Abstract
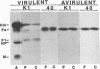
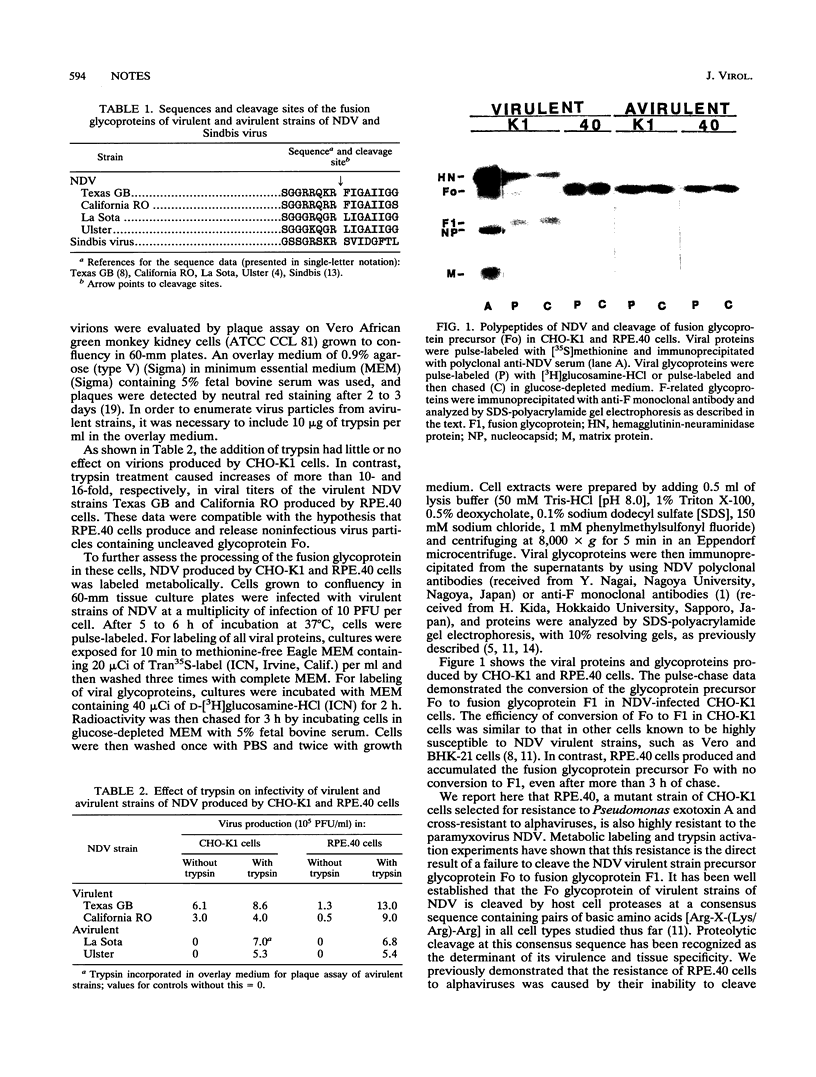
RPE.40, a mutant strain of CHO-K1 cells isolated for resistance to Pseudomonas exotoxin A and cross-resistant to alphaviruses, is also highly resistant to virulent strains of Newcastle disease virus. The resistance of RPE.40 cells to Newcastle disease virus results from the failure to cleave the viral envelope precursor glycoprotein Fo to fusion glycoprotein F1 at the consensus sequence (Lys/Arg)-Arg-Gln-(Lys/Arg)-Arg.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abenes G., Kida H., Yanagawa R. Antigenic mapping and functional analysis of the F protein of Newcastle disease virus using monoclonal antibodies. Arch Virol. 1986;90(1-2):97–110. doi: 10.1007/BF01314148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr P. J. Mammalian subtilisins: the long-sought dibasic processing endoproteases. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90129-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedgood R. M., Stallcup M. R. A novel intermediate in processing of murine leukemia virus envelope glycoproteins. Proteolytic cleavage in the late Golgi region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7060–7065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. L., Syddall R. J., Iorio R. M., Sheehan J. P., Bratt M. A. Quantitative basic residue requirements in the cleavage-activation site of the fusion glycoprotein as a determinant of virulence for Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):354–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.354-356.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh B., Ogasawara T., Toyoda T., Inocencio N. M., Hamaguchi M., Nagai Y. An endoprotease homologous to the blood clotting factor X as a determinant of viral tropism in chick embryo. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4189–4195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. Strains of CHO-K1 cells resistant to Pseudomonas exotoxin A and cross-resistant to diphtheria toxin and viruses. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):998–1009. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.998-1009.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G. Structure, function, and intracellular processing of paramyxovirus membrane proteins. Virus Res. 1988 May;10(2-3):113–135. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Hamaguchi M., Toyoda T. Molecular biology of Newcastle disease virus. Prog Vet Microbiol Immunol. 1989;5:16–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Inocencio N. M., Gotoh B. Paramyxovirus tropism dependent on host proteases activating the viral fusion glycoprotein. Behring Inst Mitt. 1991 Jul;(89):35–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D. Activation of precursors to both glycoporteins of Newcastle disease virus by proteolytic cleavage. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90412-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of the viral glycoproteins and its significance for the virulence of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):494–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Shimokata K., Yoshida T., Hamaguchi M., Iinuma M., Maeno K., Matsumoto T., Klenk H. D., Rott R. The spread of a pathogenic and an apathogenic strain of Newcastle disease virus in the chick embryo as depending on the protease sensitivity of the virus glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1979 Nov;45(2):263–272. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 26S mRNA of Sindbis virus and deduced sequence of the encoded virus structural proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2062–2066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi T., Matsuda Y., Kiyokage R., Kawahara N., Kiyotani K., Katunuma N., Nagai Y., Yoshida T. Identification of endoprotease activity in the trans Golgi membranes of rat liver cells that specifically processes in vitro the fusion glycoprotein precursor of virulent Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):504–512. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90420-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieneke-Gröber A., Vey M., Angliker H., Shaw E., Thomas G., Roberts C., Klenk H. D., Garten W. Influenza virus hemagglutinin with multibasic cleavage site is activated by furin, a subtilisin-like endoprotease. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2407–2414. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda T., Sakaguchi T., Hirota H., Gotoh B., Kuma K., Miyata T., Nagai Y. Newcastle disease virus evolution. II. Lack of gene recombination in generating virulent and avirulent strains. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda T., Sakaguchi T., Imai K., Inocencio N. M., Gotoh B., Hamaguchi M., Nagai Y. Structural comparison of the cleavage-activation site of the fusion glycoprotein between virulent and avirulent strains of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umino Y., Kohama T., Sugiura A. Plaque formation of Newcastle disease virus in primary chicken kidney cells. Behring Inst Mitt. 1991 Jul;(89):59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. G., Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. A mutant CHO-K1 strain with resistance to Pseudomonas exotoxin A and alphaviruses fails to cleave Sindbis virus glycoprotein PE2. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2332–2339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2332-2339.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]