificity and DNA-binding affinity are greatly enhanced through cooperative DNA binding with Hox cofactors (for review, see Mann and Chan 1996). The identification of extradenticle (Exd) in Drosophila as well as the vertebrate ortholog Pbx1 showed how a hox/cofactor heterodimer could achieve precise transcriptional regulation by enhanced DNA-sequence specificity (Chan et al. 1994; van Dijk and Murre 1994).
Pbx1 (as well as Pbx2 and Pbx3) and Exd are members of the TALE (three-amino-acid loop extension) family of atypical homeodomain proteins, whose members are characterized by a three-residue insertion in the first helix of the homeodomain involved in their interaction with Hox proteins (Bertolino et al. 1995). Examination of Pbx1 has shown that, in addition to the homeodomain, a short 16-residue C-terminal tail (conserved in Exd) is essential for maximal cooperative interactions with Hox partners as well as for maximal monomeric binding of Pbx1 to DNA (Lu and Kamps 1996). Cooperative binding of Hox proteins of paralog groups 1–10 is also dependent on a conserved hexapeptide sequence (consensus Y/F-P-W-M-K/R) located N-terminal to the Hox homeodomain (Knoepfler and Kamps 1995). This hexapeptide is separated from the N terminus of the homeodomain by a linker that varies in length and sequence among the different Hox proteins. Disruption of this hexapeptide by deletion or by mutation of one or more of its residues abrogates this in vitro cooperative binding between Pbx1 and Hox (Knoepfler and Kamps 1995).
The importance of regulated Hox gene expression was first recognized in the study of homeotic mutations in Drosophila and mice. In humans, the importance of Hox genes and their cofactors is well exemplified in the study of hematopoiesis in which one sees an ordered (3′– 5′ in the A, B, and C gene clusters) expression of Hox during maturation of the hematopoietic stem cell to the fully differentiated blood cells (Sauvageau et al. 1994). Furthermore, the examination of human leukemias has revealed both a general pattern of Hox gene dysregulation as well as specific recurring translocations involving Hox genes and their cofactors. For example, the t(10;14) translocation leads to the overexpression of Hox11 accompanied by T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL; Hatano et al. 1991), whereas the t(7;11) translocation joins the Nucleoporin98 gene with HoxA9, resulting in acute myeloid leukemia (Borrow et al. 1996; Nakamura et al. 1996). In addition, the Hox cofactor Pbx1 was originally identified as the C-terminal portion of the fusion oncogene created in the t(1;19) translocation found in 25% of pediatric pre–B cell ALL (Kamps et al. 1990; Nourse et al. 1990). The t(1;19) results in the fusion of the transcriptional activation domains of E2a with the majority of Pbx1 including its DNA-binding homeodomain. Presumably, the transforming ability of the resultant E2aPbx1 fusion oncoprotein is dependent on its ability to interact with Hox proteins.
Recently, the structure of the human HoxB1—Pbx1 heterodimer bound to DNA was elucidated by X-ray crystallography (Piper et al. 1999). The structure was comprised of the minimal fragments necessary for cooperative DNA binding: The HoxB1 homeodomain + N-terminal hexapeptide and the Pbx1 homeodomain + C-terminal helix. The structure showed that HoxB1 and Pbx1 bind to overlapping sites on opposite faces of the DNA helix. All contacts with Pbx1 are mediated through the conserved Hox hexapeptide that contacts Pbx1 in a pocket located between the three-residue insertion and the third helix of the Pbx1 homeodomain. In contrast, the C-terminal residues of Pbx1 are not involved in binding either DNA or HoxB1. The linker region between the HoxB1 homeodomain and the hexapeptide (not conserved within the Hox family of proteins) is unstructured, suggesting that it is not involved in establishing the contact between the Hox hexapeptide and the Pbx1 homeodomain. The structure of the homologous Drosophilia Ubx–Exd heterodimer on a similar DNA sequence has also been solved by X-ray crystallography (Passner et al. 1999) and shows very similar features. In particular, contact between the two proteins is mediated entirely by the Ubx hexapeptide region that adopts an essentially identical structure to that of HoxB1 and binds to a hydrophobic pocket in the Exd homeodomain (Wilson and Desplan 1999). Previous in vitro studies have shown that disruption of the cooperative DNA binding by Pbx1 and Hox proteins can be accomplished by simple mutations in the hexapeptide domain as well as by the inclusion, in the binding reaction of a high concentration of a synthetic ∼15-residue peptide containing the hexapeptide domain (Knoepfler and Kamps 1995). The structure of the Pbx1 homeodomain, both free in solution and complexed to DNA, has also been determined by NMR spectroscopy. A model for the interaction was proposed that suggested the formation of the additional helix of Pbx1 involved in the interaction with HoxB1 protein was triggered by the interaction of Pbx1 with the DNA oligonucleotide (Jabet et al. 1999).
Herein we investigate the question of whether the HoxB1 hexapeptide Thr-Phe-Asp-Trp-Met-Lys or the consensus sequence hexapeptide Leu-Phe-Pro-Trp-Met-Arg are self-assembling domains, capable of independently folding into the same structure as the wild-type protein in the absence of Pbx1, DNA, or any other portion of HoxB1. NMR studies over the last decade have focussed on the observation of nascent structures in peptides in solution as well as their relevance to function (Dyson et al. 1988). Very recent NMR studies (Forman-Kay 1999; Cavanagh and Akke 2000) have highlighted the importance of backbone and side-chain dynamics in the formation of protein–protein complexes and have focussed on the understanding of the entropic contributions in the interface of the protein–protein interaction to the stability of the complex. We show that both of these small peptides are capable of folding into stable turn structures that are equivalent to the structure of this region in the HoxB1 protein bound to Pbx1. These results are important for understanding the mechanism and energetics of the Hox/Pbx1 interaction. In addition, these studies are critical for the potential design and synthesis of small, specific, stable nonpeptide or cyclical peptide inhibitors that might be important in the treatment of specific types of leukemias.
