Abstract
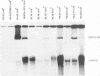
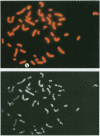
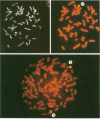
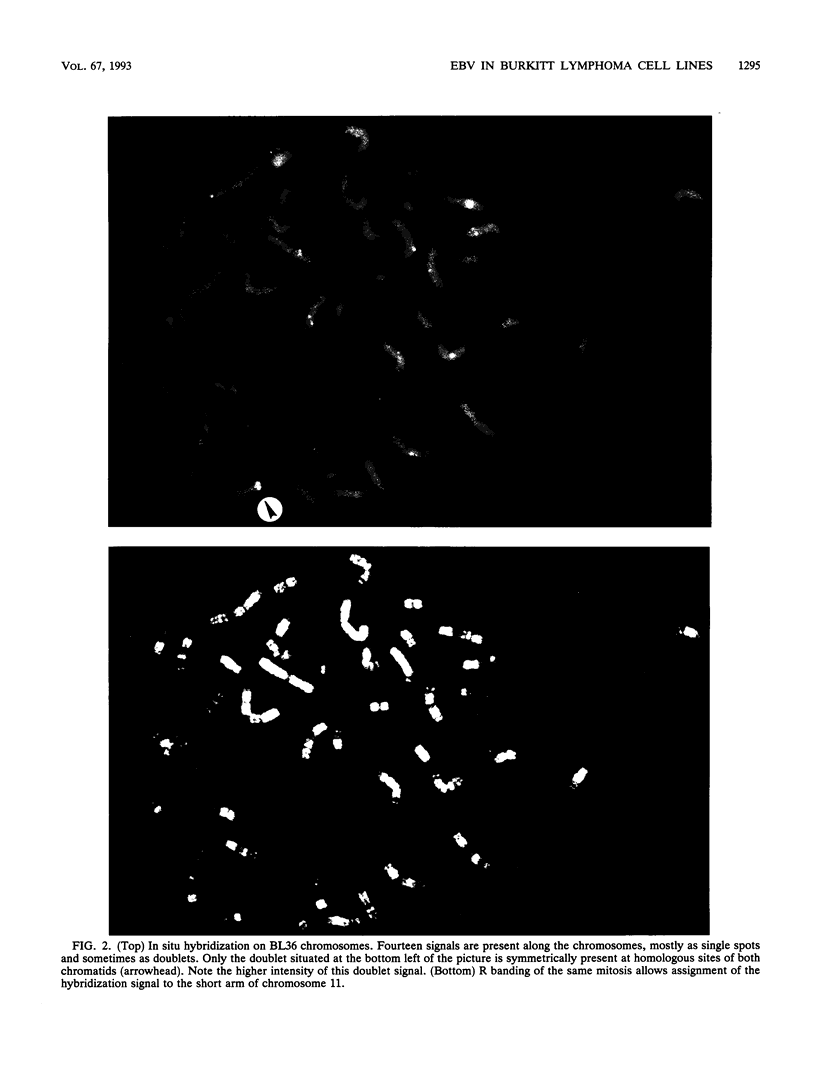
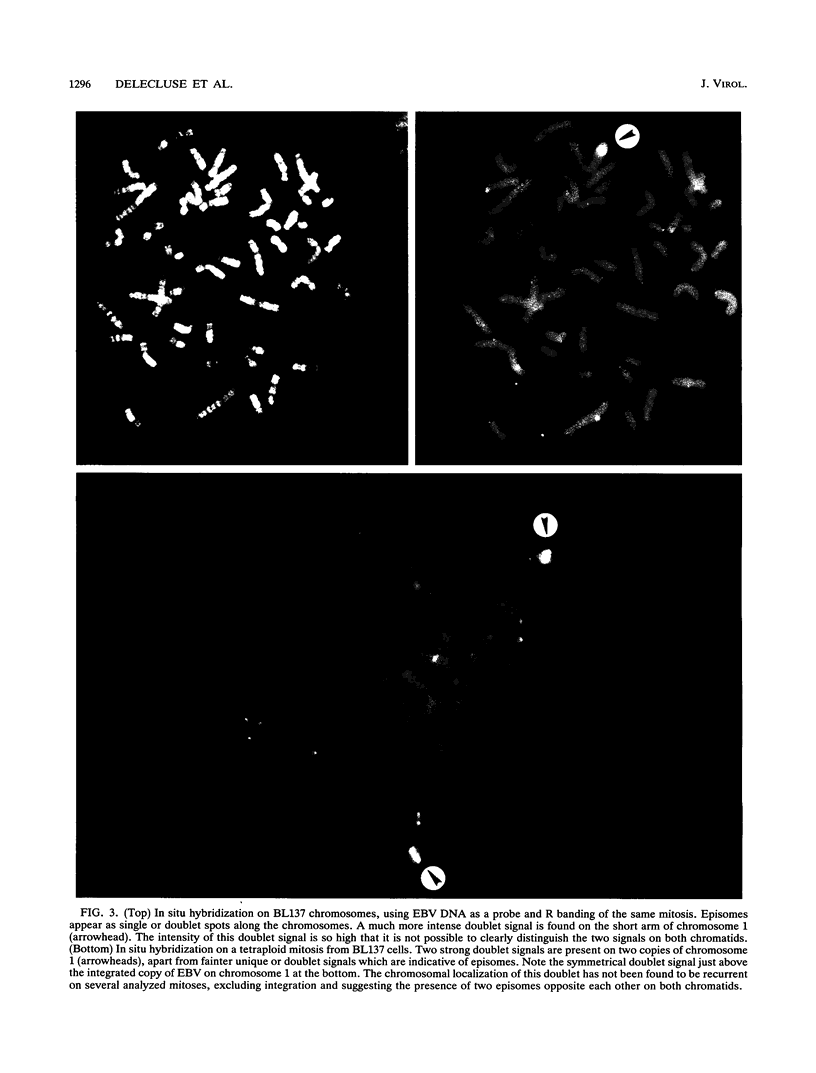
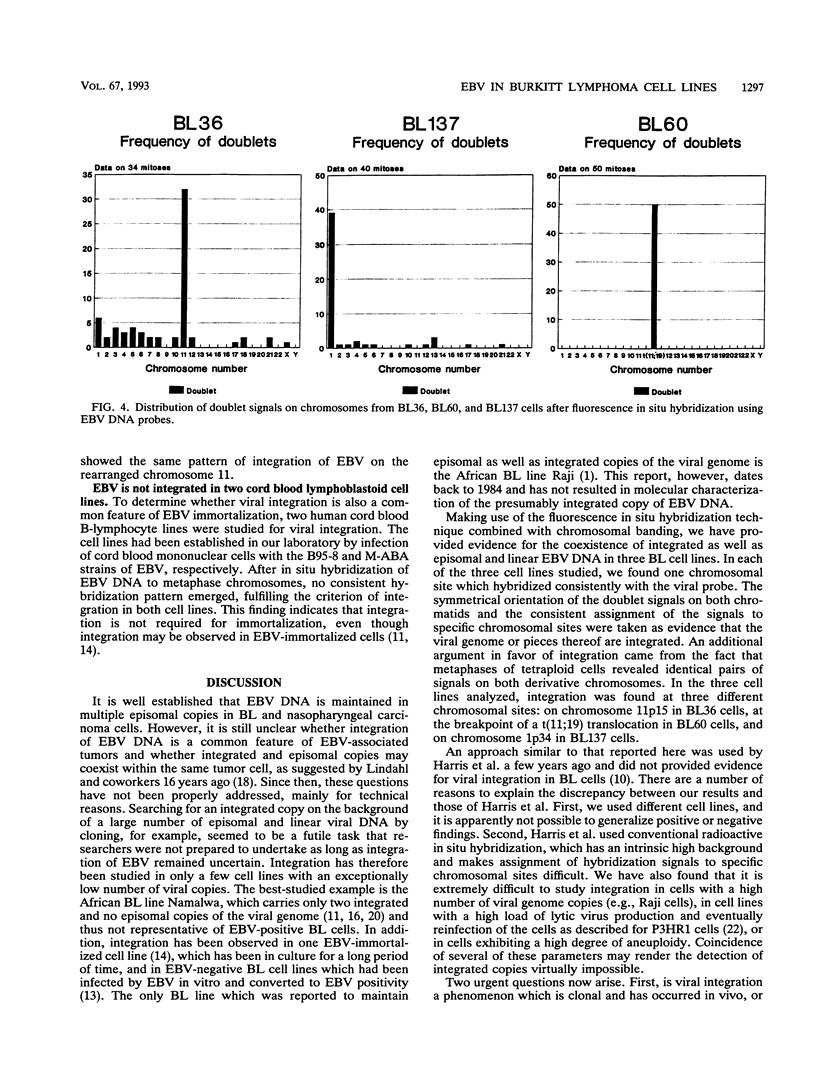
The Epstein-Barr virus genome is present in more than 95% of the African cases of Burkitt lymphoma. In this tumor, the viral genome is usually maintained in multiple episomal copies. Viral integration has been described only for Namalwa, a cell line lacking episomes. In this study, we have addressed the question of whether integrated and episomal copies can coexist in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Gel electrophoresis was used to demonstrate the presence of episomal as well as free linear DNA in three Burkitt lymphoma cell lines. The numbers of episomal copies per cell were estimated to be 5 to 10 in BL36 and BL137 cells and below 1 in BL60 cells, indicating that BL60 does not represent a homogeneous cell population. Fluorescence in situ hybridization was combined with chromosomal banding to study the association of the viral DNA with metaphase chromosomes. A symmetrical pattern of signals at both chromatids located at the same chromosomal sites in many if not all metaphases was taken as evidence for viral integration. In each of the three cell lines, one site of integration was identified: at chromosome 11p15 in BL36 cells, at chromosome 1p34 in BL137 cells, and at the site of a reciprocal t(11;19) translocation in BL60 cells. Integrated, episomal and linear copies of Epstein-Barr virus DNA thus coexist in Burkitt lymphoma cells. The biological significance of viral integration in Burkitt lymphoma cells remains to be elucidated.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anvret M., Karlsson A., Bjursell G. Evidence for integrated EBV genomes in Raji cellular DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1149–1161. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Bassat H., Goldblum N., Mitrani S., Goldblum T., Yoffey J. M., Cohen M. M., Bentwich Z., Ramot B., Klein E., Klein G. Establishment in continuous culture of a new type of lymphocyte from a "Burkitt like" malignant lymphoma (line D.G.-75). Int J Cancer. 1977 Jan;19(1):27–33. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delecluse H. J., Hammerschmidt W. Status of Marek's disease virus in established lymphoma cell lines: herpesvirus integration is common. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):82–92. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.82-92.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Allan G. J., Shanahan F., Vousden K. H., Crook T. p53 is frequently mutated in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2879–2887. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaidano G., Ballerini P., Gong J. Z., Inghirami G., Neri A., Newcomb E. W., Magrath I. T., Knowles D. M., Dalla-Favera R. p53 mutations in human lymphoid malignancies: association with Burkitt lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5413–5417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Medveczky P., Sairenji T., Mulder C. Detection of circular and linear herpesvirus DNA molecules in mammalian cells by gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):393–397. doi: 10.1038/340393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Frizzera G., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Simmons R. L. Epstein-Barr virus, immunodeficiency, and B cell lymphoproliferation. Transplantation. 1985 May;39(5):461–472. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198505000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A., Young B. D., Griffin B. E. Random association of Epstein-Barr virus genomes with host cell metaphase chromosomes in Burkitt's lymphoma-derived cell lines. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):328–332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.328-332.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A., Ripley S., Heller M., Kieff E. Chromosome site for Epstein-Barr virus DNA in a Burkitt tumor cell line and in lymphocytes growth-transformed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1987–1991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Diehl V., Kohn G., Zur Hausen H., Henle G. Herpes-type virus and chromosome marker in normal leukocytes after growth with irradiated Burkitt cells. Science. 1967 Sep 1;157(3792):1064–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3792.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley E. A., Agger S., McNeil J. A., Lawrence J. B., Calendar A., Lenoir G., Thorley-Lawson D. A. When Epstein-Barr virus persistently infects B-cell lines, it frequently integrates. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1245–1254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1245-1254.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley E. A., Klaman L. D., Agger S., Lawrence J. B., Thorley-Lawson D. A. The prototypical Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphoblastoid cell line IB4 is an unusual variant containing integrated but no episomal viral DNA. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3958–3963. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3958-3963.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaschka-Dierich C., Adams A., Lindahl T., Bornkamm G. W., Bjursell G., Klein G., Giovanella B. C., Singh S. Intracellular forms of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in human tumour cells in vivo. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):302–306. doi: 10.1038/260302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Villnave C. A., Singer R. H. Sensitive, high-resolution chromatin and chromosome mapping in situ: presence and orientation of two closely integrated copies of EBV in a lymphoma line. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Adams A., Bjursell G., Bornkamm G. W., Kaschka-Dierich C., Jehn U. Covalently closed circular duplex DNA of Epstein-Barr virus in a human lymphoid cell line. