Abstract
A Burkitt lymphoma cell line infected in vitro with a transformation-defective mutant recombinant Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) was used to attempt marker rescue of transformation competence by transfection with cloned wild-type DNA. EBV replication was induced in the transfected cells, and wild-type EBV DNA recombined via flanking homologous sequences adjacent to the deletion, resulting in a virus which transformed primary B lymphocytes in vitro. This strategy should be useful for molecular genetic analysis of the role of part or all of any gene in cell growth transformation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbot S. D., Rowe M., Cadwallader K., Ricksten A., Gordon J., Wang F., Rymo L., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 induces expression of the virus-encoded latent membrane protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2126–2134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2126-2134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 mutations define essential domains for transformation and transactivation. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2545–2554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2545-2554.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Mannick J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 is a key determinant of lymphocyte transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9558–9562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):393–397. doi: 10.1038/340393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. P., Staunton D., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded protein found in plasma membranes of transformed cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):710–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.710-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
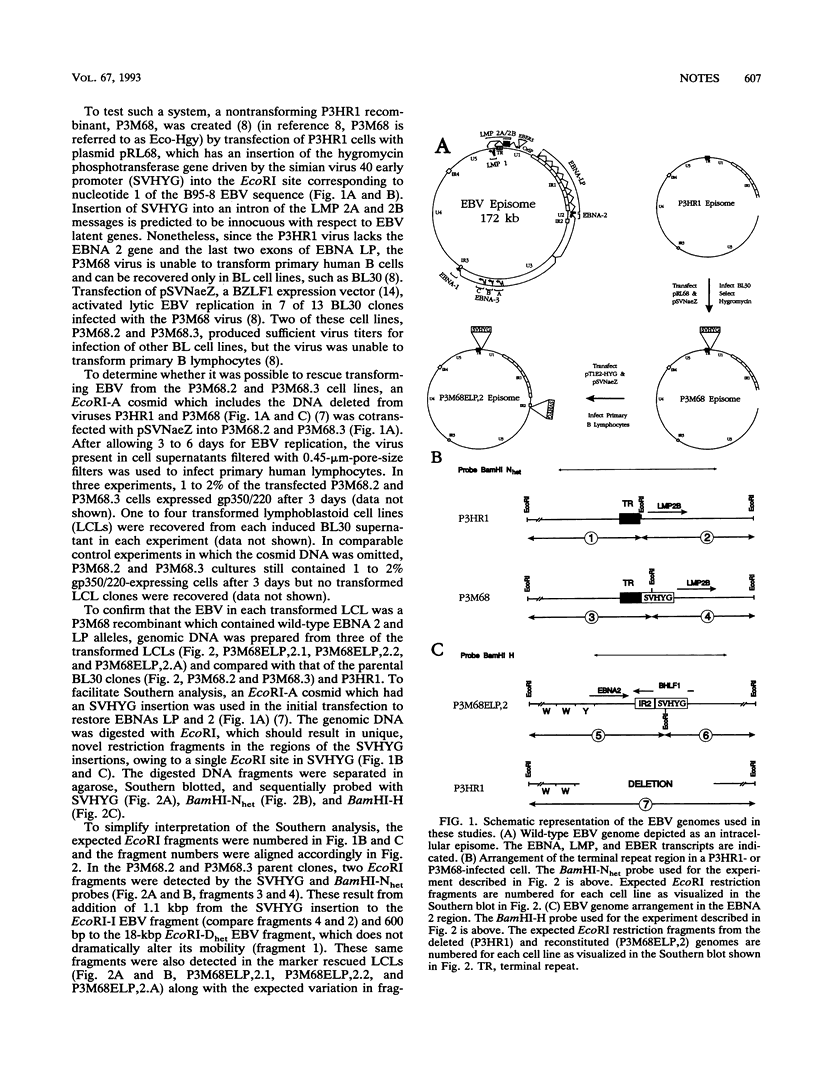
- Marchini A., Cohen J. I., Wang F., Kieff E. A selectable marker allows investigation of a nontransforming Epstein-Barr virus mutant. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3214–3219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3214-3219.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchini A., Longnecker R., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-negative B-lymphoma cell lines for clonal isolation and replication of EBV recombinants. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4972–4981. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4972-4981.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G., Clements G. Establishment and characterization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBC)-negative lymphoblastoid B cell line (BJA-B) from an exceptional, EBV-genome-negative African Burkitt's lymphoma. Biomedicine. 1975 Jul;22(4):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Heston L., Miller G. Identification of a rare Epstein-Barr virus variant that enhances early antigen expression in Raji cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Young L. S., Rowe M. Influence of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA 2 on the growth phenotype of virus-transformed B cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1310-1317.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Farley J., Strominger J. L., Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Transformation by Epstein-Barr virus requires DNA sequences in the region of BamHI fragments Y and H. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):286–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.286-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan S., Tomkinson B., Kieff E. Recombinant Epstein-Barr virus with small RNA (EBER) genes deleted transforms lymphocytes and replicates in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1546–1550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Marchini A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) recombinants: use of positive selection markers to rescue mutants in EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1701–1709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1701-1709.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Tsang S. F., Kurilla M. G., Cohen J. I., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates latent membrane protein LMP1. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3407–3416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3407-3416.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]