Results
In the HoxB1–Pbx1–DNA complex (Piper et al. 1999) and similarly in the Ubx–Exd–DNA structure (Passner et al. 1999), contacts between the HoxB1 homeodomain (or Ubx) and Pbx1 (or Exd) are mediated entirely by the hexapeptide (TFDWMK). This peptide, corresponding to residues −24 to −19 of the HoxB1 homeodomain, was synthesized for solution structural studies with the addition of acetyl and amide groups to remove effects of artificial charges at the N- and C termini, which would not be present in the intact protein. The hexapeptide region has a core pentapeptide motif that is highly conserved among Hox proteins (F/Y-P-W-M-R/K; Knoepfler and Kamps 1995). Thus, the hexapeptide Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 representing the consensus sequence was also studied. The consensus peptide exists in two conformations caused by cis–trans isomerization of the Phe–Pro peptide bond.
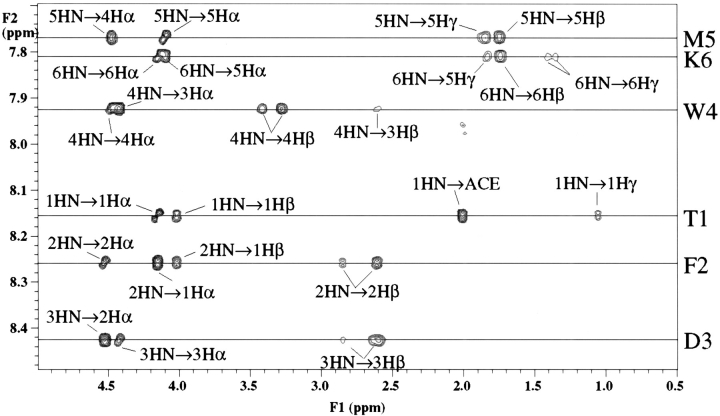
1H 1D and 1H −1H 2D NMR spectra were obtained at 300 MHz, 500 MHz, and 600 MHz for both peptides. Spectra were collected at 5°C to maximize nascent or existing structure in the peptide. The amide region of the 2D ROESY NMR spectrum for Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 is shown in Figure 1 ▶. Complete NMR resonance assignments of both peptides were obtained using a combination of DQF–COSY, TOCSY and ROESY experiments and standard NMR sequence assignment methods (Wüthrich 1986). 3JHNHα coupling constants were measured from high resolution 1-D NMR spectra obtained at 600 MHz for Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 and 500 MHz for Ac(LFPWMR)NH2. The Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide exhibits cis–trans isomerism about the proline residue leading to ∼10% of the cis form of the peptide. The presence of the bulky tryptophan residue following the proline should result in a relatively higher proportion than normal of the cis conformation of the peptide (Nardi et al. 2000). The chemical shift assignments and coupling constants for these peptides are listed in Table 1, Table 2, and Table 3.
Fig. 1.
NH-aliphatic region of the 1H 2D NMR ROESY spectrum of Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 at 600 MHz taken at 5°C. with a 150 ms mixing time.
Table 1.
Chemical shiftsa and coupling constants for Ac(TFDWMK)NH2
| Residue | HN | Hα | Hβ | Others | 3JHNHα |
| Acetyl | CH3 2.02 | ||||
| Thr-1 | 8.15 | 4.15 | 4.02 | Hγ1 8.03, Hγ2* 1.06 | 7.31 |
| Phe-2 | 8.26 | 4.53 | 2.86 | Hδ* 7.11, Hɛ* 7.30, Hζ 7.30 | 7.49 |
| 2.61 | |||||
| Asp-3 | 8.43 | 4.43 | 2.64 | 5.35 | |
| 2.60 | |||||
| Trp-4 | 7.93 | 4.48 | 3.42 | Hδ1 7.40, Hɛ1 10.27, Hɛ3 7.56 | 4.82 |
| 3.28 | Hζ2 7.41, Hζ3 7.17, Hη2 7.21 | ||||
| Met-5 | 7.77 | 4.11 | 1.75 | Hγ* 1.87, 1.83, Hɛ* 2.00 | 6.80 |
| Lys-6 | 7.81 | 4.14 | 1.75 | Hγ* 1.41, 1.35, Hδ* 1.64, Hɛ* 2.93 | 6.93 |
| Hζ* 7.60 | |||||
| Amide | 7.45 |
a Residue chemical shifts were recorded at 5°C and corrected to an internal shift standard of DSS.
Table 2.
Chemical shiftsaand coupling constants for trans Ac(LFPWMR)NH2
| Residue | HN | Hα | Hβ | Others | 3JHNHα |
| Acetyl | CH3 1.91 | ||||
| Leu-1 | 8.14 | 4.07 | 1.18 | Hγ 1.38 | 6.65 |
| 1.31 | Hδ* 0.81, 0.75 | ||||
| Phe-2 | 7.81 | 4.63 | 2.30 | Hδ* 7.19 | 8.22 |
| 2.15 | Hɛ* 7.38 | ||||
| Pro-3 | — | 4.25 | 2.30 | Hγ* 2.09 | — |
| 2.02 | Hδ* 3.73, 3.59 | ||||
| Trp-4 | 7.36 | 4.65 | 3.43 | Hδ1 7.29, Hɛ1 10.37, Hɛ3 7.61 | |
| 3.32 | Hζ2 7.18, Hζ3 7.22, Hη2 7.30 | ||||
| Met-5 | 7.68 | 4.34 | 2.06 | Hγ* 2.17, 1.98 | 7.61 |
| 1.79 | Hɛ* 2.08 | ||||
| Arg-6 | 7.95 | 4.20 | 1.86 | Hγ* 1.59, Hδ* 3.17, Hɛ 7.22 | 7.19 |
| 1.75 | HH11 6.90, HH21 6.47 | ||||
| Amide | 7.59 |
a Residue chemical shifts were recorded at 5°C and corrected to an internal shift standard of DSS.
Table 3.
