Abstract
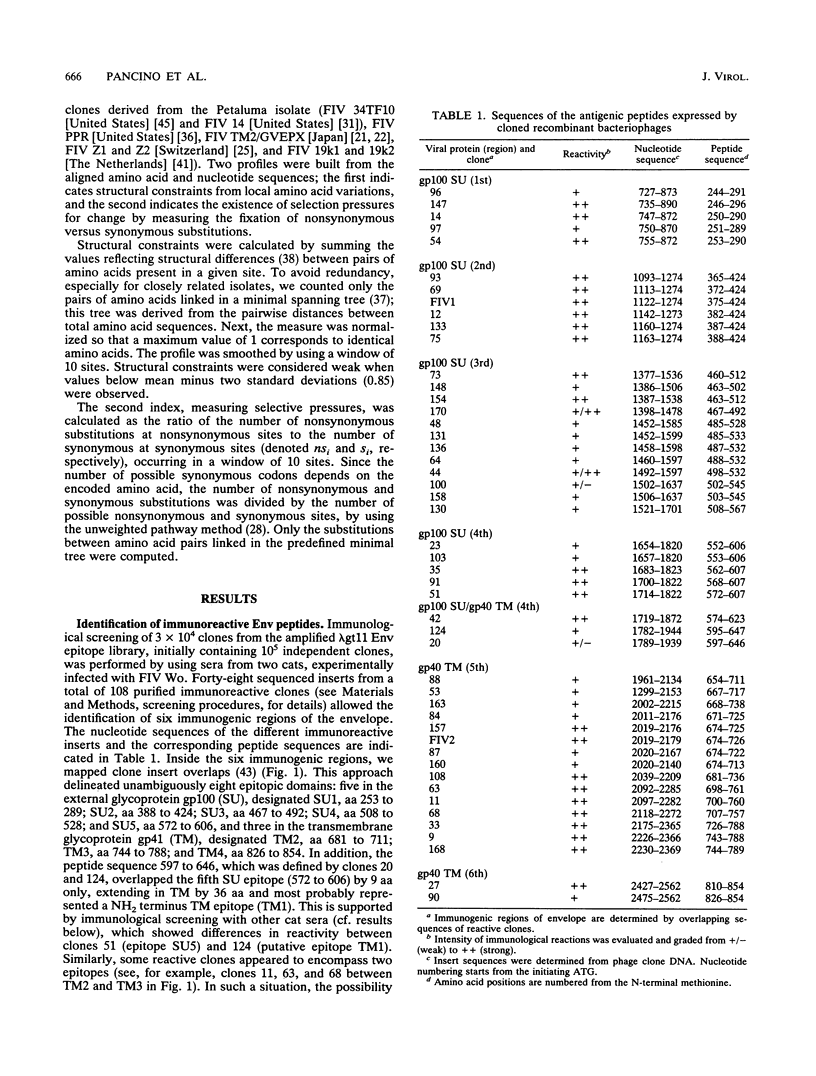
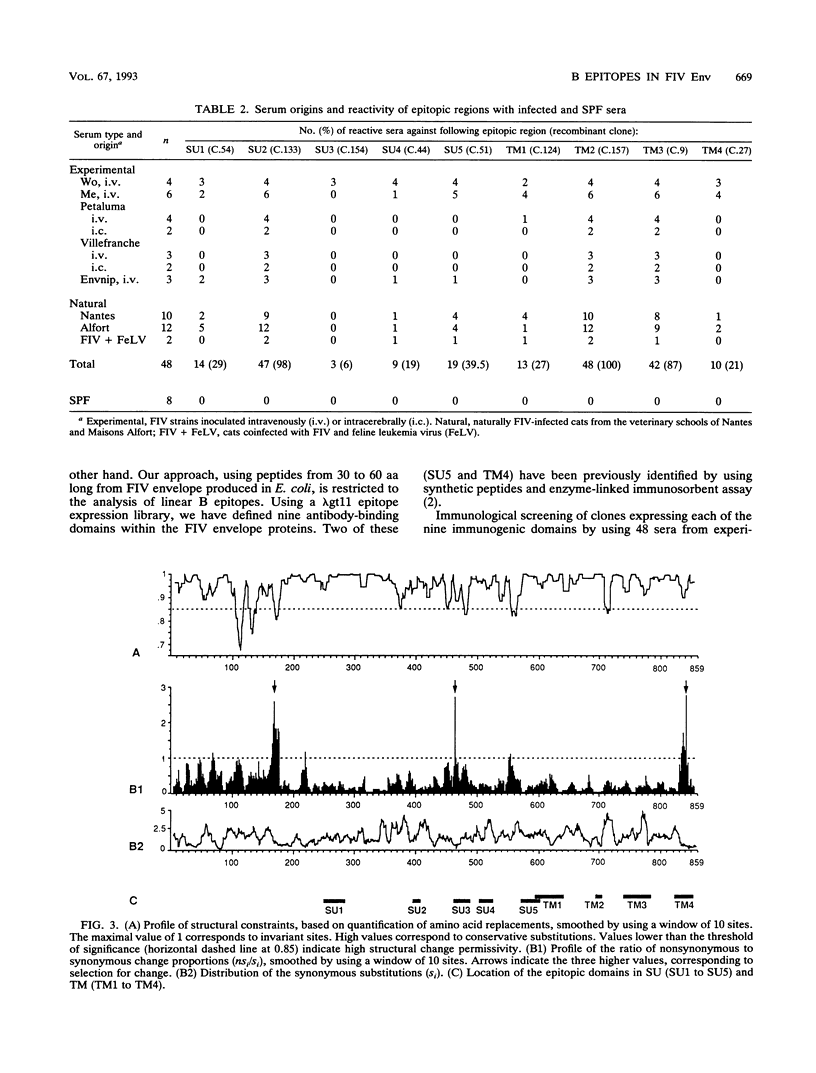
In order to map linear B epitopes in feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) envelope glycoproteins (Env), a random library of FIV Env polypeptides fused to beta-galactosidase and expressed in Escherichia coli was screened by using sera from experimentally FIV-infected cats. We mapped five antibody-binding domains in the surface envelope glycoprotein (SU1 to SU5) and four in the transmembrane envelope glycoprotein (TM1 to TM4). Immunological analysis with 48 serum samples from naturally or experimentally infected cats of diverse origins revealed a broad group reactivity for epitopes SU2, TM2, and TM3, whereas SU3 appeared as strictly type specific. To study selection pressures acting on the identified immunogenic domains, we analyzed structural constraints and distribution of synonymous and nonsynonymous mutations (amino acids unchanged or changed). Two linear B epitopes (SU3 and TM4) appeared to be submitted to positive selection for change, a pattern of evolution predicting their possible involvement in antiviral protection. These experiments provide a pertinent choice of oligopeptides for further analysis of the protective response against FIV envelope glycoproteins, as a model to understand the role of antibody escape in lentiviral persistence and to design feline AIDS vaccines.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alizon M., Wain-Hobson S., Montagnier L., Sonigo P. Genetic variability of the AIDS virus: nucleotide sequence analysis of two isolates from African patients. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90860-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas A., Guillet J. G., Chouchane L., Moraillon A., Sonigo P., Strosberg A. D. Localisation of three epitopes of the env protein of feline immunodeficiency virus. Mol Immunol. 1992 May;29(5):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90192-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baillou A., Janvier B., Mayer R., Kanki P., M'Boup S., Denis F., Goudeau A., Essex M., Barin F. Site-directed serology using synthetic oligopeptides representing the C-terminus of the external glycoproteins of HIV-1, HIV-2, or SIVmac may distinguish subtypes among primate lentiviruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Sep;7(9):767–771. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. M., Rushlow K. E., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C. Detailed mapping of the antigenicity of the surface unit glycoprotein of equine infectious anemia virus by using synthetic peptide strategies. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):732–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.732-742.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broliden P. A., von Gegerfelt A., Clapham P., Rosen J., Fenyö E. M., Wahren B., Broliden K. Identification of human neutralization-inducing regions of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):461–465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner D., Pedersen N. C. Infection of peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo with feline immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5483–5488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5483-5488.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. P., Desrosiers R. C. Selection of genetic variants of simian immunodeficiency virus in persistently infected rhesus monkeys. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1843–1854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1843-1854.