Abstract
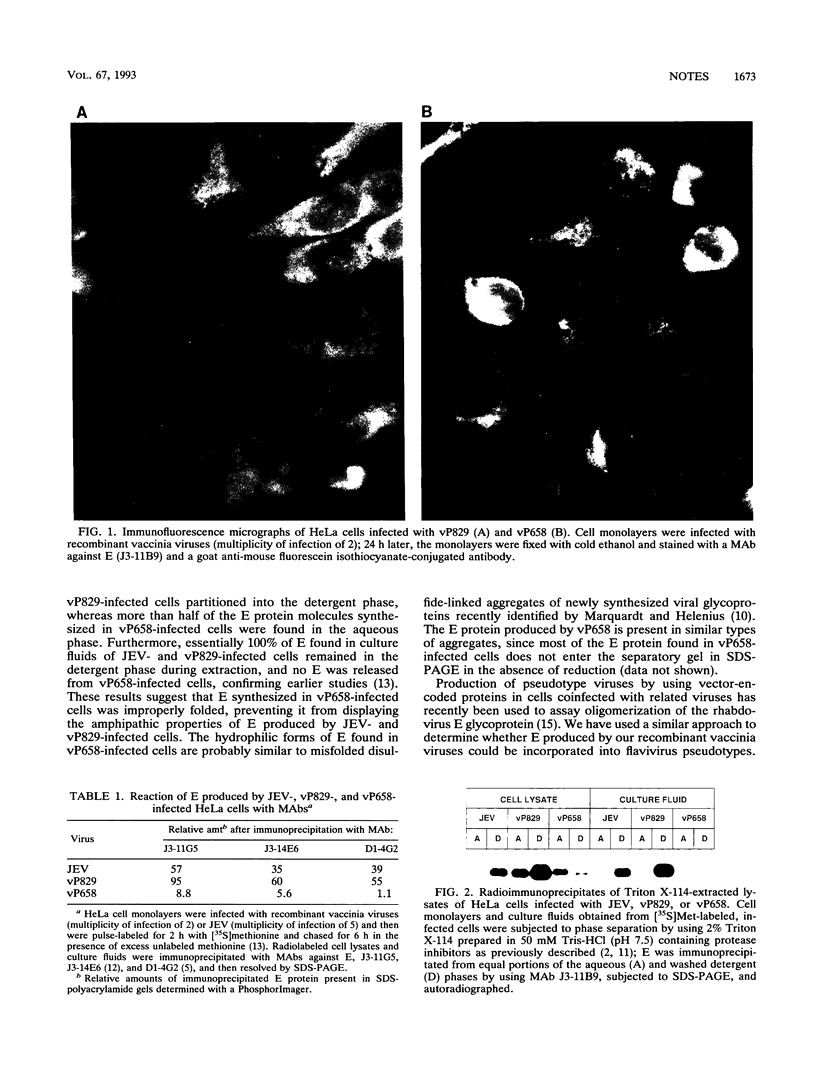
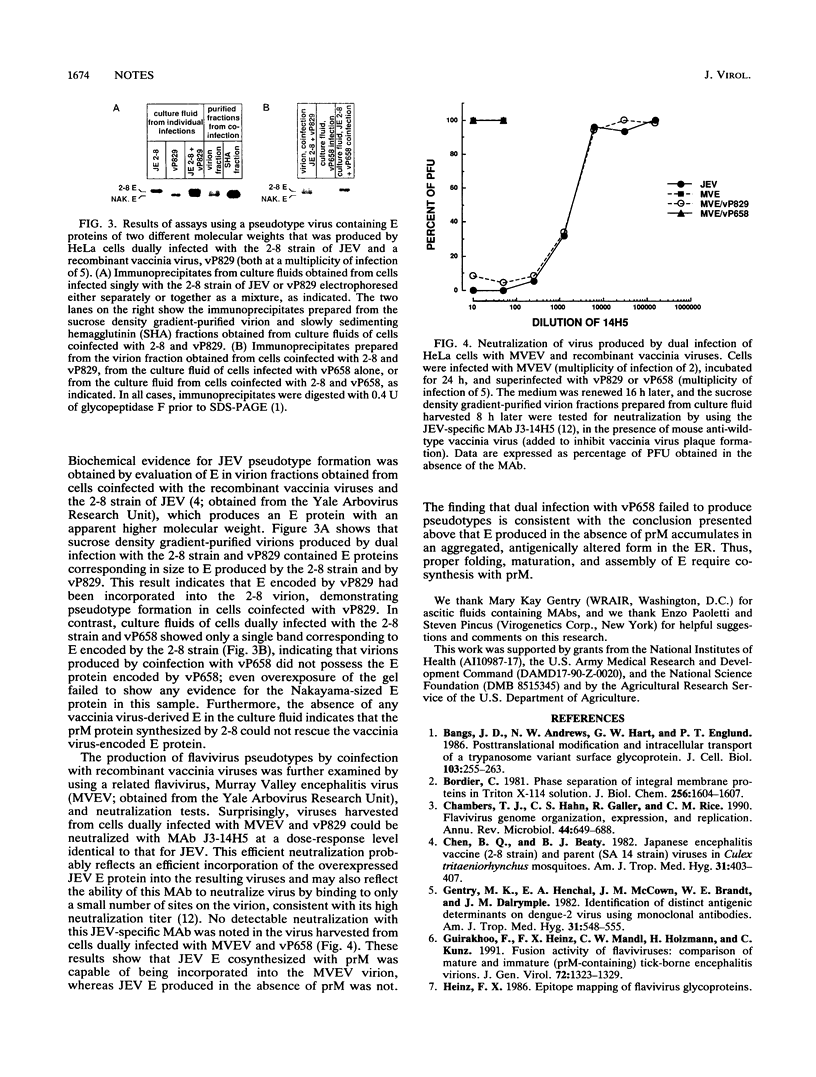
The role of the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) premembrane (prM) protein in maturation of the envelope (E) glycoprotein was evaluated by using recombinant vaccinia viruses encoding E in the presence (vP829) or absence (vP658) of prM. Immunofluorescence analyses showed that E appeared to be localized in the endoplasmic reticulum of cells infected with JEV, vP829, or vP658. However, reactivity with monoclonal antibodies and behavior in Triton X-114 indicated that E produced in the absence of prM behaved abnormally. Furthermore, E produced in the presence of prM by recombinant vaccinia viruses could be incorporated into flavivirus pseudotypes, whereas E synthesized in the absence of prM could not. These results demonstrate that cosynthesis of prM is required for proper folding, membrane association, and assembly of the flavivirus E protein.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangs J. D., Andrews N. W., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Posttranslational modification and intracellular transport of a trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):255–263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Hahn C. S., Galler R., Rice C. M. Flavivirus genome organization, expression, and replication. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:649–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B. Q., Beaty B. J. Japanese encephalitis vaccine (2-8 strain) and parent (SA 14 strain) viruses in Culex tritaeniorhynchus mosquitoes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982 Mar;31(2):403–407. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. K., Henchal E. A., McCown J. M., Brandt W. E., Dalrymple J. M. Identification of distinct antigenic determinants on dengue-2 virus using monoclonal antibodies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982 May;31(3 Pt 1):548–555. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirakhoo F., Heinz F. X., Mandl C. W., Holzmann H., Kunz C. Fusion activity of flaviviruses: comparison of mature and immature (prM-containing) tick-borne encephalitis virions. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jun;72(Pt 6):1323–1329. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-6-1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz F. X. Epitope mapping of flavivirus glycoproteins. Adv Virus Res. 1986;31:103–168. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi E., Pincus S., Fonseca B. A., Shope R. E., Paoletti E., Mason P. W. Comparison of protective immunity elicited by recombinant vaccinia viruses that synthesize E or NS1 of Japanese encephalitis virus. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90788-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi E., Pincus S., Paoletti E., Shope R. E., Burrage T., Mason P. W. Mice immunized with a subviral particle containing the Japanese encephalitis virus prM/M and E proteins are protected from lethal JEV infection. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):714–720. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90526-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt T., Helenius A. Misfolding and aggregation of newly synthesized proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):505–513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W., Dalrymple J. M., Gentry M. K., McCown J. M., Hoke C. H., Burke D. S., Fournier M. J., Mason T. L. Molecular characterization of a neutralizing domain of the Japanese encephalitis virus structural glycoprotein. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):2037–2049. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-2037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W. Maturation of Japanese encephalitis virus glycoproteins produced by infected mammalian and mosquito cells. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):354–364. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90161-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W., Pincus S., Fournier M. J., Mason T. L., Shope R. E., Paoletti E. Japanese encephalitis virus-vaccinia recombinants produce particulate forms of the structural membrane proteins and induce high levels of protection against lethal JEV infection. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):294–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. Cell-associated West Nile flavivirus is covered with E+pre-M protein heterodimers which are destroyed and reorganized by proteolytic cleavage during virus release. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2521–2526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2521-2526.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitt M. A., Buonocore L., Prehaud C., Rose J. K. Membrane fusion activity, oligomerization, and assembly of the rabies virus glycoprotein. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):681–688. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90539-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]