Chemical shiftsaand coupling constants for cis Ac(LFPWMR)NH2
| Residue | HN | Hα | Hβ | Others | 3JHNHα |
| Acetyl | CH3 2.00 | ||||
| Leu-1 | 8.23 | 4.37 | 1.54 | Hγ 1.63 | 7.59 |
| Hδ* 0.92, 0.88 | |||||
| Phe-2 | 8.30 | 4.33 | 2.96 | Hδ* 7.14 | 6.48 |
| 2.91 | Hɛ* 7.31 | ||||
| Pro-3 | — | 3.57 | 1.72 | Hγ* 1.58, 1.29 | — |
| 1.47 | Hδ* 3.63, 3.55 | ||||
| Trp-4 | 8.41 | 4.53 | 3.27 | Hδ1 7.24, Hɛ1 10.21, Hɛ3 7.59 | 6.44 |
| Hζ2 7.63, Hζ3 7.18, Hη2 7.26 | |||||
| Met-5 | 8.13 | 4.34 | 1.95 | Hγ* 2.41, 2.34 | — |
| 1.84 | Hɛ* 2.03 | ||||
| Arg-6 | 8.19 | 4.10 | 1.78 | Hγ* 1.57, Hδ* 3.24 | 6.85 |
| 1.67 | |||||
| Amide | 7.65 |
a Residue chemical shifts were recorded at 5°C and corrected to an internal shift standard of DSS.
For small peptides, such as Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 and Ac(LFPWMR)NH2, distance restraints were obtained from cross-peak intensities in 2D ROESY NMR spectra obtained at 600 MHz and 300 MHz, both with mixing times of 150 ms. For the Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 peptide, strong dαN connectivities were found between residues 1 and 2, residues 2 and 3, residues 3 and 4, residues 4 and 5, as well as residues 5 and 6 (Fig. 1 ▶). Relatively weak dNN connectivities were found between residues 2 and 3, as well as residues 3 and 4 with a stronger dNN ROE between residues 4 and 5. For the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide in the trans form, strong dαN connectivities were found between residues 1 and 2, residues 3 and 4, residues 4 and 5, as well as residues 5 and 6. Relatively weak dNN connectivities were found between residues 4 and 5, and residues 5 and 6. For the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide in the cis form, strong dαN connectivities were found between residues 1 and 2, residues 3 and 4, residues 4 and 5, as well as residues 5 and 6. Relatively weak dNN connectivities were found between residues 1 and 2 and between residues 4 and 5. A complete summary of the NMR ROE information is shown in Figure 2 ▶. Experimental distance restraints were calibrated using the program NMRView (Johnson and Blevins 1994) with some in-house modifications. Torsion angle φ restraints were obtained by converting measured 3JHNHα NMR coupling constants to φ angles and adding a range of +/− 10°. Only the Trp and Met residues in Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 had coupling constants <6.0 Hz, which is indicative of φ values that are significantly different from values typical of random coil or extended structure. In the trans form of the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide, only F2 had a coupling constant >8 Hz, indicative of a φ value different from random coil. The coupling constant for Trp4 in the trans form of the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide could not be measured because of overlap with the side-chain resonances of Phe2. In total, for the Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 peptide there were 36 intraresidue, 31 sequential (|i − j| = 1) and nine short-range (1 < |i − j| ≤ 5) distance restraints as well as two dihedral φ restraints used in the structural calculations. For the trans form of the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide, there were 52 intraresidue, 22 sequential, and eight short-range distance restraints in addition to one dihedral φ restraint used for the structural calculations. For the cis form of Ac(LFPWMR)NH2, there were 30 intraresidue, 19 sequential, and two short-range restraints.
Fig. 2.
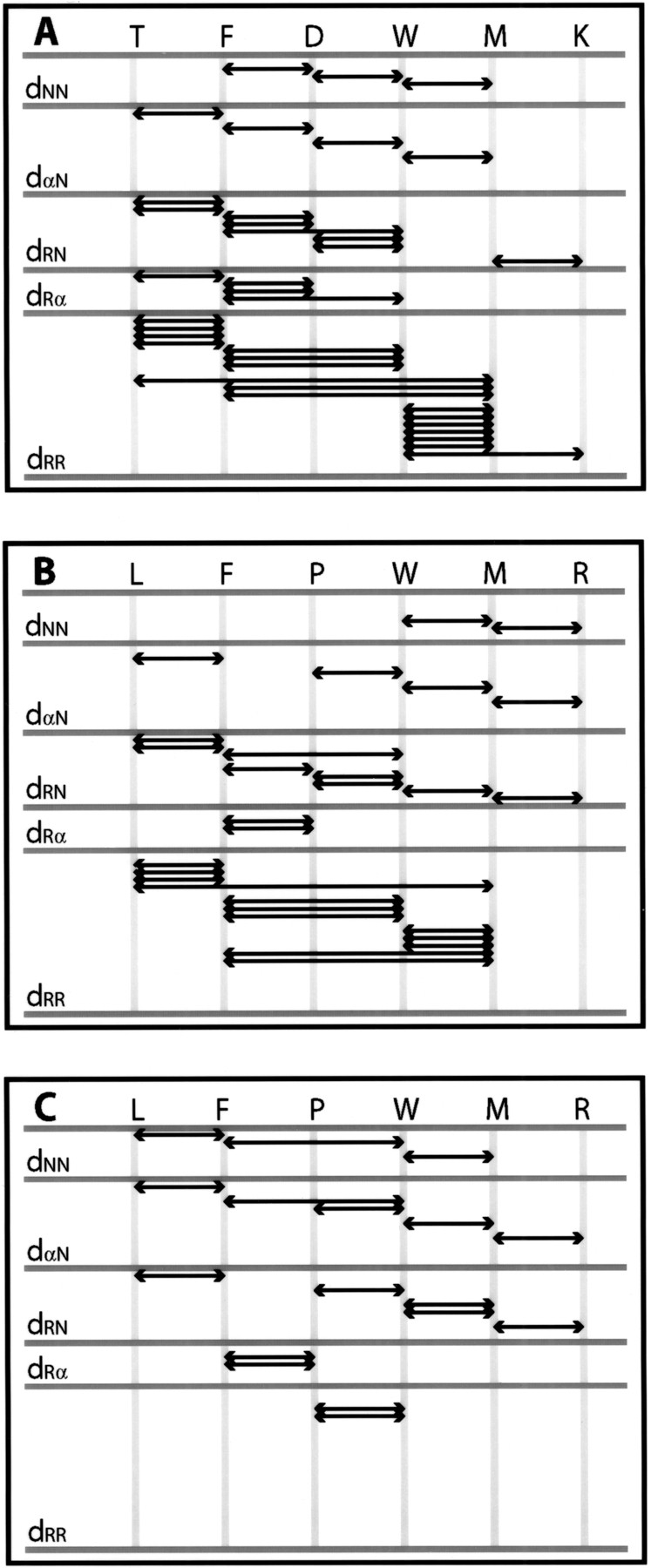
Summary of ROE interactions defining the preferred conformations of (A) Ac(TFDWMK)NH2, (B) trans-Ac(LFPWMR)NH2, and (C) cis-Ac(LFPWMR)NH2. Shown are the dNN, dαN, dRN, dRα, and dRR connectivities. dNN refers to the sequential NH–NH ROE, dαN refers to the sequential Hα–NH ROE, dRN refers to any side chain–NH ROE, dRα refers to any side chain–Hα ROE, and dRR refers to any side chain–side chain ROE.