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanh T. C., Dreesman G. R., Kanda P., Linette G. P., Sparrow J. T., Ho D. D., Kennedy R. C. Induction of anti-HIV neutralizing antibodies by synthetic peptides. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3065–3071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courgnaud V., Lauré F., Fultz P. N., Montagnier L., Bréchot C., Sonigo P. Genetic differences accounting for evolution and pathogenicity of simian immunodeficiency virus from a sooty mangabey monkey after cross-species transmission to a pig-tailed macaque. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):414–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.414-419.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dow S. W., Poss M. L., Hoover E. A. Feline immunodeficiency virus: a neurotropic lentivirus. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(7):658–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellerbrok H., D'Auriol L., Vaquero C., Sitbon M. Functional tolerance of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope signal peptide to mutations in the amino-terminal and hydrophobic regions. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5114–5118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5114-5118.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R., Ball J. M., Garry R. F., Griffin M. C., Montelaro R. C. A general model for the transmembrane proteins of HIV and other retroviruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):431–440. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Fine mapping of an immunodominant domain in the transmembrane glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2639–2641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2639-2641.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Debouck C., Meloen R. H., Smit L., Bakker M., Asher D. M., Wolff A. V., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization epitope with conserved architecture elicits early type-specific antibodies in experimentally infected chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4478–4482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J. Immunodominant B-cell epitopes of the HIV-1 envelope recognized by infected and immunized hosts. AIDS. 1988;2 (Suppl 1):S41–S45. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198800001-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. A., Michel H., Sakaguchi K., Shabanowitz J., Appella E., Hunt D. F., Engelhard V. H. HLA-A2.1-associated peptides from a mutant cell line: a second pathway of antigen presentation. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1264–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.1546329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horal P., Svennerholm B., Jeansson S., Rymo L., Hall W. W., Vahlne A. Continuous epitopes of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) transmembrane glycoprotein and reactivity of human sera to synthetic peptides representing various HIV-1 isolates. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2718–2723. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2718-2723.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Langlois A. J., McDanal C., Ross K. L., Eckler L. I., Jellis C. L., Profy A. T., Rusche J. R., Bolognesi D. P., Putney S. D. Principal neutralizing domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6768–6772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyomasu T., Miyazawa T., Furuya T., Shibata R., Sakai H., Sakuragi J., Fukasawa M., Maki N., Hasegawa A., Mikami T. Identification of feline immunodeficiency virus rev gene activity. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4539–4542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4539-4542.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa T., Fukasawa M., Hasegawa A., Maki N., Ikuta K., Takahashi E., Hayami M., Mikami T. Molecular cloning of a novel isolate of feline immunodeficiency virus biologically and genetically different from the original U.S. isolate. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1572–1577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1572-1577.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrow S., Höflacher B., Mellert W., Erfle V., Wahren B., Wolf H. Use of synthetic oligopeptides in identification and characterization of immunological functions in the amino acid sequence of the envelope protein of HIV-1. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(1):21–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moraillon A., Barré-Sinoussi F., Parodi A., Moraillon R., Dauguet C. In vitro properties and experimental pathogenic effect of three strains of feline immunodeficiency viruses (FIV) isolated from cats with terminal disease. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Apr;31(1):41–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90140-O. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa S., Lutz H., Aubert A., Bishop D. H. Identification of conserved and variable regions in the envelope glycoprotein sequences of two feline immunodeficiency viruses isolated in Zurich, Switzerland. Virus Res. 1991 Sep;21(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(91)90071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers G., MacInnes K., Korber B. The emergence of simian/human immunodeficiency viruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Mar;8(3):373–386. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Gojobori T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Sep;3(5):418–426. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Lee E. S. B cell epitope mapping of human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoproteins with long (19- to 36-residue) synthetic peptides. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):85–95. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak M. A., Anderson R. M., McLean A. R., Wolfs T. F., Goudsmit J., May R. M. Antigenic diversity thresholds and the development of AIDS. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):963–969. doi: 10.1126/science.1683006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted R. A., Hirsch V. M., Purcell R. H., Johnson P. R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of feline immunodeficiency virus: genome organization and relationship to other lentiviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8088–8092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Matthews T. J., Clark M. E., Cianciolo G. J., Randall R. R., Langlois A. J., White G. C., Safai B., Snyderman R., Bolognesi D. P. A conserved region at the COOH terminus of human immunodeficiency virus gp120 envelope protein contains an immunodominant epitope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2479–2483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C., Ho E. W., Brown M. L., Yamamoto J. K. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic virus from domestic cats with an immunodeficiency-like syndrome. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):790–793. doi: 10.1126/science.3643650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C., Torten M., Rideout B., Sparger E., Tonachini T., Luciw P. A., Ackley C., Levy N., Yamamoto J. Feline leukemia virus infection as a potentiating cofactor for the primary and secondary stages of experimentally induced feline immunodeficiency virus infection. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):598–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.598-606.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips T. R., Talbott R. L., Lamont C., Muir S., Lovelace K., Elder J. H. Comparison of two host cell range variants of feline immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4605–4613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4605-4613.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risler J. L., Delorme M. O., Delacroix H., Henaut A. Amino acid substitutions in structurally related proteins. A pattern recognition approach. Determination of a new and efficient scoring matrix. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Javaherian K., McDanal C., Petro J., Lynn D. L., Grimaila R., Langlois A., Gallo R. C., Arthur L. O., Fischinger P. J. Antibodies that inhibit fusion of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells bind a 24-amino acid sequence of the viral envelope, gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebelink K. H., Chu I. H., Rimmelzwaan G. F., Weijer K., Osterhaus A. D., Bosch M. L. Isolation and partial characterization of infectious molecular clones of feline immunodeficiency virus obtained directly from bone marrow DNA of a naturally infected cat. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1091-1097.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Balfe P., Ludlam C. A., Bishop J. O., Brown A. J. Analysis of sequence diversity in hypervariable regions of the external glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5840–5850. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5840-5850.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Herz J. Topological mapping of complement component C9 by recombinant DNA techniques suggests a novel mechanism for its insertion into target membranes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1951–1957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syu W. J., Lee W. R., Du B., Yu Q. C., Essex M., Lee T. H. Role of conserved gp41 cysteine residues in the processing of human immunodeficiency virus envelope precursor and viral infectivity. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6349–6352. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6349-6352.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbott R. L., Sparger E. E., Lovelace K. M., Fitch W. M., Pedersen N. C., Luciw P. A., Elder J. H. Nucleotide sequence and genomic organization of feline immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5743–5747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. J., Steel S., Wisniewolski R., Wang C. Y. Detection of antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type III by using a synthetic peptide of 21 amino acid residues corresponding to a highly antigenic segment of gp41 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6159–6163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei M. L., Cresswell P. HLA-A2 molecules in an antigen-processing mutant cell contain signal sequence-derived peptides. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):443–446. doi: 10.1038/356443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto J. K., Sparger E., Ho E. W., Andersen P. R., O'Connor T. P., Mandell C. P., Lowenstine L., Munn R., Pedersen N. C. Pathogenesis of experimentally induced feline immunodeficiency virus infection in cats. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Aug;49(8):1246–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



