Abstract
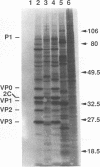
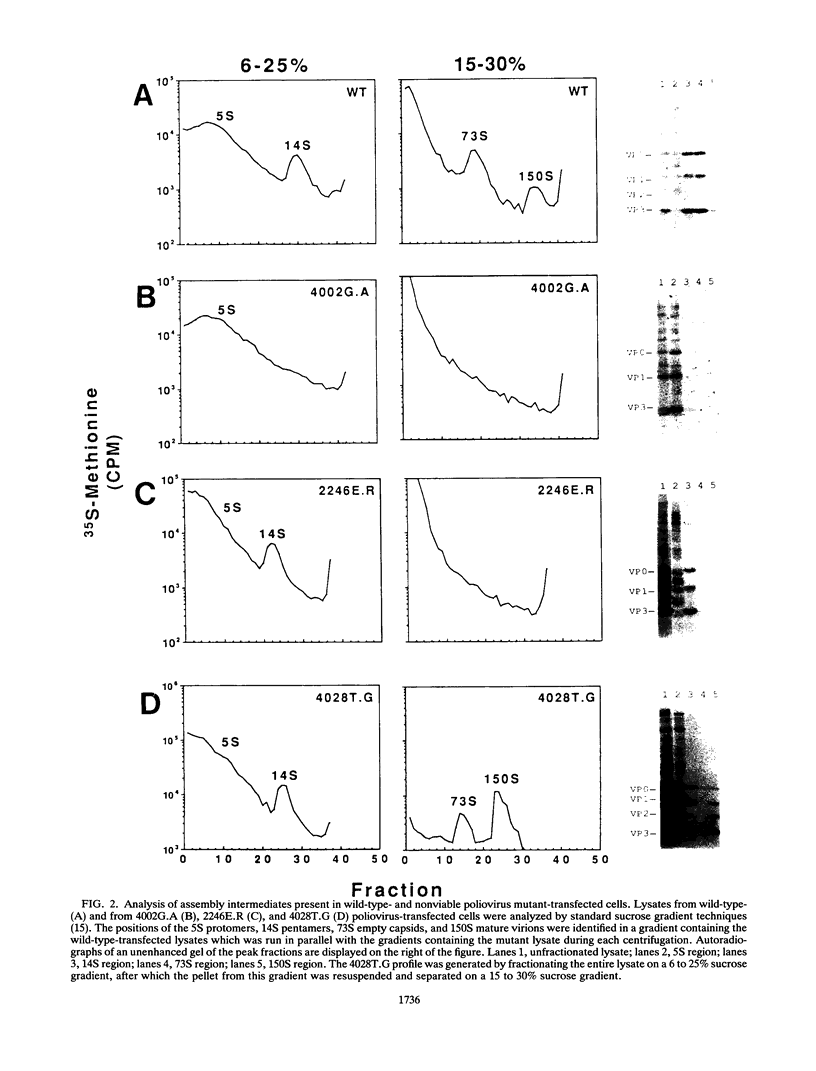
Nonviable poliovirus capsid mutants were studied by an efficient infection-transfection system. Phenotypically, nonviable poliovirus capsid mutants appear to segregate into three classes: those that form only protomers, those that can form pentamers, and one that can form completed virions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansardi D. C., Porter D. C., Morrow C. D. Coinfection with recombinant vaccinia viruses expressing poliovirus P1 and P3 proteins results in polyprotein processing and formation of empty capsid structures. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2088–2092. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2088-2092.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansardi D. C., Porter D. C., Morrow C. D. Myristylation of poliovirus capsid precursor P1 is required for assembly of subviral particles. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4556–4563. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4556-4563.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Hölscher C., Reuer Q., Harber J., Wimmer E. Myristoylation of the poliovirus polyprotein is required for proteolytic processing of the capsid and for viral infectivity. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2433–2436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2433-2436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn R. J., Tada H., Ypma-Wong M. F., Dunn J. J., Semler B. L., Wimmer E. Construction of a "mutagenesis cartridge" for poliovirus genome-linked viral protein: isolation and characterization of viable and nonviable mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):519–523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc D., Drugeon G., Haenni A. L., Girard M., van der Werf S. Role of myristoylation of poliovirus capsid protein VP4 as determined by site-directed mutagenesis of its N-terminal sequence. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2661–2668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc D., Girard M., van der Werf S. A Gly1 to Ala substitution in poliovirus capsid protein VP0 blocks its myristoylation and prevents viral assembly. J Gen Virol. 1991 May;72(Pt 5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-5-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc D., Masson G., Girard M., van der Werf S. Lack of myristoylation of poliovirus capsid polypeptide VP0 prevents the formation of virions or results in the assembly of noninfectious virus particles. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4099–4107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4099-4107.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A., Paul A. V., Wimmer E. Cell-free, de novo synthesis of poliovirus. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1647–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.1661029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscufo N., Chow M. Myristate-protein interactions in poliovirus: interactions of VP4 threonine 28 contribute to the structural conformation of assembly intermediates and the stability of assembled virions. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):6849–6857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.6849-6857.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscufo N., Simons J., Chow M. Myristoylation is important at multiple stages in poliovirus assembly. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2372–2380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2372-2380.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C., Birnby D., Chow M. Folding and processing of the capsid protein precursor P1 is kinetically retarded in neutralization site 3B mutants of poliovirus. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1641–1648. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1641-1648.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C., Page G., Zhou H., Chow M. Identification of residues in VP2 that contribute to poliovirus neutralization antigenic site 3B. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90856-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P. Role of 3'-end sequences in infectivity of poliovirus transcripts made in vitro. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):467–470. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.467-470.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Andino R., Baltimore D. An RNA sequence of hundreds of nucleotides at the 5' end of poliovirus RNA is involved in allowing viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2291–2299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2291-2299.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]