Abstract
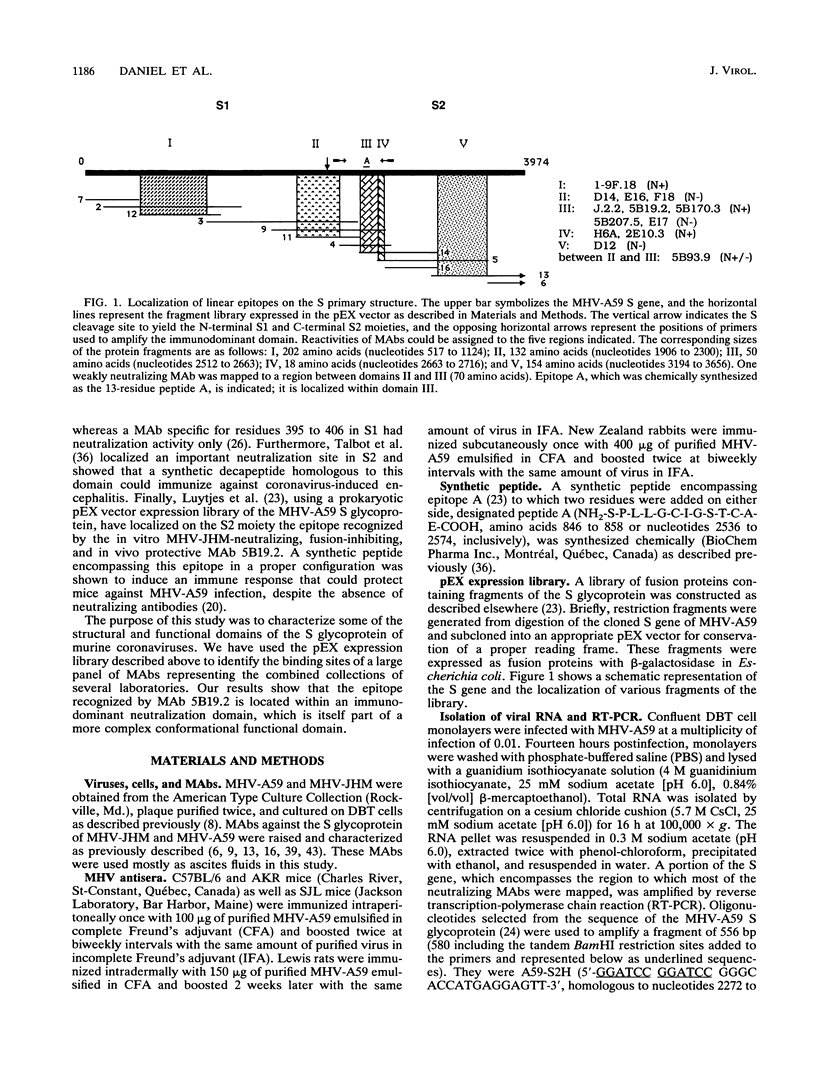
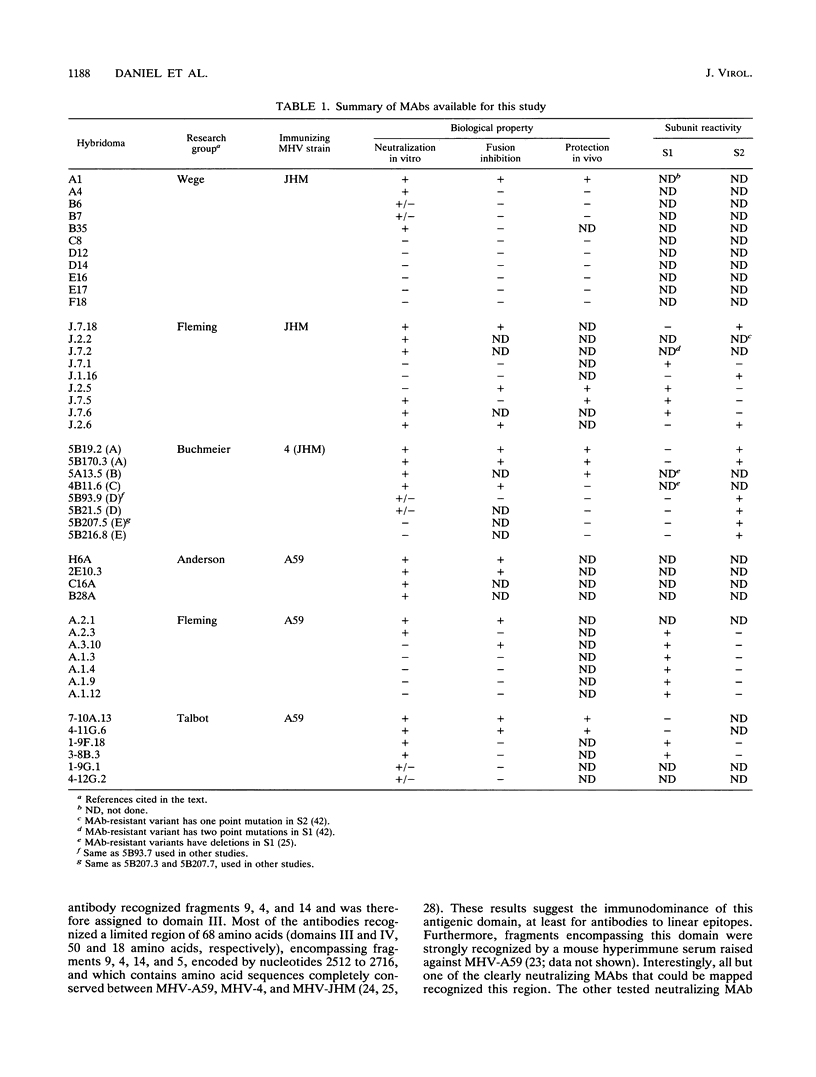
Numerous studies have demonstrated that the spike glycoprotein of coronaviruses bears major determinants of pathogenesis. To elucidate the antigenic structure of the protein, a panel of monoclonal antibodies was studied by competitive ELISA, and their reactivities were assayed against fragments of the murine coronavirus murine hepatitis virus strain A59 S gene expressed in prokaryotic vectors. An immunodominant linear domain was localized within the predicted stalk, S2, of the peplomer. It is recognized by several neutralizing antibodies. Other domains were also identified near the proteolytic cleavage site, in the predicted globular head, S1, and in another part of the stalk. Furthermore, competition results suggest that the immunodominant functional domain forms part of a complex three-dimensional structure. Surprisingly, some antibodies which have no antiviral biological activities were shown to bind the immunodominant neutralization domain.
Full text
PDF


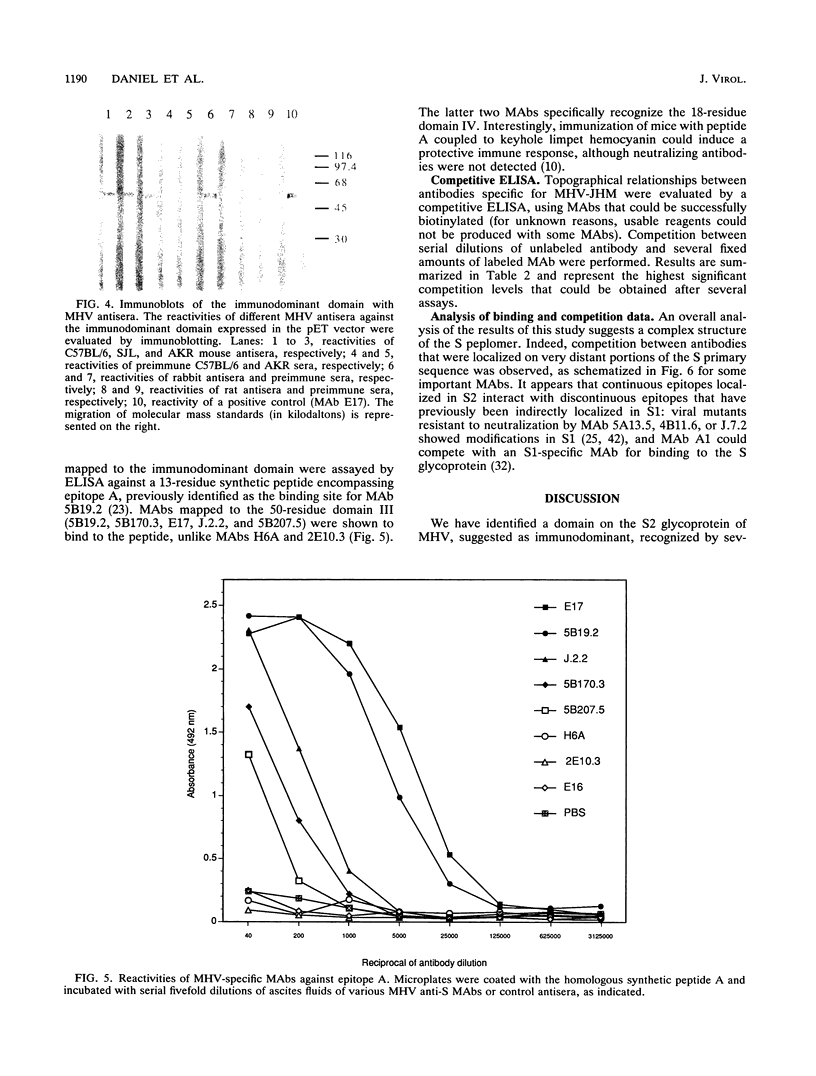
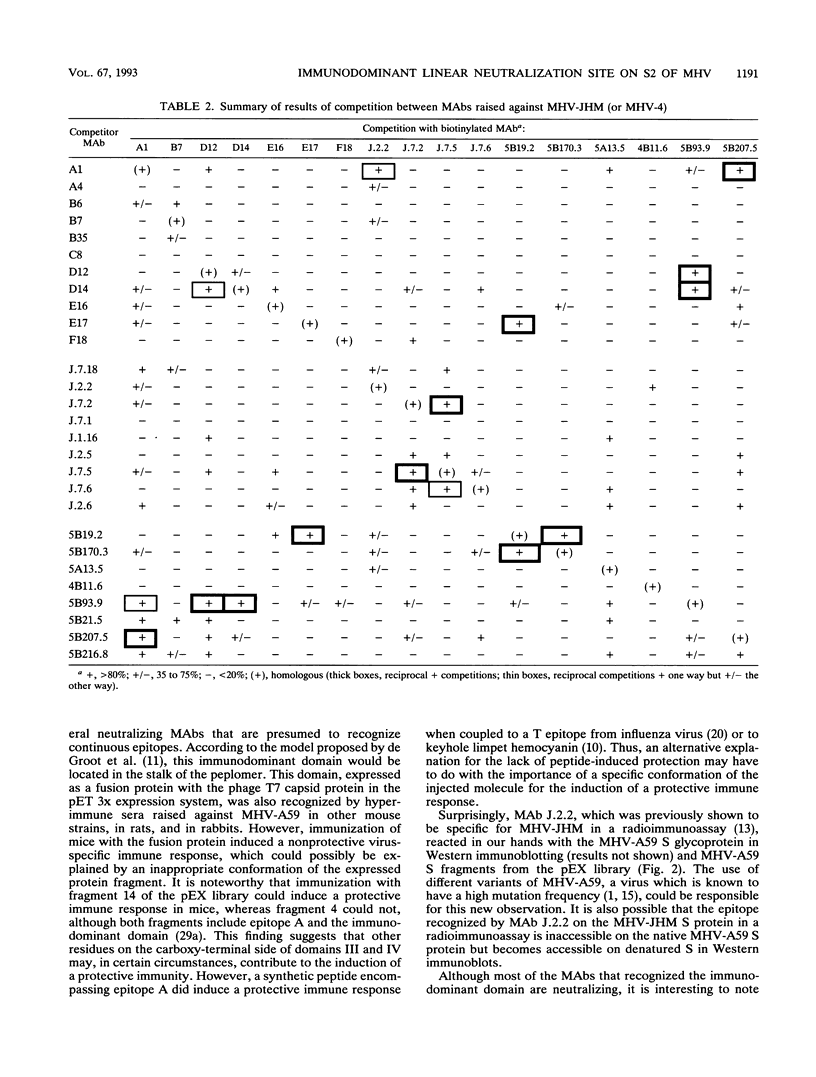
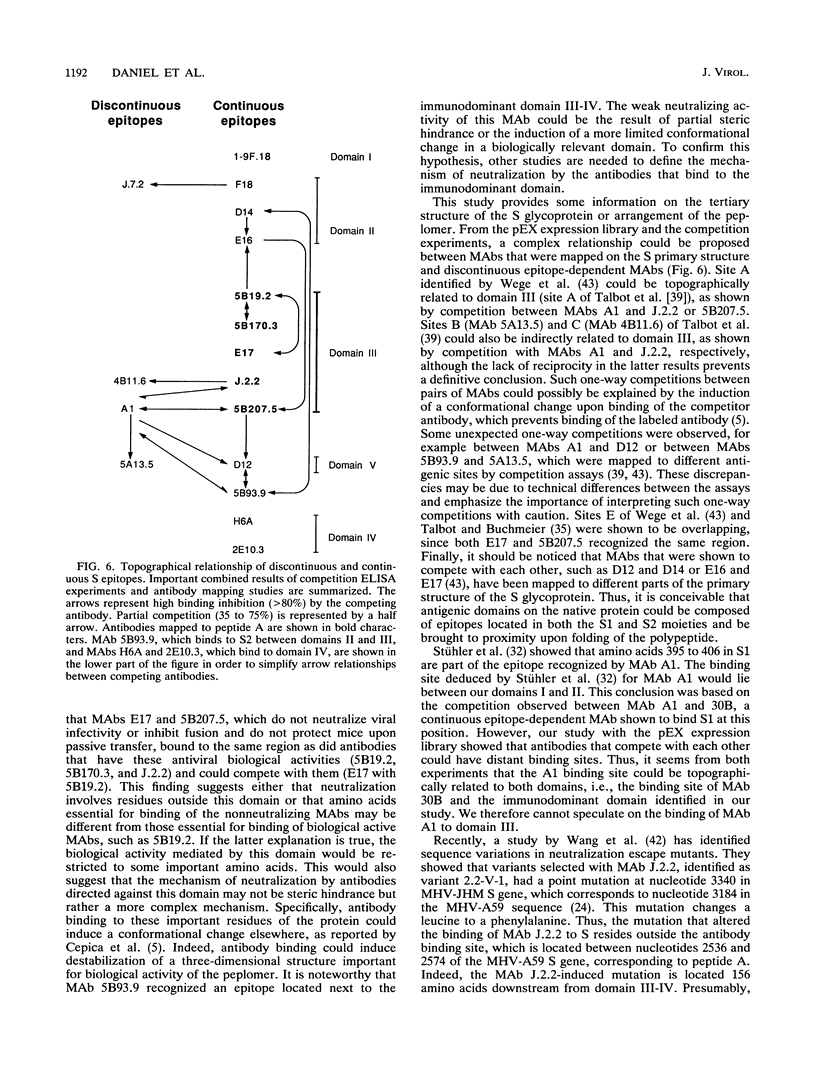


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banner L. R., Lai M. M. Random nature of coronavirus RNA recombination in the absence of selection pressure. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):441–445. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90795-D. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Lewicki H. A., Talbot P. J., Knobler R. L. Murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM)-induced neurologic disease is modulated in vivo by monoclonal antibody. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90033-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D., Brian D. A., Enjuanes L., Holmes K. V., Lai M. M., Laude H., Siddell S. G., Spaan W., Taguchi F., Talbot P. J. Recommendations of the Coronavirus Study Group for the nomenclature of the structural proteins, mRNAs, and genes of coronaviruses. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):306–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90259-T. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D. Coronavirus IBV: structural characterization of the spike protein. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2577–2583. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepica A., Yason C., Ralling G. The use of ELISA for detection of the antibody-induced conformational change in a viral protein and its intermolecular spread. J Virol Methods. 1990 Apr;28(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90082-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. R., Knobler R. L., Powell H., Buchmeier M. J. Monoclonal antibodies to murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM) define the viral glycoprotein responsible for attachment and cell--cell fusion. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):358–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90095-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel R. G., Lampert P. W., Talbot P. J., Buchmeier M. J. Site-specific alteration of murine hepatitis virus type 4 peplomer glycoprotein E2 results in reduced neurovirulence. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.463-471.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel C., Talbot P. J. Physico-chemical properties of murine hepatitis virus, strain A 59. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1987;96(3-4):241–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01320963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel C., Talbot P. J. Protection from lethal coronavirus infection by affinity-purified spike glycoprotein of murine hepatitis virus, strain A59. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90057-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmas B., Laude H. Assembly of coronavirus spike protein into trimers and its role in epitope expression. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5367–5375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5367-5375.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Stohlman S. A., Harmon R. C., Lai M. M., Frelinger J. A., Weiner L. P. Antigenic relationships of murine coronaviruses: analysis using monoclonal antibodies to JHM (MHV-4) virus. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):296–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90498-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Trousdale M. D., el-Zaatari F. A., Stohlman S. A., Weiner L. P. Pathogenicity of antigenic variants of murine coronavirus JHM selected with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):869–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.869-875.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. M., Parker S. E., Buchmeier M. J. Neutralization-resistant variants of a neurotropic coronavirus are generated by deletions within the amino-terminal half of the spike glycoprotein. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):731–741. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.731-741.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore W., Fleming J. O., Stohlman S. A., Weiner L. P. Characterization of the structural proteins of the murine coronavirus strain A59 using monoclonal antibodies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1987 Jun;185(2):177–186. doi: 10.3181/00379727-185-42532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koolen M. J., Borst M. A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Immunogenic peptide comprising a mouse hepatitis virus A59 B-cell epitope and an influenza virus T-cell epitope protects against lethal infection. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6270–6273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6270-6273.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamarre A., Lecomte J., Talbot P. J. Antiidiotypic vaccination against murine coronavirus infection. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4256–4262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Geerts D., Posthumus W., Meloen R., Spaan W. Amino acid sequence of a conserved neutralizing epitope of murine coronaviruses. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1408–1412. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1408-1412.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Sturman L. S., Bredenbeek P. J., Charite J., van der Zeijst B. A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Primary structure of the glycoprotein E2 of coronavirus MHV-A59 and identification of the trypsin cleavage site. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90142-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. E., Gallagher T. M., Buchmeier M. J. Sequence analysis reveals extensive polymorphism and evidence of deletions within the E2 glycoprotein gene of several strains of murine hepatitis virus. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):664–673. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge E., Stauber R., Pfleiderer M., Siddell S. G. Analysis of murine coronavirus surface glycoprotein functions by using monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):254–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.254-262.