Abstract
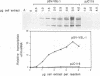
The 241-kDa large (L) protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is the multifunctional catalytic component of the viral RNA polymerase. A protocol has been developed for the synthesis of recombinant L protein that will support viral mRNA synthesis in vitro. COS cells were transfected with a transient expression vector (pSV-VSL1 [M. Schubert, G. G. Harmison, C. D. Richardson, and E. Meier, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:7984-7988, 1985]) which contains the simian virus 40 late promoter for the transcription of a cDNA copy of the L protein of the Indiana serotype of VSV. Cytoplasmic extracts of these cells efficiently transcribed VSV mRNAs in vitro in conjunction with N protein-RNA template purified from virus and recombinant phosphoprotein synthesized in Escherichia coli. mRNA synthesis was completely dependent upon addition of both bacterial phosphoprotein and extracts from cells transfected with the L gene. Extracts from mock-transfected cells or from cells transfected with the expression vector alone did not support VSV RNA synthesis. RNA synthesis was proportional to the concentration of cell extract used, with an optimum of 0.2 mg/ml. Rhabdoviruses and paramyxoviruses contain a highly conserved GDNQ motif which was mutated in the transfected L gene. All constructs with mutations within the core GDN abrogated transcriptional activity except for the mutant containing GDD, which retained 25% activity. Conserved amino acid changes outside of the core GDN and changes corresponding to other paromyxovirus and rhabdovirus L proteins retained variable transcriptional activity. These findings provide experimental evidence that the GDN of negative-strand, nonsegmented RNA viruses is a variant of the GDD motif of plus-strand RNA viruses and of the XDD motif of DNA viruses and reverse transcriptases.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus, II. An RNA polymerase in the virion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):572–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K., Barik S. Gene expression of vesicular stomatitis virus genome RNA. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90495-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barik S., Banerjee A. K. Cloning and expression of the vesicular stomatitis virus phosphoprotein gene in Escherichia coli: analysis of phosphorylation status versus transcriptional activity. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1719–1726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1719-1726.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barik S., Banerjee A. K. Sequential phosphorylation of the phosphoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus by cellular and viral protein kinases is essential for transcription activation. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1109–1118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1109-1118.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barik S., Rud E. W., Luk D., Banerjee A. K., Kang C. Y. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the L gene of vesicular stomatitis virus (New Jersey serotype): identification of conserved domains in L proteins of nonsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):332–337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90218-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Crowley J. C., Silverman J. I., Menonna J., Cook S. D., Dowling P. C. Measles virus L protein evidences elements of ancestral RNA polymerase. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90563-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi T. J., Kuwata S., Koonin E. V., Heaton L. A., Jackson A. O. Structure of the L (polymerase) protein gene of sonchus yellow net virus. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90678-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. P., Banerjee A. K. Specific interactions of vesicular stomatitis virus L and NS proteins with heterologous genome ribonucleoprotein template lead to mRNA synthesis in vitro. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):628–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.628-634.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delarue M., Poch O., Tordo N., Moras D., Argos P. An attempt to unify the structure of polymerases. Protein Eng. 1990 May;3(6):461–467. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.6.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Wagner R. R. L protein requirement for in vitro RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1325–1335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1325-1335.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Yu Y. Both NS and L proteins are required for in vitro RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1348–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1348-1356.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldhaus A. L., Lesnaw J. A. Nucleotide sequence of the L gene of vesicular stomatitis virus (New Jersey): identification of conserved domains in the New Jersey and Indiana L proteins. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galinski M. S., Mink M. A., Pons M. W. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the human parainfluenza 3 virus gene encoding the L protein. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):499–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90594-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. S., Chattopadhyay D., Banerjee A. K. Identification of a domain within the phosphoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus that is essential for transcription in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8873–8877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond D. C., Evans R. K., Lesnaw J. A. The L protein of vesicular stomatitis virus transcription complexes is specifically photolabelled by 5-azido-uridine 5'-triphosphate, an analogue of the RNA polymerase substrate uridine 5'-triphosphate. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jan;73(Pt 1):61–66. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond D. C., Haley B. E., Lesnaw J. A. Identification and characterization of serine/threonine protein kinase activity intrinsic to the L protein of vesicular stomatitis virus New Jersey. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jan;73(Pt 1):67–75. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikami S. M., Moyer S. A. Host range mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus defective in in vitro RNA methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7694–7698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. M., Smith E. F., Buckley D. W. Aberrant polyadenylation by a vesicular stomatitis virus mutant is due to an altered L protein. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.515-521.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi Y., Hirashima A. Interference with viral infection by defective RNA replicase. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3946–3949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3946-3949.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablonski S. A., Luo M., Morrow C. D. Enzymatic activity of poliovirus RNA polymerase mutants with single amino acid changes in the conserved YGDD amino acid motif. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4565–4572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4565-4572.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin H., Elliott R. M. Mutagenesis of the L protein encoded by Bunyamwera virus and production of monospecific antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1992 Sep;73(Pt 9):2235–2244. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-9-2235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamer G., Argos P. Primary structural comparison of RNA-dependent polymerases from plant, animal and bacterial viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7269–7282. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano M., Okamoto K., Bando H., Kondo K., Tsurudome M., Komada H., Nishio M., Ito Y. Characterizations of the human parainfluenza type 2 virus gene encoding the L protein and the intergenic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2739–2746. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Ward C. D., Lamb R. A. Molecular cloning of the NP and L genes of simian virus 5: identification of highly conserved domains in paramyxovirus NP and L proteins. Virus Res. 1992 Mar;22(3):259–279. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90057-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattnaik A. K., Wertz G. W. Cells that express all five proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus from cloned cDNAs support replication, assembly, and budding of defective interfering particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1379–1383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattnaik A. K., Wertz G. W. Replication and amplification of defective interfering particle RNAs of vesicular stomatitis virus in cells expressing viral proteins from vectors containing cloned cDNAs. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2948–2957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2948-2957.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Blumberg B. M., Bougueleret L., Tordo N. Sequence comparison of five polymerases (L proteins) of unsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses: theoretical assignment of functional domains. J Gen Virol. 1990 May;71(Pt 5):1153–1162. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-5-1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Sauvaget I., Delarue M., Tordo N. Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert M., Harmison G. G., Meier E. Primary structure of the vesicular stomatitis virus polymerase (L) gene: evidence for a high frequency of mutations. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):505–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.505-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert M., Harmison G. G., Richardson C. D., Meier E. Expression of a cDNA encoding a functional 241-kilodalton vesicular stomatitis virus RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7984–7988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Iwasaki K., Shibuta H. Determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the Sendai virus genome RNA and the predicted amino acid sequences of the F, HN and L proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1545–1563. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleat D. E., Chikkala N. F., Gautam S., Banerjee A. K. Restricted replication of vesicular stomatitis virus in T lymphocytes is coincident with a deficiency in a cellular protein kinase required for viral transcription. J Gen Virol. 1992 Dec;73(Pt 12):3125–3132. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-12-3125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague J., Condra J. H., Arnheiter H., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a recombinant DNA gene coding for the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):773–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.773-781.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tordo N., Poch O., Ermine A., Keith G., Rougeon F. Completion of the rabies virus genome sequence determination: highly conserved domains among the L (polymerase) proteins of unsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90600-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yusoff K., Millar N. S., Chambers P., Emmerson P. T. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the L gene of Newcastle disease virus: homologies with Sendai and vesicular stomatitis viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):3961–3976. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]