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):511–530. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90331-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Heller M., Petti L., O'Shiro E., Kieff E. Persistence of the entire Epstein-Barr virus genome integrated into human lymphocyte DNA. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1322–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.6095452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Heston L., Countryman J. P3HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA is an independent replicon maintained by cell-to-cell spread. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):45–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.45-52.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polack A., Delius H., Zimber U., Bornkamm G. W. Two deletions in the Epstein-Barr virus genome of the Burkitt lymphoma nonproducer line Raji. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):146–157. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polack A., Hartl G., Zimber U., Freese U. K., Laux G., Takaki K., Hohn B., Gissmann L., Bornkamm G. W. A complete set of overlapping cosmid clones of M-ABA virus derived from nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its similarity to other Epstein-Barr virus isolates. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Marchini A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) recombinants: use of positive selection markers to rescue mutants in EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1701–1709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1701-1709.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman K. G., Magnusson K. P., Ramqvist T., Klein G. Mutant p53 detected in a majority of Burkitt lymphoma cell lines by monoclonal antibody PAb240. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1633–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J., Pawlita M., Bullerdiek J., zur Hausen H. Suppression of the malignant phenotype in somatic cell hybrids between Burkitt's lymphoma cells and Epstein-Barr virus-immortalized lymphoblastoid cells despite deregulated c-myc expression. Cancer Res. 1990 May 15;50(10):3095–3100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., Bister K., zur Hausen H. Retinoic acid inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus induction. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):553–554. doi: 10.1038/278553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zur Hausen H., Schulte-Holthausen H. Presence of EB virus nucleic acid homology in a "virus-free" line of Burkitt tumour cells. Nature. 1970 Jul 18;227(5255):245–248. doi: 10.1038/227245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., O'Neill F. J., Freese U. K., Hecker E. Persisting oncogenic herpesvirus induced by the tumour promotor TPA. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):373–375. doi: 10.1038/272373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]