Abstract
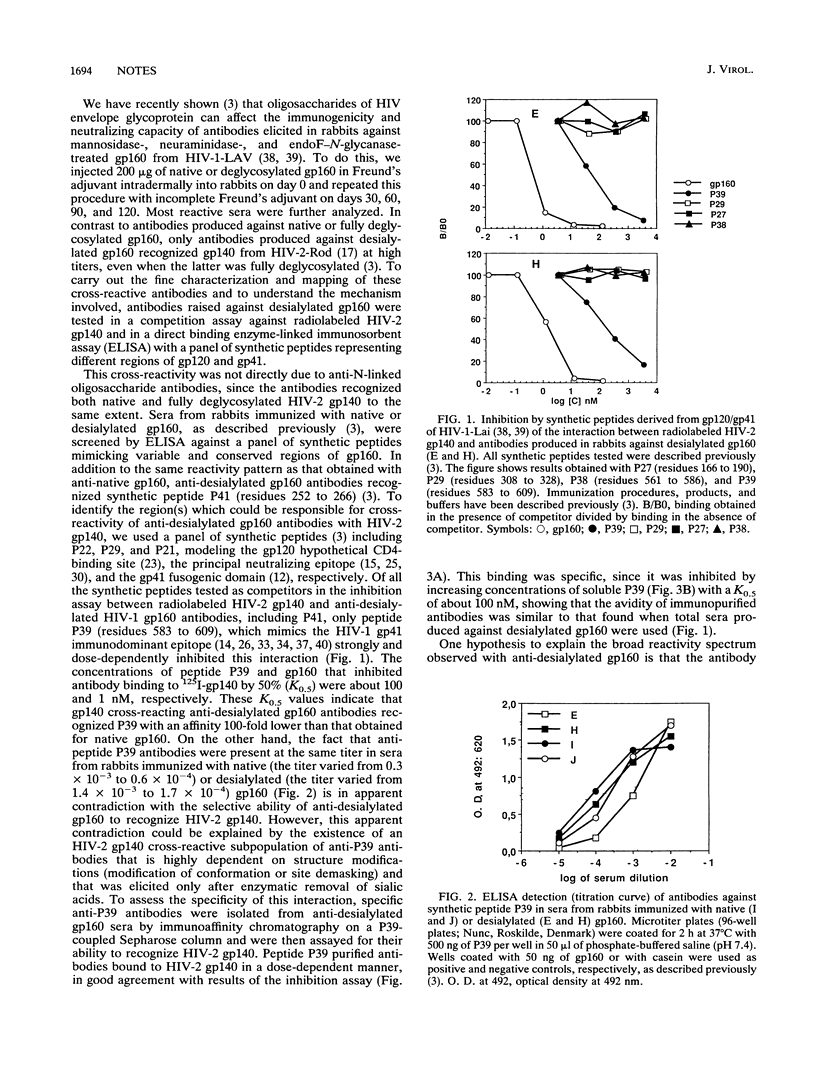
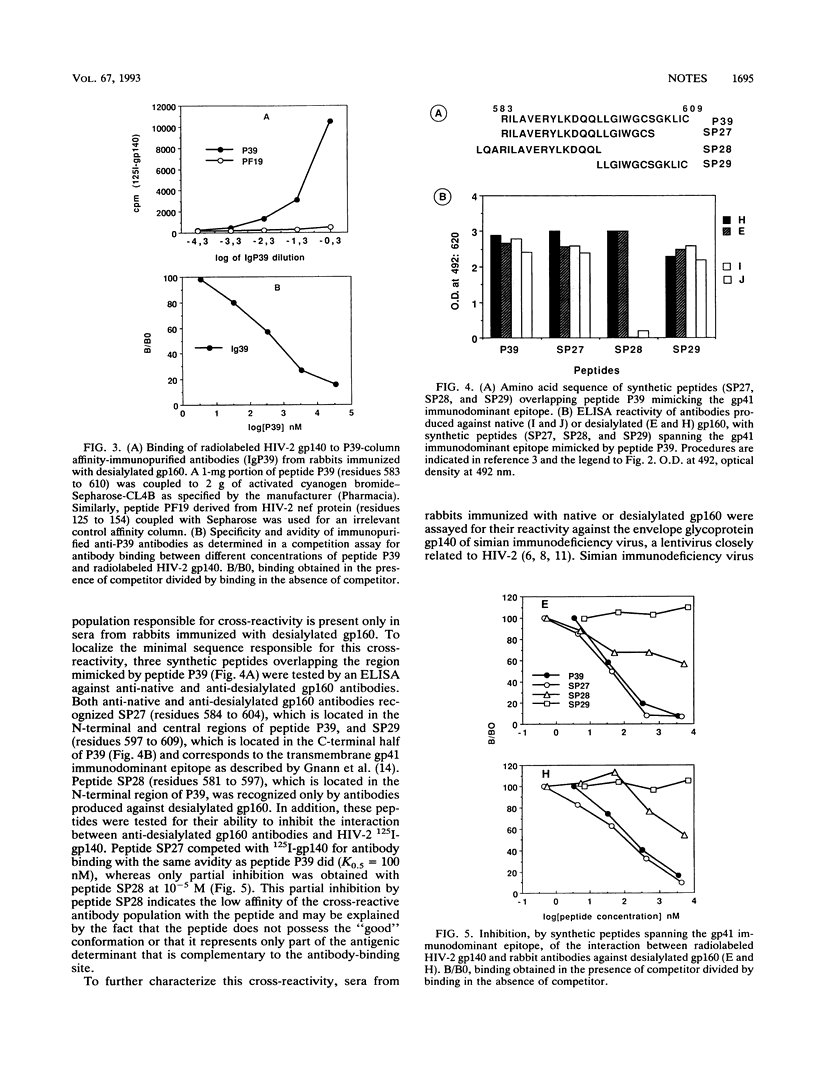
In a previous report we have shown that, in contrast to antibodies produced against native or fully deglycosylated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp160 in rabbits, antibodies raised against desialylated HIV-1 gp160 also recognize gp140 from HIV-2 at high titers. Here, we characterize the fine specificity of these cross-reactive antibodies. Inhibition assays with a panel of synthetic peptides as competitors showed that cross-reactivity to gp140 was due to antibodies that were specific for the region encompassing HIV-1 gp41 immunodominant epitope, mimicked by peptide P39 (residues 583 to 609), the latter being able to totally inhibit the formation of complexes between radiolabeled HIV-2 gp140 and antibodies elicited by desialylated HIV-1 gp160. In addition, anti-desialylated gp160 antibodies retained on a P39 affinity column still bound HIV-2 gp140. Fine mapping has enabled us to localize the cross-reactive epitope within the N-terminal extremity of the gp41 immunodominant region. Interestingly, this cross-reactive antibody population did not recognize glycosylated or totally deglycosylated simian immunodeficiency virus gp140 despite an amino acid homology with HIV-1 within this region that is comparable to that of HIV-2. This cross-reactivity between HIV-1 and HIV-2 did not correlate with cross-neutralization. These results illustrate the influence of carbohydrate moieties on the specificity of the antibodies produced and clearly indicate that such procedures may be an efficient way to raise specific immune responses that are not type specific. Moreover, this cross-reactivity might explain the double-positive reactivity observed, in some human sera, against both HIV-1 and HIV-2 envelope antigens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander S., Elder J. H. Carbohydrate dramatically influences immune reactivity of antisera to viral glycoprotein antigens. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1328–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.6505693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahraoui E., Benjouad A., Guetard D., Kolbe H., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. Study of the interaction of HIV-1 and HIV-2 envelope glycoproteins with the CD4 receptor and role of N-glycans. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 May;8(5):565–573. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjouad A., Gluckman J. C., Rochat H., Montagnier L., Bahraoui E. Influence of carbohydrate moieties on the immunogenicity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 recombinant gp160. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2473–2483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2473-2483.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botarelli P., Houlden B. A., Haigwood N. L., Servis C., Montagna D., Abrignani S. N-glycosylation of HIV-gp120 may constrain recognition by T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3128–3132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttiger B., Karlsson A., Andreasson P. A., Nauclér A., Costa C. M., Norrby E., Biberfeld G. Envelope cross-reactivity between human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 detected by different serological methods: correlation between cross-neutralization and reactivity against the main neutralizing site. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3492–3499. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3492-3499.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D., Stephens D. M., Willers C., Lachmann P. J. Glycosylation governs the binding of antipeptide antibodies to regions of hypervariable amino acid sequence within recombinant gp120 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):2889–2898. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-2889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Embretson J. E., Anderson D. C., Mullins J. I., Fultz P. N. Sequence analysis and acute pathogenicity of molecularly cloned SIVSMM-PBj14. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):636–640. doi: 10.1038/345636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., McGee J. S., Alexander S. Carbohydrate side chains of Rauscher leukemia virus envelope glycoproteins are not required to elicit a neutralizing antibody response. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):340–342. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.340-342.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenouillet E., Clerget-Raslain B., Gluckman J. C., Guétard D., Montagnier L., Bahraoui E. Role of N-linked glycans in the interaction between the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus and its CD4 cellular receptor. Structural enzymatic analysis. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):807–822. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Gurgo C., Guo H. G., Gallo R. C., Collalti E., Fargnoli K. A., Hall L. F., Wong-Staal F., Reitz M. S., Jr Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus and its relationship to the human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):539–543. doi: 10.1038/328539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R. Detection of a fusion peptide sequence in the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, McCormick J. B., Mitchell S., Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Synthetic peptide immunoassay distinguishes HIV type 1 and HIV type 2 infections. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1346–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.2888192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Schwimmbeck P. L., Nelson J. A., Truax A. B., Oldstone M. B. Diagnosis of AIDS by using a 12-amino acid peptide representing an immunodominant epitope of the human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):261–267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Debouck C., Meloen R. H., Smit L., Bakker M., Asher D. M., Wolff A. V., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization epitope with conserved architecture elicits early type-specific antibodies in experimentally infected chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4478–4482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruters R. A., Neefjes J. J., Tersmette M., de Goede R. E., Tulp A., Huisman H. G., Miedema F., Ploegh H. L. Interference with HIV-induced syncytium formation and viral infectivity by inhibitors of trimming glucosidase. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):74–77. doi: 10.1038/330074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer T. J., Allen R. G., Heynen C. A., Kennedy M. M., Knigge M. F., Paul D. A., Dawson G. J. Discrimination of HIV-2 infection from HIV-1 infection by western blot and radioimmunoprecipitation analysis. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Apr;6(4):515–524. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huso D. L., Narayan O., Hart G. W. Sialic acids on the surface of caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus define the biological properties of the virus. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1974–1980. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1974-1980.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G., Rott R., Schwarz R. T. Carbohydrate-induced conformational changes of Semliki forest virus glycoproteins determine antigenicity. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):286–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D. R., McDougal J. S., Maddon P. J. The CD4 molecule and HIV infection. Immunodefic Rev. 1990;2(1):43–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews T. J., Weinhold K. J., Lyerly H. K., Langlois A. J., Wigzell H., Bolognesi D. P. Interaction between the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type IIIB envelope glycoprotein gp120 and the surface antigen CD4: role of carbohydrate in binding and cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5424–5428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Schröder H. C., Reuter P., Maidhof A., Uhlenbruck G., Winkler I. Polyclonal antibodies to mannan from yeast also recognize the carbohydrate structure of gp120 of the AIDS virus: an approach to raise neutralizing antibodies to HIV-1 infection in vitro. AIDS. 1990 Feb;4(2):159–162. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199002000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Garrity R. R., Goudsmit J. Neutralization of HIV-1: a paradox of humoral proportions. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2437–2455. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.1712328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Lee E. S. B cell epitope mapping of human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoproteins with long (19- to 36-residue) synthetic peptides. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):85–95. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Närvänen A., Korkolainen M., Suni J., Korpela J., Kontio S., Partanen P., Vaheri A., Huhtala M. L. Synthetic env gp41 peptide as a sensitive and specific diagnostic reagent in different stages of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Med Virol. 1988 Oct;26(2):111–118. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890260202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Tishon A., Lewicki H., Dyson H. J., Feher V. A., Assa-Munt N., Wright P. E. Mapping the anatomy of the immunodominant domain of the human immunodeficiency virus gp41 transmembrane protein: peptide conformation analysis using monoclonal antibodies and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1727–1734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1727-1734.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Processing of the structural proteins of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the presence of monensin and cerulenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9283–9286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Hoke G. M., Sarngadharan M. G. Role of oligosaccharides in the processing and maturation of envelope glycoproteins of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3384–3388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Clark M. E., Langlois A. J., Matthews T. J., Weinhold K. J., Randall R. R., Bolognesi D. P., Haynes B. F. Type-specific neutralization of the human immunodeficiency virus with antibodies to env-encoded synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M. Evidence that mannosyl residues are involved in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) pathogenesis. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Fall;3(3):265–282. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Weiss R. A. The CD4 antigen: physiological ligand and HIV receptor. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):631–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Gnann J. W., Jr, Langlois A. J., Shriver K., Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. B- and T-lymphocyte responses to an immunodominant epitope of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2531–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2531-2536.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafferman A., Lennox J., Grosfeld H., Sadoff J., Redfield R. R., Burke D. S. Patterns of antibody recognition of selected conserved amino acid sequences from the HIV envelope in sera from different stages of HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Feb;5(1):33–39. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Stevens D. J., Daniels R. S., Douglas A. R., Knossow M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. A carbohydrate side chain on hemagglutinins of Hong Kong influenza viruses inhibits recognition by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1779–1783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley M. L., Friedman H. M. Binding of complement component C3b to glycoprotein C is modulated by sialic acid on herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):857–861. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.857-861.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Naso R. B., Rosen J., Whalley A., Hom Y. L., Hoey K., Kennedy C. J., McCutchan J. A., Spector S. A., Richman D. D. Antibody to a synthetic oligopeptide in subjects at risk for human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1498–1504. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1498-1504.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Sonigo P., Danos O., Cole S., Alizon M. Nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, LAV. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Vartanian J. P., Henry M., Chenciner N., Cheynier R., Delassus S., Martins L. P., Sala M., Nugeyre M. T., Guétard D. LAV revisited: origins of the early HIV-1 isolates from Institut Pasteur. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):961–965. doi: 10.1126/science.2035026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. J., Steel S., Wisniewolski R., Wang C. Y. Detection of antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type III by using a synthetic peptide of 21 amino acid residues corresponding to a highly antigenic segment of gp41 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6159–6163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