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt I., Skinner M., Siddell S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the surface projection glycoprotein of coronavirus MHV-JHM. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):47–56. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Ricard C. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein of murine coronavirus: activation of cell-fusing activity of virions by trypsin and separation of two different 90K cleavage fragments. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.904-911.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühler A., Wege H., Siddell S. G. Localization of antigenic sites on the surface glycoprotein of mouse hepatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jul;72(Pt 7):1655–1658. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-7-1655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takase-Yoden S., Kikuchi T., Siddell S. G., Taguchi F. Localization of major neutralizing epitopes on the S1 polypeptide of the murine coronavirus peplomer glycoprotein. Virus Res. 1991 Mar;18(2-3):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(91)90011-J. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Buchmeier M. J. Antigenic variation among murine coronaviruses: evidence for polymorphism on the peplomer glycoprotein, E2. Virus Res. 1985 Jun;2(4):317–328. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90028-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Dionne G., Lacroix M. Vaccination against lethal coronavirus-induced encephalitis with a synthetic decapeptide homologous to a domain in the predicted peplomer stalk. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3032–3036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3032-3036.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Knobler R. L., Buchmeier M. J. Western and dot immunoblotting analysis of viral antigens and antibodies: application to murine hepatitis virus. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Oct 12;73(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90043-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Salmi A. A., Knobler R. L., Buchmeier M. J. Topographical mapping of epitopes on the glycoproteins of murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM): correlation with biological activities. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90032-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennema H., Heijnen L., Zijderveld A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Intracellular transport of recombinant coronavirus spike proteins: implications for virus assembly. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):339–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.339-346.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F. I., Fleming J. O., Lai M. M. Sequence analysis of the spike protein gene of murine coronavirus variants: study of genetic sites affecting neuropathogenicity. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):742–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90041-M. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Dörries R., Wege H. Hybridoma antibodies to the murine coronavirus JHM: characterization of epitopes on the peplomer protein (E2). J Gen Virol. 1984 Nov;65(Pt 11):1931–1942. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-11-1931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Siddell S., ter Meulen V. The biology and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:165–200. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Winter J., Meyermann R. The peplomer protein E2 of coronavirus JHM as a determinant of neurovirulence: definition of critical epitopes by variant analysis. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):87–98. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weismiller D. G., Sturman L. S., Buchmeier M. J., Fleming J. O., Holmes K. V. Monoclonal antibodies to the peplomer glycoprotein of coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus identify two subunits and detect a conformational change in the subunit released under mild alkaline conditions. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3051–3055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3051-3055.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. K., Jiang G. S., Holmes K. V. Receptor for mouse hepatitis virus is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen family of glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5533–5536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., Luytjes W., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A., Spaan W. J., Lenstra J. A. Evidence for a coiled-coil structure in the spike proteins of coronaviruses. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):963–966. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90422-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]