Ensembles of 60 structures were computed from the experimental restraints derived from the NMR data as described in the Materials and Methods section. For Ac(TFDWMK)NH2, 23 were accepted with no ROE violations >0.2 Å, no dihedral violations >5°, and low ETOT (<15 kcal/mole). The structural statistics are shown in Table 4. For the trans form of Ac(LFPWMR)NH2, 17 structures were accepted with no ROE violations >0.2 Å, no dihedral violations >5°, and low ETOT (<17 kcal/mole). For the cis form of Ac(LFPWMR)NH2, 18 structures were accepted with no ROE violations >0.2 Å; and low ETOT (<13 kcal/mole). The ensembles of NMR structures superimposed on the representative structures are shown for all three structures in Figure 3A–C ▶. The backbone RMSDs within the families of structures for residues 1–5 are given in Table 4.
Table 4.
Structural statistics and atomic r.m.s. differences for 23 calculated Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 structures, 17 calculated .trans Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 structures, and 18 calculated cis Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 structures
| Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 | Trans-Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 | Cis-Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 | |
| ETOT (kcal/mol)a | 11.36 ± 2.09 | 14.04 ± 1.32 | 12.18 ± 0.44 |
| ENOE (kcal/mol)a | 1.44 ± 0.38 | 0.41 ± 0.13 | 0.27 ± 0.12 |
| EVDW (kcal/mol)a | 0.42 ± 0.74 | 0.41 ± 0.56 | 0.05 ± 0.16 |
| Deviations from Ideal Geometryb | |||
| Bonds (Å) | 0.0036 ± 0.0002 | 0.0039 ± 0.0002 | 0.0035 ± 0.0002 |
| Angles (°) | 0.4758 ± 0.0407 | 0.5360 ± 0.0216 | 0.5098 ± 0.0077 |
| Improper (°) | 0.1929 ± 0.0323 | 0.2929 ± 0.0105 | 0.2878 ± 0.0112 |
| Atomic r.m.s. differences (Å)c | |||
| Backbone atoms | 0.36 ± 0.06 | 0.32 ± 0.08 | 0.55 ± 0.05 |
| Heavy atoms | 0.63 ± 0.06 | 0.54 ± 0.07 | 1.17 ± 0.16 |
a The values for ENOE are calculated from a square well potential with a force constant of 50 kcal • mole−1 • Å2. EVDW is calculated with a force constant of 4 kcal • mole−1 • Å−4 and the final van der Waal's radii were set to 0.75 times the value used in the CHARMM force field.
b The values for bonds, angles, and impropers show the deviation from ideal values based on perfect stereochemistry.
c R.m.s. differences of the final simulated annealing structures superimposed on the average structures (residues 1–5).
Fig. 3.
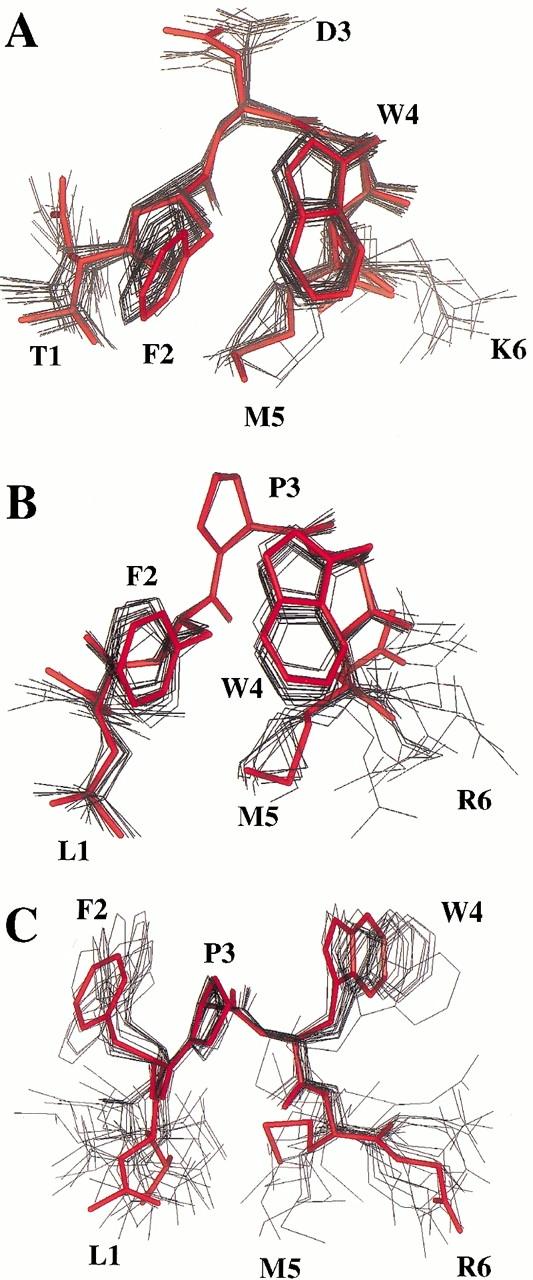
(A) Superimposition of 23 calculated NMR structures for Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 (black) with a representative structure (red). (B) Superimposition of 17 calculated NMR structures for the trans form of Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 (black) with a representative structure (red). (C) Superimposition of 18 calculated NMR structures for the cis form of Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 (black) with a representative structure (red). The representative structure is a structure in the ensemble that has the lowest RMSD to its own average structure. Figure was prepared using Insight II (MSI).
