Abstract
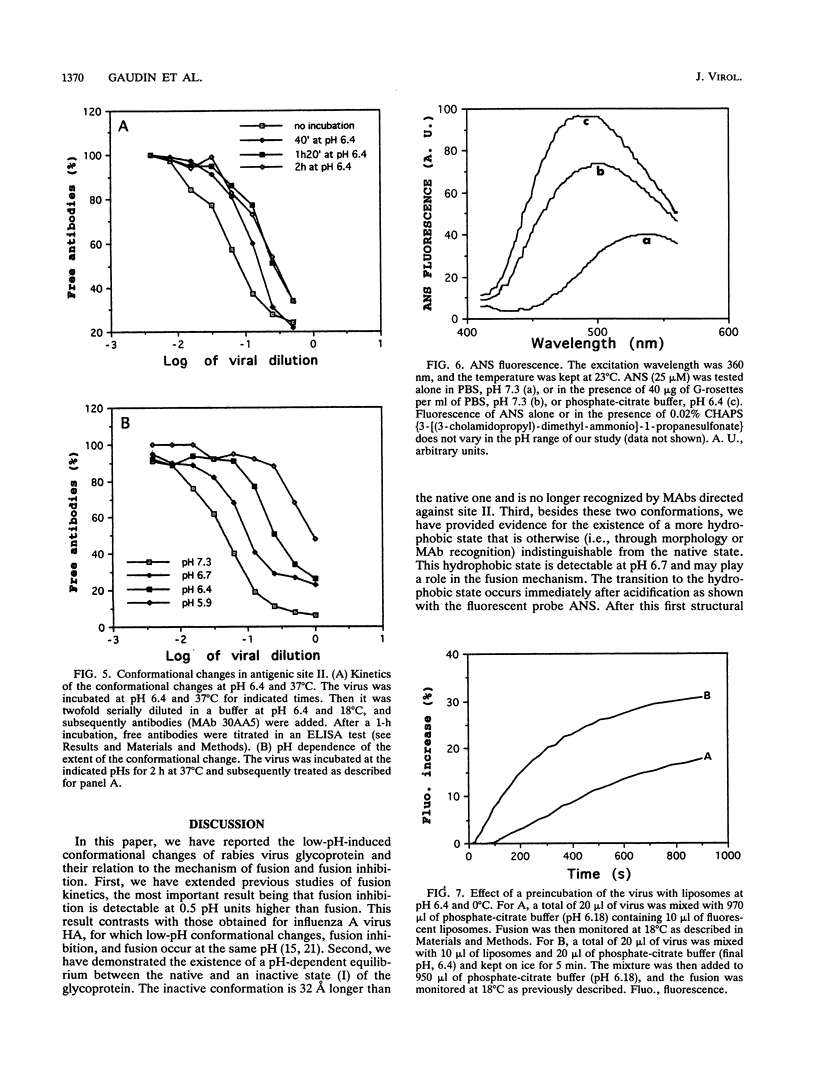
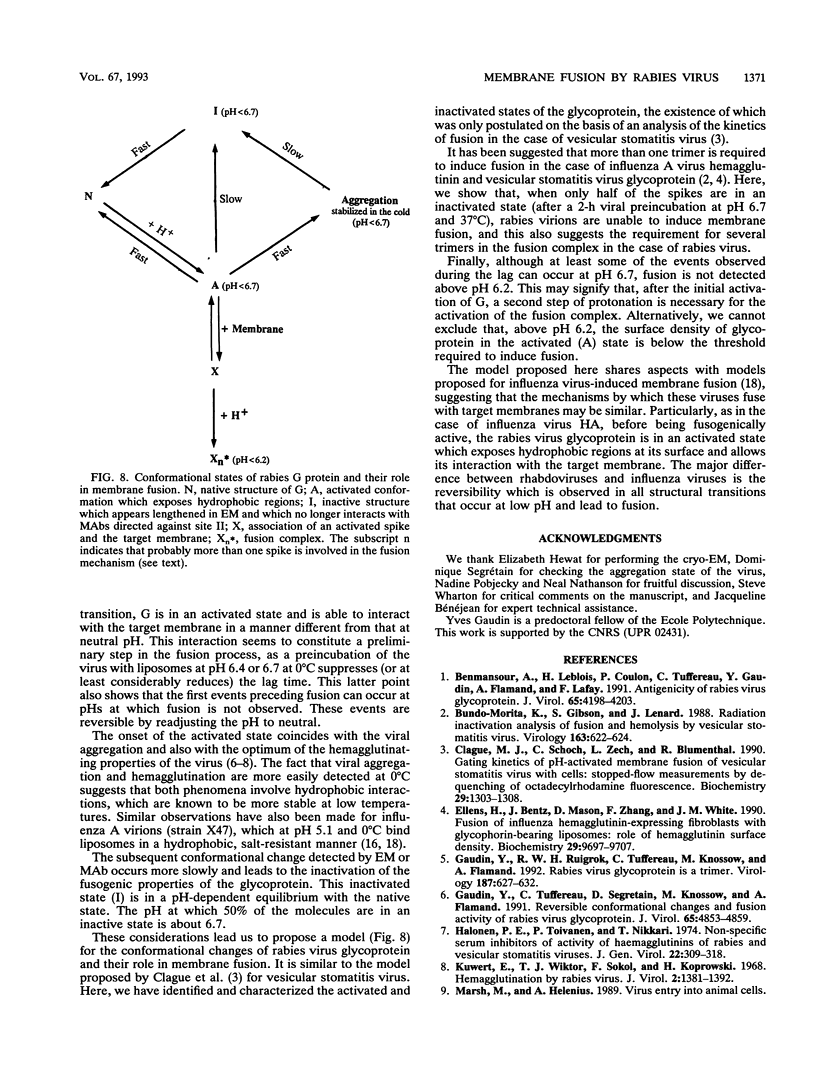
Fusion of rabies virus with membranes occurs at acidic pH and is mediated by the viral spike glycoprotein (G). In this paper, we provide the basis for a description of structural transitions associated with exposure to low pH and of their role in membrane fusion. First, we have extended previous studies of fusion kinetics and we have shown that low-pH inhibition of fusion is detectable at 0.5 pH units higher than fusion. Second, low-pH-induced conformational changes were analyzed by using electron microscopy and monoclonal antibody binding assays. The existence of a pH-dependent equilibrium between the native and a low-pH inactive conformation was demonstrated. Third, besides these two conformations, we, using the fluorescent probe ANS (8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid), provide evidence for the existence of a transient third state which appears to be more hydrophobic than the native state. Our results suggest that this transient state is responsible for viral aggregation at low pH and could play a role in the first steps of the fusion mechanism.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benmansour A., Leblois H., Coulon P., Tuffereau C., Gaudin Y., Flamand A., Lafay F. Antigenicity of rabies virus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4198–4203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4198-4203.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundo-Morita K., Gibson S., Lenard J. Radiation inactivation analysis of fusion and hemolysis by vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):622–624. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90304-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clague M. J., Schoch C., Zech L., Blumenthal R. Gating kinetics of pH-activated membrane fusion of vesicular stomatitis virus with cells: stopped-flow measurements by dequenching of octadecylrhodamine fluorescence. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 6;29(5):1303–1308. doi: 10.1021/bi00457a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellens H., Bentz J., Mason D., Zhang F., White J. M. Fusion of influenza hemagglutinin-expressing fibroblasts with glycophorin-bearing liposomes: role of hemagglutinin surface density. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 16;29(41):9697–9707. doi: 10.1021/bi00493a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudin Y., Ruigrok R. W., Tuffereau C., Knossow M., Flamand A. Rabies virus glycoprotein is a trimer. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):627–632. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90465-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudin Y., Tuffereau C., Segretain D., Knossow M., Flamand A. Reversible conformational changes and fusion activity of rabies virus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4853–4859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4853-4859.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P. E., Toivanen P., Nikkari T. Non-specific serum inhibitors of activity of haemagglutinins of rabies and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Gen Virol. 1974 Mar;22(3):309–318. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-3-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwert E., Wiktor T. J., Sokol F., Koprowski H. Hemagglutination by rabies virus. J Virol. 1968 Dec;2(12):1381–1392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.12.1381-1392.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mifune K., Ohuchi M., Mannen K. Hemolysis and cell fusion by rhabdoviruses. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 25;137(2):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80370-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehaud C., Coulon P., LaFay F., Thiers C., Flamand A. Antigenic site II of the rabies virus glycoprotein: structure and role in viral virulence. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.1-7.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruigrok R. W., Wrigley N. G., Calder L. J., Cusack S., Wharton S. A., Brown E. B., Skehel J. J. Electron microscopy of the low pH structure of influenza virus haemagglutinin. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):41–49. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04175.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Coulon P., Rollin P. E., Flamand A. Rabies virulence: effect on pathogenicity and sequence characterization of rabies virus mutations affecting antigenic site III of the glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):926–934. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.926-934.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Booy F. P., Wilschut J. Effects of low pH on influenza virus. Activation and inactivation of the membrane fusion capacity of the hemagglutinin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17744–17749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Doms R. W., Helenius A. Protein-mediated membrane fusion. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:187–211. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., White J. M., Helenius A. Intermediates in influenza induced membrane fusion. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4231–4241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Hoekstra D., Pagano R. E. Use of resonance energy transfer to monitor membrane fusion. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4093–4099. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton S. A. The role of influenza virus haemagglutinin in membrane fusion. Microbiol Sci. 1987 Apr;4(4):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Membrane fusion activity of influenza virus. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):217–222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitt M. A., Buonocore L., Prehaud C., Rose J. K. Membrane fusion activity, oligomerization, and assembly of the rabies virus glycoprotein. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):681–688. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90539-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Skehel J. J. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Reagan K. J., Koprowski H. Characterization of saturable binding sites for rabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):691–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.691-697.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



