Abstract
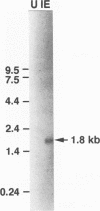
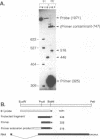
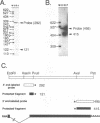
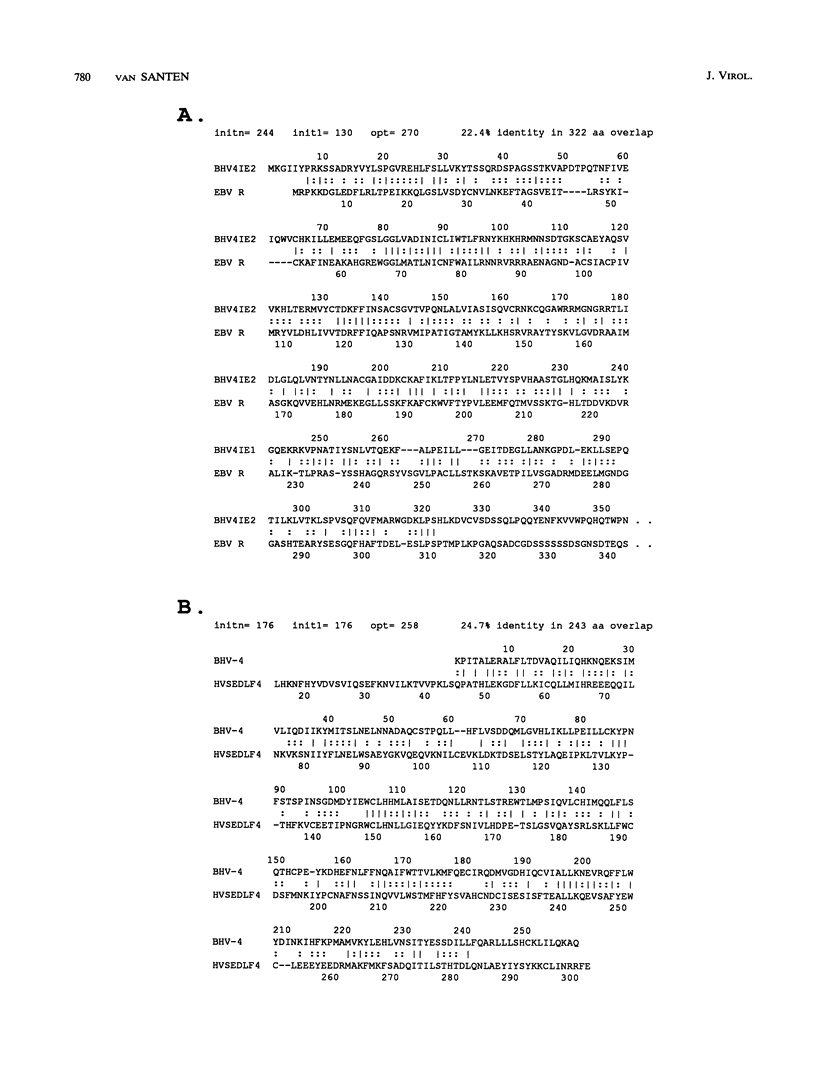
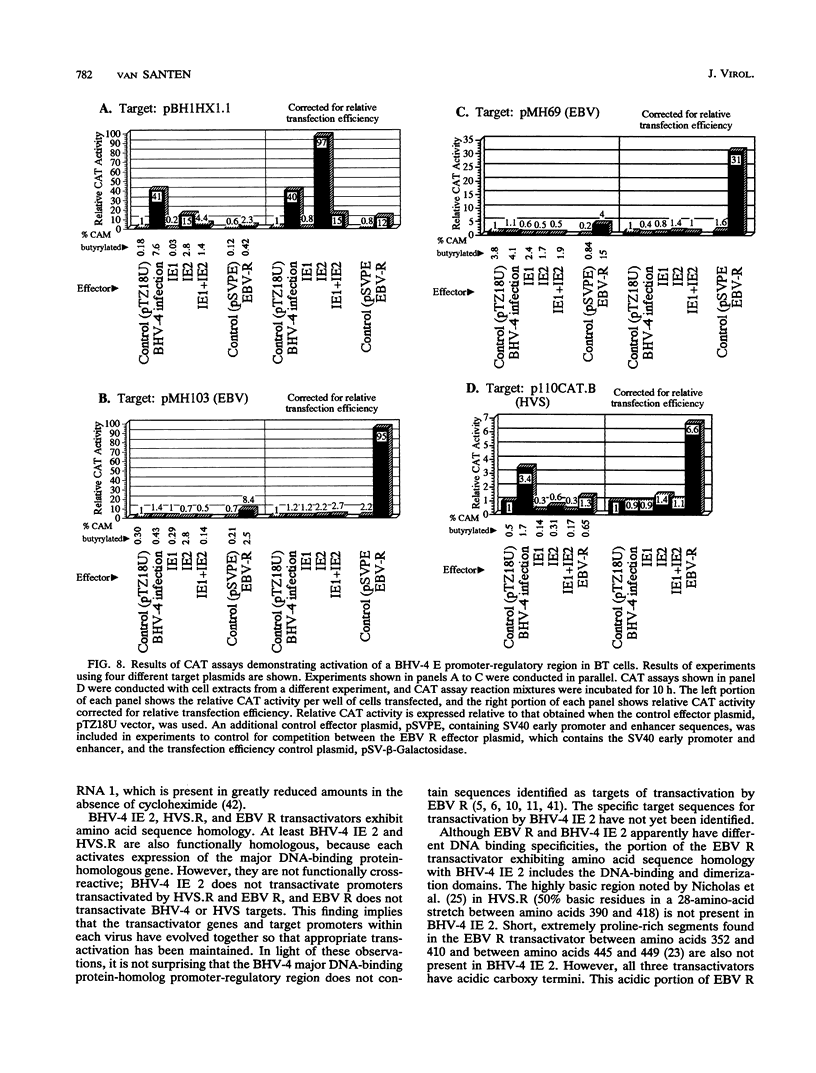
Immediate-early (IE) RNA 2, the less abundant of two bovine herpesvirus 4 (BHV-4) RNAs detected in Madin-Darby bovine kidney cells infected in the presence of cycloheximide, is a 1.8-kb cytoplasmic polyadenylated RNA transcribed from the 8.3-kb HindIII fragment F. The structure of IE RNA 2 has been determined by S1 nuclease and exonuclease VII mapping, primer extension analysis, and sequencing of a partial cDNA. IE RNA 2 consists of a short, approximately 60-nucleotide 5' exon spliced to a 1.8-kb 3' exon. DNA sequence analysis revealed an open reading frame encoding 551 amino acids with sequence homology to the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) R transactivator and its homolog in herpesvirus saimiri, HVS.R.IE 2 and HVS.R show higher homology to each other than to the EBV R transactivator. The homology is highest in the approximately 320 amino-terminal amino acids. All three proteins have acidic carboxyl termini but have little amino acid sequence homology in this region. In transient expression cotransfection assays, IE 2 activated expression from the BHV-4 early promoter-regulatory region of the major DNA-binding protein homolog over 100-fold in bovine turbinate cells. IE 1 was not necessary for this transactivation and did not augment it. However, IE 2 did not transactivate EBV or herpesvirus saimiri early promoter-regulatory regions that are transactivated by the EBV R transactivator or HVS.R.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggin M., Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in P3HR1-superinfected Raji cells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3120–3132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3120-3132.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bublot M., Lomonte P., Lequarre A. S., Albrecht J. C., Nicholas J., Fleckenstein B., Pastoret P. P., Thiry E. Genetic relationships between bovine herpesvirus 4 and the gammaherpesviruses Epstein-Barr virus and herpesvirus saimiri. Virology. 1992 Oct;190(2):654–665. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90903-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. Y., Van Santen V. L. Immediate-early, early, and late RNAs in bovine herpesvirus-4-infected cells. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90266-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Gruffat H., Manet E., Calender A., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DR enhancer contains two functionally different domains: domain A is constitutive and cell specific, domain B is transactivated by the EBV early protein R. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):615–623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.615-623.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. A., Leahy J., Hardwick J. M. An enhancer within the divergent promoter of Epstein-Barr virus responds synergistically to the R and Z transactivators. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.313-321.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. The products of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) immediate early genes 1, 2 and 3 can activate HSV-1 gene expression in trans. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2507–2513. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruffat H., Duran N., Buisson M., Wild F., Buckland R., Sergeant A. Characterization of an R-binding site mediating the R-induced activation of the Epstein-Barr virus BMLF1 promoter. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.46-52.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruffat H., Manet E., Rigolet A., Sergeant A. The enhancer factor R of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6835–6843. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Lieberman P. M., Hayward S. D. A new Epstein-Barr virus transactivator, R, induces expression of a cytoplasmic early antigen. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2274–2284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2274-2284.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Tse L., Applegren N., Nicholas J., Veliuona M. A. The Epstein-Barr virus R transactivator (Rta) contains a complex, potent activation domain with properties different from those of VP16. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5500–5508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5500-5508.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Shipman C., Jr, Wagner E. K. Viral DNA synthesis is required for the efficient expression of specific herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA species. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):10–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Dhar R., Khoury G. Mapping the spliced and unspliced late lytic SV40 RNAs. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):971–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manet E., Gruffat H., Trescol-Biemont M. C., Moreno N., Chambard P., Giot J. F., Sergeant A. Epstein-Barr virus bicistronic mRNAs generated by facultative splicing code for two transcriptional trans-activators. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1819–1826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manet E., Rigolet A., Gruffat H., Giot J. F., Sergeant A. Domains of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transcription factor R required for dimerization, DNA binding and activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2661–2667. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J., Cameron K. R., Coleman H., Newman C., Honess R. W. Analysis of nucleotide sequence of the rightmost 43 kbp of herpesvirus saimiri (HVS) L-DNA: general conservation of genetic organization between HVS and Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):296–310. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90759-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J., Coles L. S., Newman C., Honess R. W. Regulation of the herpesvirus saimiri (HVS) delayed-early 110-kilodalton promoter by HVS immediate-early gene products and a homolog of the Epstein-Barr virus R trans activator. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2457–2466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2457-2466.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J., Gompels U. A., Craxton M. A., Honess R. W. Conservation of sequence and function between the product of the 52-kilodalton immediate-early gene of herpesvirus saimiri and the BMLF1-encoded transcriptional effector (EB2) of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3250–3257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3250-3257.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J., Smith E. P., Coles L., Honess R. Gene expression in cells infected with gammaherpesvirus saimiri: properties of transcripts from two immediate-early genes. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):189–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham G., Economou A., Rooney C. M., Rowe D. T., Farrell P. J. Structure and function of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2110–2116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2110-2116.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., O'Hare P., Sha L., LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. trans-activation and autoregulation of gene expression by the immediate-early region 2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1167–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1167-1179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. How RNA polymerase II terminates transcription in higher eukaryotes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekulovich R. E., Leary K., Sandri-Goldin R. M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 can act as a trans-repressor or a trans-activator in combination with ICP4 and ICP0. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4510–4522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4510-4522.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Spector D. J., Leisure K. M., Stinski M. F. Participation of two human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene regions in transcriptional activation of adenovirus promoters. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truman D., Ludwig H., Storz J. Bovines Herpesvirus Typ 4 (BHV-4): Untersuchungen zur Biologie und Verbreitung in Rinderbeständen und bei Besamungsbullen. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1986 Sep;33(7):485–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V. L., Chang L. Y. Cloning and mapping of EcoRI, HindIII, and PstI fragments of bovine herpesvirus 4 (DN-599) genome. Intervirology. 1992;34(1):44–52. doi: 10.1159/000150262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V. L. Characterization of the bovine herpesvirus 4 major immediate-early transcript. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5211–5224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5211-5224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]