The preferred conformations of Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 and the trans form of Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 resemble a type-I turn (Fig. 3A,B ▶). Type-I turns, or αα in the nomenclature of Wilmut and Thornton (1990), are characterized by (φ, ψ) angles of (−60°, −30°) in the i + 1 position followed by (−90°, 0°) in the i + 2 position of the turn. These angles can deviate as much as 30° in the actual structure (Wilmot and Thornton 1990). Table 5 and Table 6 illustrate the (φ, ψ) angles of the 6-mer peptides in solution. In the Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 peptide, residue 3 has (φ, ψ) angles of (−81°, −32°) and residue 4 has (φ, ψ) angles of (−71°, −20°)). A backbone H-bond is possible in the structure involving the carbonyl oxygen of residue 2 and the amide hydrogen of residue 5 (distance is ∼2.9 Å in the average NMR structure and ∼2.4 Å in the crystal structure). In addition, another hydrogen is possible involving the backbone carbonyl oxygen of residue 3 with the backbone amide hydrogen of residue 6 (∼2.5 Å in the average NMR structure and and ∼1.9 Å in the crystal structure). For the trans form of Ac(LFPWMR)NH2, residue 3 has (φ, ψ) angles of (−80°, −15°) and residue 4 has (φ, ψ) angles of (−101°, 2°). A backbone H-bond is possible in the structure involving the carbonyl oxygen of residue 3 and the amide hydrogen of residue 6. For the cis form of Ac(LFPWMR)NH2, the (φ, ψ) angles are completely different from the trans form of Ac(LFPWMR)NH2, the Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 peptide and the X-ray crystal structure of the TFDWMK complex (Table 6). The cis form of the peptide appears to form a structure that may be described at a type-VIII turn, with characteristic (φ, ψ) angles of (−60°, −30°)) in the i + 1 position, and (−120°, 120°) in the i + 2 position (Wilmot and Thornton 1990).
Table 5.
Comparison of (φ, ψ) and χ1 angles for the Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 calculated NMR structures1 with the X-ray structure of the hexapeptide in complex with Pbx1 and DNA
| NMR structures | X-ray structure | |||||
| Residue | φ | ψ | χ1 | φ | ψ | χ1 |
| T1 | — | 143 ± 26 | 47 ± 5 | — | 99 | 65 |
| F2 | 44 ± 54 | 131 ± 17 | −56 ± 4 | −76 | 176 | −51 |
| D3 | −81 ± 0 | −32 ± 7 | −146 ± 40 | −55 | −46 | −69 |
| W4 | −71 ± 7 | −20 ± 14 | 44 ± 8 | −60 | −30 | 64 |
| M5 | −68 ± 15 | 28 ± 74 | −65 ± 79 | −72 | −10 | −51 |
| K6 | −31 ± 86 | — | −50 ± 37 | −112 | — | — |
Table 6.
Comparison of (φ, ψ) and χ1 angles for the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide
| Trans | Cis | |||||
| Residue | φ | ψ | χ1 | φ | ψ | χ1 |
| L1 | — | −63 ± 11 | −75 ± 33 | — | 77 ± 36 | −127 ± 36 |
| F2 | −129 ± 13 | 158 ± 3 | −68 ± 9 | 139 ± 70 | 143 ± 7 | −95 ± 32 |
| P3 | −80 ± 1 | −15 ± 9 | 24 ± 0 | −80 ± 1 | −42 ± 4 | 24 ± 0 |
| W4 | −101 ± 14 | 2 ± 13.0 | 43 ± 2 | −120 ± 13 | 165 ± 11 | −97 ± 4 |
| M5 | −87 ± 20 | 58 ± 90 | −64 ± 42 | −138 ± 12 | 92 ± 43 | 160 ± 89 |
| R6 | −75 ± 59 | — | −75 ± 79 | −103 ± 50 | — | −90 ± 72 |
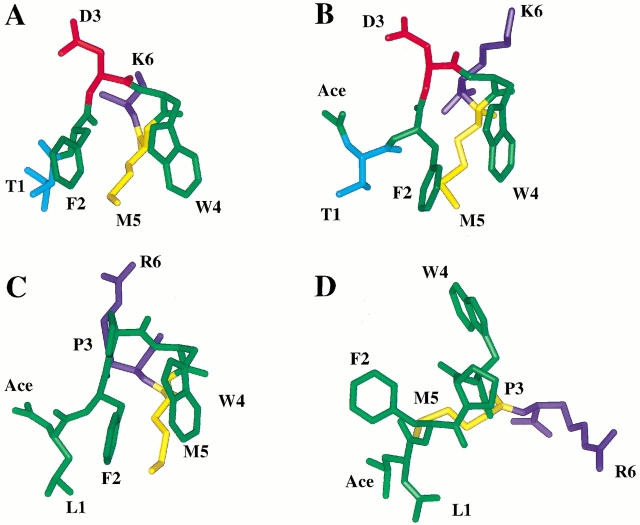
Figure 4 ▶ depicts a comparison of a member of the major conformation of each ensemble of NMR structures to the X-ray structure (coordinates 1B72 from the Protein Data Bank) of the same region. It is immediately clear that the Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 peptide and the trans form of the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide has adopted an overall structure that is very similar to that of the same region in the intact ternary complex (Table 5). The RMSD between the Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 peptide and the X-ray structure is 0.92 over residues 1–5. Between the trans form of the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide and the X-ray structure, the RMSD is 0.94. The cis form of the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide has an RMSD of 1.66 with the X-ray structure.
Fig. 4.
(A) Crystal structure of the 6-mer peptide from complex with Pbx1 and DNA. (B) A representative structure of the Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 peptide. (C) A representative structure of the trans form of the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide. (D) A representative structure of the cis form of the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide. The representative structure is a structure in the ensemble that has the lowest RMSD to its own average structure. Figure was prepared using Insight II (MSI).
To further characterize the structuring of the 6-mer peptides, amide proton NMR chemical shift temperature coefficients (Δδ/ΔT) were measured. Exposed NHs typically have gradients in the range of −6.0 ppb/°C to −8.5 ppb/°C, whereas hydrogen-bonded NHs have Δδ/ΔT of −2.0 ppb/°C ± 1.4 ppb/°C (Andersen et al. 1997). To measure Δδ/ΔT values for the peptides, 1D spectra were acquired at 5°C, 10°C, 15°C, 20°C, and 25°C. Chemical shift deviations were derived from the lowest temperature set included (5°C). Random coil chemical shifts (Wishart et al. 1995) were corrected to 5°C according to (Mertuka et al. 1995). Table 7 shows the Δδ/ΔT for each residue in addition to the NH and Hα chemical shift deviations for the 6-mer peptides at 5°C and 20°C. For the Ac(TFPWMK)NH2 peptide, it is possible that residues 5 and 6 are able to form hydrogen bonds. Indeed, the greatest chemical shift deviations occur for residues M5 and K6 (Table 4), and their Δδ/ΔT values are within the −2.0 ppb/°C ± 1.4 ppb/°C range for hydrogen-bonded NHs. The hydrogen bond potential of these residues could account for the good stability of the peptide. Interestingly, the trans form of the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide has a small Δδ/ΔT value for residue M5, indicating that it could be hydrogen bonded (most likely to F2). The largest chemical shift deviations from random coil values occur for residues W4 and M5. The cis form of this peptide does not have significant chemical shift deviations from random coil and has no Δδ/ΔT values that indicate hydrogen bonds are present to stabilize the structure.
Table 7.
NH and Hα 1H NMR chemical shift deviations and NH temperature coefficients
| Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 | ||||
| Residue | NH CSD (5°C) | NH CSD (20°C) | Δδ/ΔT | Hα CSD |
| T1 | −0.12 | −0.14 | −9.0 | −0.20 |
| F2 | −0.18 | −0.19 | −9.0 | −0.09 |
| D3 | −0.03 | 0.00 | −5.6 | −0.21 |
| W4 | −0.46 | −0.46 | −7.8 | −0.18 |
| M5 | −0.66 | −0.58 | −2.6 | −0.37 |
| K6 | −0.63 | −0.55 | −3.1 | −0.18 |
| Trans Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 | ||||
| L1 | −0.18 | −0.16 | −8.2 | −0.27 |
| F2 | −0.46 | −0.47 | −7.1 | −0.27 |
| P3 | — | — | — | −0.19 |
| W4 | −1.03 | −1.05 | −7.6 | −0.01 |
| M5 | −0.74 | −0.68 | −2.9 | −0.14 |
| R6 | −0.41 | −0.37 | −4.4 | −0.14 |
| Cis Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 | ||||
| L1 | −0.07 | −0.06 | −6.8 | 0.03 |
| F2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | −8.4 | −0.57 |
| P3 | — | — | — | −0.87 |
| W4 | 0.02 | 0 | −9.4 | −0.13 |
| M5 | −0.3 | −0.24 | −4.5 | −0.14 |
| R6 | −0.16 | −0.16 | −6.2 | −0.24 |
NH chemical shift deviations were calculated at the appropriate temperature with random coil chemical shift correction as described in Andersen et al. (1997); Mertuka et al. (1995); and Wishart et al. (1995). Hα chemical shift deviations were calculated from peptide data at 5°C and random coil data at 25°C from Wishart et al. (1995).
Discussion
The preferred conformation of the hexapeptide Ac(TFDWMK)NH2, which corresponds to residues −24 to −19 of the HoxB1 homeodomain, was studied to determine if it is a self-assembling domain retaining the structure of the bound form of this part of the intact HoxB1 protein. In addition, Ac(LFPWMR)NH2, which corresponds to the consensus sequence of the hexapeptide, was studied to determine if it has a similar structure to the hexapeptide Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 and the intact HoxB1 protein.
NMR spectroscopic analysis of the Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 peptide reveals the major conformation of the peptide to be a stable folded structure that is strikingly similar to this portion of HoxB1 in the X-ray structure where HoxB1 was complexed with Pbx1 and DNA (Fig. 4 ▶). In addition, the trans form of the consensus sequence Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 is also structured and the preferred conformation is similar to the X-ray structure. Similar φ, ψ, and χ1 angles are found between the X-ray structure bound to Pbx1 and DNA and the two hexapeptides (Table 5 and Table 6). In addition, similar hydrogen-bonding patterns are found between the three structures. Although the preferred NMR and X-ray structures are not identical (RMSDs between the X-ray structure and the NMR structures are close to 1 Å), this is to be expected because the rest of the Hox1 protein is missing in the NMR-determined structure and the X-ray structure was of the complexed form rather than the free form of this region of the protein.
The cis form of the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide has a different preferred structure from the trans form, the X-ray structure or the hexapeptide Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 in solution. The presence of an aromatic group C-terminal to the proline appears to enhance the population of the cis form of the peptide (Nardi et al. 2000). It is likely, therefore, that the presence of the proline in the consensus sequence would attenuate the binding ability of this peptide to Pbx1.
The well-defined preferred peptide conformational structures determined here, as evident from the low RMSDs, are mainly caused by the specific hexapeptide sequence. The hydrophobic residues (phenylalanine, tryptophan, and methionine) have a tendency to interact with one another (Fig. 2 ▶). In addition, because of the interacting hydrophobic residues, the backbone can orient itself into a turn structure such that hydrogen bonds form to stabilize the backbone conformation. For a type-I turn, it is expected that one would see the ROE dαN(i,i + 2) between Asp3-Met5 and Trp4-Lys6. These ROEs are expected to be weak (because, in the X-ray structure, these atoms are 3.5 Å–4 Å apart). One of the ROEs (Asp3 Hα to Met5 NH) overlaps with another ROE (Trp4 Hα to Met5 NH) and thus was not included in the data set. The other ROE is present (Trp4 Hα to Lys6 NH), but is weak, and was not chosen to be part of the original data set. Interestingly, the major structures of the 6-mers are dependent mostly on side-chain interactions, rather than strictly backbone ROEs as shown in Figure 2 ▶.
The major structures observed here for Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 and the trans form of Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 appear to be relatively stable in solution since the chemical shift deviations at 20°C are similar to those at 5°C (Table 7), indicating a high proportion of structure is still present at 20°C. Analysis of the free energy of folding of the ensemble of Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 peptide structures utilizing the STC program (Lavigne et al. 2000), which bases its calculations on the differences in accessible surface area of polar and nonpolar residues between unfolded and folded states, indicates a ΔG of ∼0.1 ± 0.3 kcal/mole at 5°C, indicating that ≥50% of the peptide is folded at this temperature. Further STC analysis of the ΔG of binding of this peptide to the Pbx1–DNA complex (using the X-ray structure complex as the protein complex structure and the NMR derived structure for the peptide free structure) reveals a ΔG of ∼−5 to −6 kcal/mole, corresponding to a KD of ∼100 μM. This binding constant is consistent with the notion that the Pbx1 and HoxB1 proteins independently bind to the DNA after which the complex is stabilized against dissociation by the binding of the hexapeptide of HoxB1 to Pbx1 (Wilson and Desplan 1999).
A truncated form of the hexapeptide studied here (a pentapeptide consisting of residues 2–6) has been previously shown to inhibit cooperative binding between Hox proteins and Pbx1 while enhancing Pbx1 DNA binding (Knoepfler and Kamps 1995). These results are important in that certain leukemias result from chromosomal translocations involving Hox or Pbx1 genes and that the genesis of these leukemias most likely requires the hexapeptide motif of the Hox protein to stabilize Pbx binding to DNA. The ability to block the interaction between these two proteins should provide a means of inhibiting transcriptional activation. Therefore, the design and synthesis of analogs that mimic the Hox hexapeptide structure may be potentially chemotherapeutic for these types of cancers by virtue of inhibiting the Hox/Pbx1 interaction.
Materials and methods
The peptides Nα-acetyl-Thr-Phe-Asp-Trp-Met-Lys-amide, and Nα-acetyl-Leu-Phe-Pro-Trp-Met-Arg-amide were synthesized using solid-phase synthesis methodology by the Alberta Peptide Institute. The correct mass was verified by electrospray mass spectrometry, and the overall purity confirmed by reverse-phase HPLC. NMR experiments were performed on a 2-mM sample of either Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 or Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 dissolved in 100 mM KCl in 90% H2O/10% D2O at pH 6.5, containing 0.5 mM DSS as an internal NMR chemical shift reference standard.
All NMR data were recorded at 5°C with either a Varian Unity 600 NMR spectrometer, a Varian INOVA 500 NMR spectrometer, or a Varian Unity 300 NMR spectrometer operating at 1H resonance frequencies of 600 MHz, 500 MHz, and 300 MHz, respectively. 2D 1H- 1H DQF–COSY, TOCSY, and ROESY spectra were collected at 300 MHz, and DQF–COSY and ROESY spectra at 600 MHz were collected for the Ac(TFDWMK)NH2 and Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptides. In addition, a TOCSY spectrum was acquired at 500 MHz for the Ac(LFPWMR)NH2 peptide. The ROESY spectra were collected with a mixing time of 150 ms, and the TOCSY spectrum with a mixing time of 80 ms. All NMR data were processed using Vnmr and analyzed using the program nmrView (Johnson and Blevins 1994).
Three-dimensional structures were computed from experimental restraints using a simulated annealing protocol (Nilges et al. 1988) implementing the SHAKE algorithm with X-PLOR version 3.8 (Brünger 1993). The initial structure was an extended chain, and the target function contained only potential terms for covalent geometry, torsion angle restraints, experimental distance restraints, and a van der Waals repulsion term for nonbonded contacts. Force constants for the NOE-derived distance restraints were set to 50 kcal/mole A−2, and dihedral angle restraints were initialized at 5 kcal/mole−1 rad−2 during the high-temperature dynamics and increased to 200 kcal/mole rad−2 during the annealing stage. Annealing proceeded stepwise from 800 K to 298 K in decrements of 50 K. The final energy- minimization step employed the 6-12 Lennard-Jones potential.
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Paul Semchuk for peptide synthesis and to Katherine Calvo and Mark Kamps for critical reading of the manuscript.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked "advertisement" in accordance with 18 USC section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
Abbreviations
NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance
DSS, 2,2-dimethyl-2-silapentane-5-sulfonate
TOCSY, total correlation spectroscopy
DQF-COSY, double-quantum filtered correlation spectroscopy
ROESY, rotating frame Overhauser effect spectroscopy
Article and publication are at http://www.proteinscience.org/cgi/doi/10.1101/ps.50901.
References
- Akam, M., 1987. The molecular basis for metameric pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Development 101 1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, N.H., Neidigh, J.W., Harris, S.M., Lee, G.M., Liu, Z., and Tong, H. 1997. Extracting information from the temperature gradients of polypeptide NH chemical shifts. 1. The importance of conformational averaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119 8547–8561. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolino, E., Reimund, B., Wildt-Perinic, D., and Clerc, R.G. 1995. A novel homeobox protein which recognizes a TGT core and functionally interferes with a retinoid-responsive motif. J. Biol. Chem. 270 31178–31188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrow, J., Shearman, A.M., Stanton, V.P.J., Becher, R., Collins, T., Williams, A.J., Dube, I., Katz, F., Kwong, Y.L., Morris, C., et al. 1996. The t(7;11)(p15;p15) translocation in acute myeloid leukaemia fuses the genes for nucleoporin NUP98 and class I homeoprotein HOXA9. Nat. Genet. 12 159–167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger, A.T. 1993. X-PLOR, Version 3.1: A system for X-ray crystallography and NMR . Yale University Press, New Haven, USA.
- Cavanagh, J. and Akke, M. 2000. May the driving force be with you—Whatever it is. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7 11–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.K., Jaffe, L., Capovilla, M., Botas, J., and Mann, R.S. 1994. The DNA binding specificity of Ultrabithorax is modulated by cooperative interactions with extradenticle, another homeoprotein. Cell 78 603–615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson, H.J., Rance, M., Houghten, A., Lerner, R.A., and Wright, P.E. 1988. Folding of immunogenic peptide fragments of proteins in water solution I. Sequence requirements for the formation of a reverse turn. J. Mol. Biol. 201 161—200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman-Kay, J. 1999. The ′Dynamics' in the thermodynamics of binding. Nat. Struct. Biol. 6 1086–1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring, W.J., Affolter, M., and Burglin, T. 1994. Homeodomain proteins. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 63 487–526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatano, M., Roberts, C.W., Minden, M., Crist, W.M., and Korsmeyer, S.J. 1991. Deregulation of a homdobox gene, HOX11 by the t(10;14) in T cell leukemia. Science 253 79–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabet, C., Gitti, R., Summers, M.F., and Wolberger, C. 1999. NMR studies of the Pbs1 TALE homeodomain protein free in solution and bound to DNA: Proposal for a mechanism of HoxB1—Pbx1—DNA complex assembly. J. Mol. Biol. 291 521–530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, B.A. and Blevins, R.A. 1994. NMRView: A computer program for the visualization and analysis of NMR data. J. Biomol. NMR 4 603–614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps, M.P., Murre, C., Sun, X.H., and Baltimore, D. 1990. A new homeobox gene contributes the DNA binding domain of the t(1;19) translocation protein in pre-B ALL. Cell 60 547–555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoepfler, P.S. and Kamps, M.P. 1995. The pentapeptide motif of Hox proteins is required for cooperative DNA binding with Pbx1, physically contacts Pbx1, and enhances DNA binding by Pbx1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15 5811–5819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon, A. 1991. DNA binding specificity of homeodomains. Biochemistry 30 11357–11367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigne, P., Bagu, J.R., Boyko, R., Willard, L., Holmes, C.F.B., and Sykes, B.D. 2000. Structure-based thermodynamic analysis of the dissociation of protein—phosphatase—1 catalytic subunit and microcystin—LR docked complexes. Protein Sci. 9 252–264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q. and Kamps, M.P. 1996. Structural determinants within Pbx1 that mediate cooperative DNA binding with pentapeptide—containing Hox proteins: Proposal for a model of a Pbx1—Hox—DNA complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16 1632–1640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann, R.S. and Chan, S.K. 1996. Extra specificity from extradenticle: the partnership between HOX and PBX/EXD homeodomain proteins.Trends Genet. 12 258–262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis, W. and Krumlauf, R. 1992. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell 68 283–302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertuka, G., Dyson, H.J., and Wright, P.E. 1995. ′Random coil' 1H chemical shifts obtained as a function of temperature and trifluoroethanol concentration for the peptide series GGXGG. J. Biomol. NMR 5 14–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, T., Largaespada, D.A., Lee, M.P., Johnson, L.A., Ohyashiki, K., Toyama, K., Chen, S.J., Willman, C.L., Chen, I.M., Feinberg, A.P., et al. 1996. Fusion of the nucleoporin gene NUP98 to HOXA9 by the chromosome translocation t(7;11)(p15;p15) in human myeloid leukaemia. Nat. Genet. 12 154–158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardi, F., Kemmink, J.. Sattler, M., and Wade, R.C. 2000. The cisproline(i—1)—aromatic(i) interaction: Folding of the Ala—cisPro—Tyr peptide characterized by NMR and theoretical approaches. J. Biomol. NMR 17 63–77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilges, M., Clore, G.M., and Gronenborn, A.M. 1988. Determination of three-dimensional structures of proteins from interproton distance data by hybrid distance geometry—dynamical simulated annealing calculations. Febs Lett. 229 317–324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourse, J., Mellentin, J.D., Galili, N., Wilkinson, J., Stanbridge, E., Smith, S.D., and Cleary, M.L. 1990. Chromosomal translocation t(1;19) results in synthesis of a homeobox fusion mRNA that codes for a potential chimeric transcription factor. Cell 60 535–545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passner, J.M., Ryoo, H.D., Shen, L., Mann, R.S., and Aggarwal, A.K. 1999. Structure of a DNA—bound Ultrabithorax—Extradenticle homeodomain complex. Nature 397 714–719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper, D.E., Batchelor, A.H., Chang, C.P., Cleary, M.L., and Wolberger, C. 1999. Structure of a HoxB1—Pbx1 heterodimer bound to DNA: Role of the hexapeptide and a fourth homeodomain helix in complex formation. Cell 96 587–597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauvageau, G., Lansdorp, P.M., Eaves, C.J., Hogge, D.E., Dragowska, W.H., Reid, D.S., Largman, C., Lawrence, H.J., and Humphries, R.K. 1994. Differential expression of homeobox genes in functionally distinct CD34+ subpopulations of human bone marrow cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 91 12223–12227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott, M.P., Tamkun, J.W., and Hartzell, G.W.D. 1989. The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 989 25–48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein, S., Fritsch, R., Lemaire, L., and Kessel, M. 1996. Checklist: Vertebrate homeobox genes. Mech. Dev. 55 91–108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk, M.A. and Murre, C. 1994. Extradenticle raises the DNA binding specificity of homeotic selector gene products. Cell 78 617–624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmot, C.M. and Thornton, J.M. 1990. b-Turns and their distortions: a proposed new nomenclature. Prot. Eng. 3 479–493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.S. and Desplan, C. 1999. Structural basis of Hox specificity. Nat. Struct. Biol. 6 297–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishart, D.S., Bigam, C.G., Holm, A., Hodges, R.S., and Sykes, B.D. 1995. 1H, 13C and 15N random coil NMR chemical shifts of the common amino acids. I. Investigations of nearest-neighbor effects. J. Biomol. NMR 5 67–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich, K. 1986. NMR of proteins and nucleic acids. John Wiley and Sons, New York.