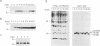Abstract
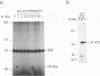
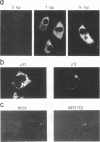
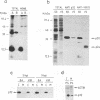
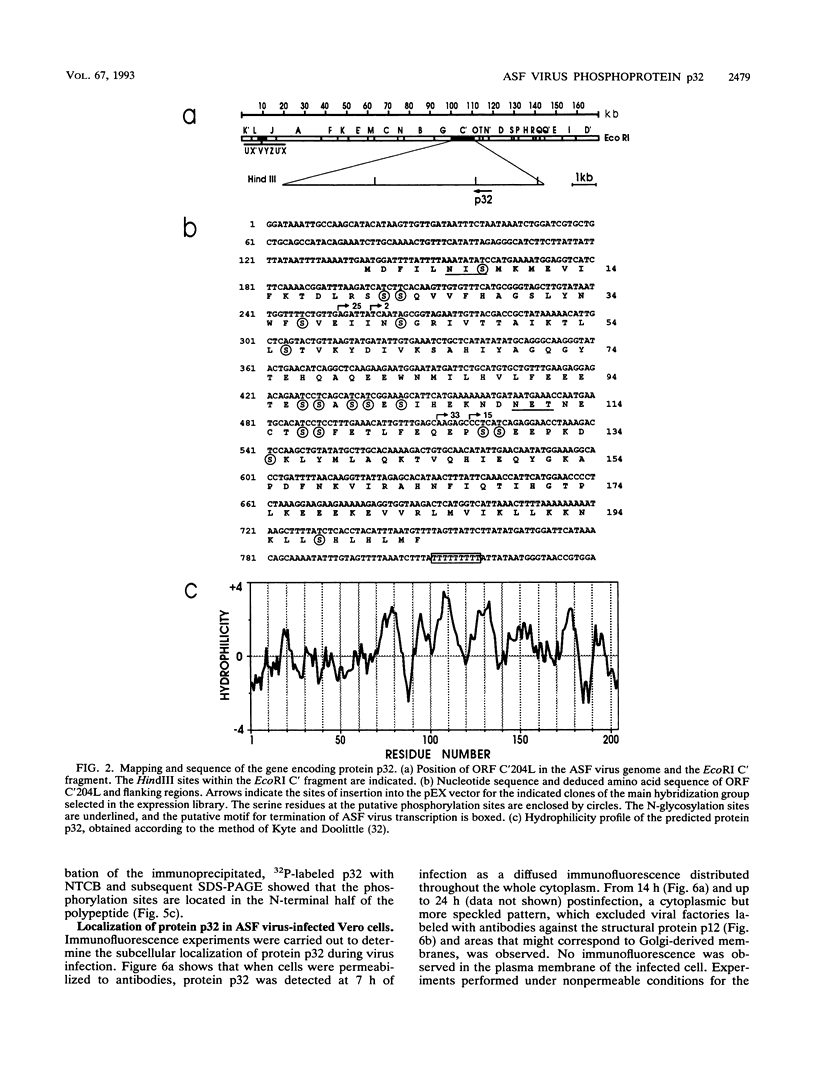
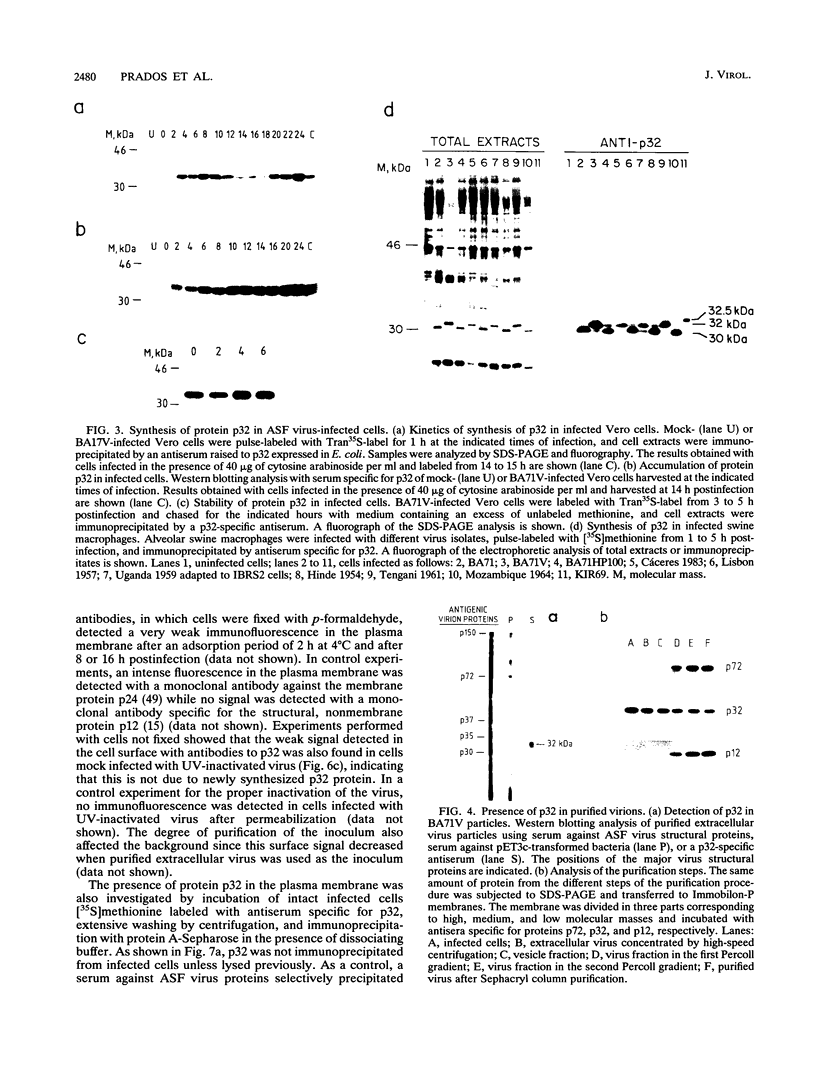
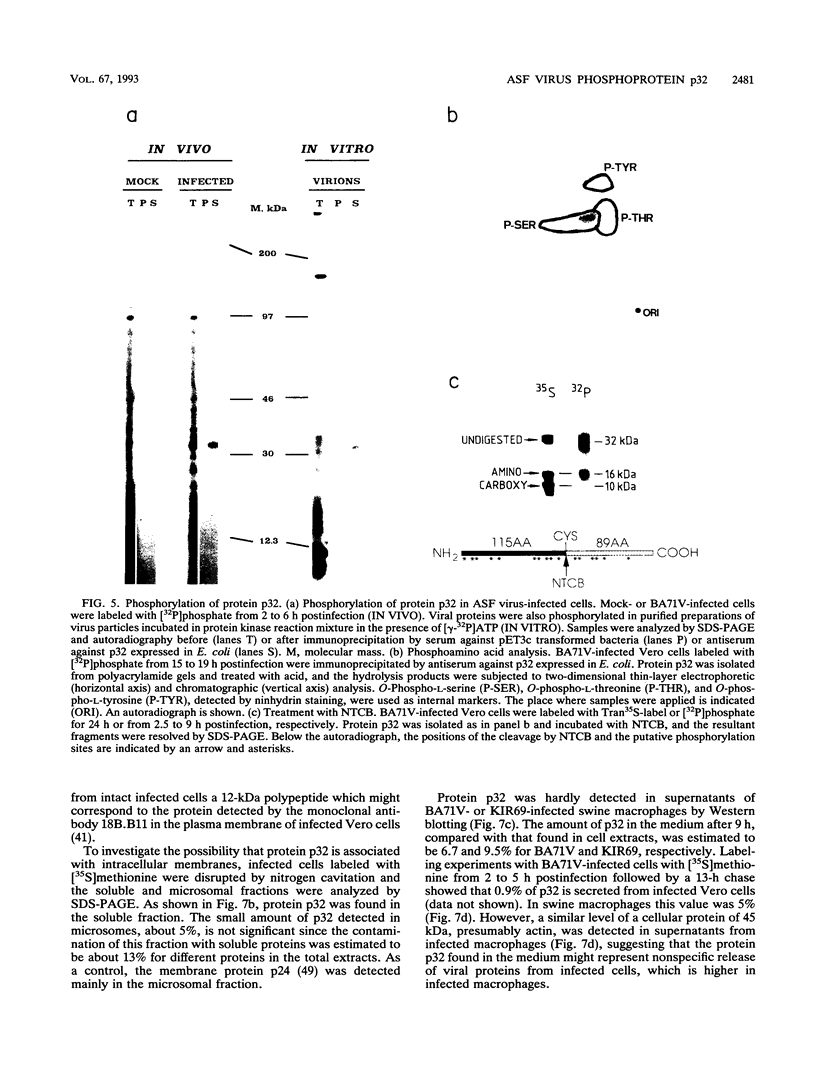
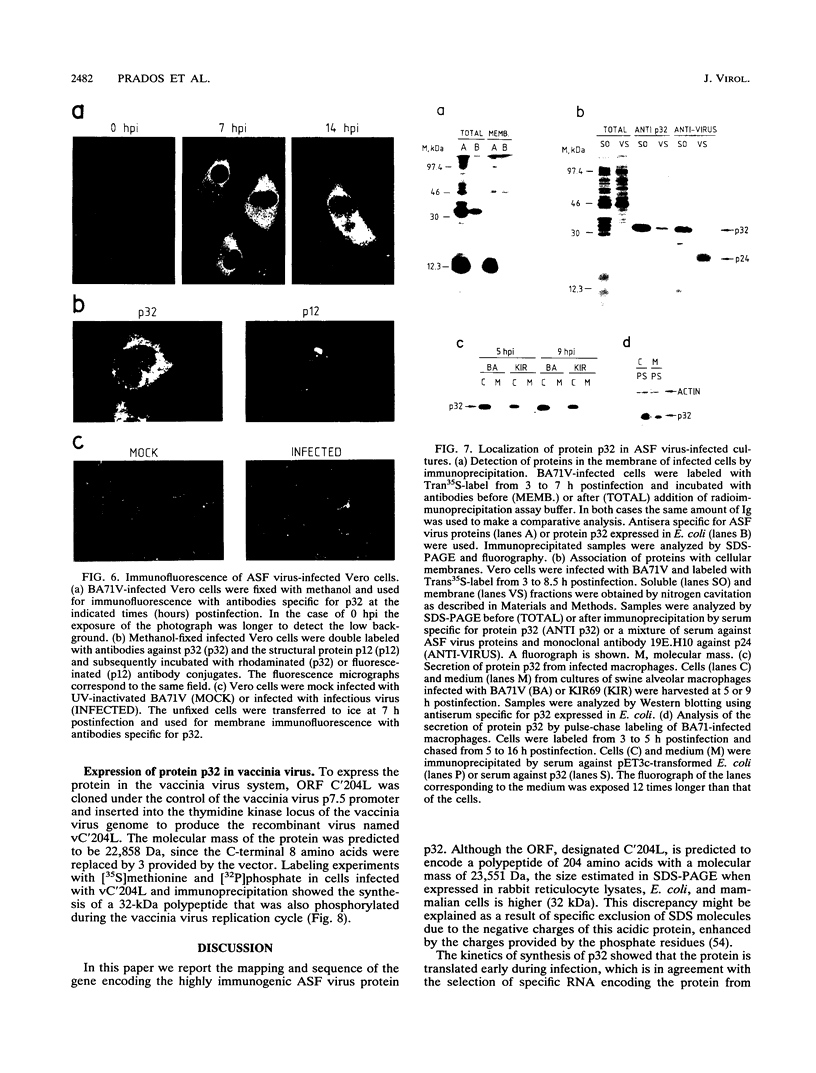
The gene encoding protein p32, the most abundant and immunogenic protein induced by African swine fever virus at early times of infection, has been mapped in the EcoRI C' fragment of the genome of the Vero cell-adapted virus strain BA71V. Sequencing analysis has shown the existence of an open reading frame, named C'204L, encoding 204 amino acids. The protein is phosphorylated in serine residues located in the 115 N-terminal amino acids and was phosphorylated when expressed in cells infected with a vaccinia virus recombinant. Protein p32 is not glycosylated in spite of the presence of two putative N-glycosylation sites in the deduced amino acid sequence of the polypeptide. Immunofluorescence experiments have shown that the protein is localized in the cytoplasm of infected cells and not in the plasma membrane. In addition, the protein has been found in the soluble fraction and not in microsomes from BA71V-infected Vero cells. Low levels of the protein have been detected in the medium from infected swine macrophages, which probably corresponds to nonspecific release of cytoplasmic proteins. The protein encoded by other virus isolates shows different electrophoretic mobilities, indicating variability of p32.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afonso C. L., Alcaraz C., Brun A., Sussman M. D., Onisk D. V., Escribano J. M., Rock D. L. Characterization of p30, a highly antigenic membrane and secreted protein of African swine fever virus. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):368–373. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90718-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguado B., Viñuela E., Alcamí A. African swine fever virus fatty acid acylated proteins. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):942–945. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90578-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcamí A., Angulo A., López-Otín C., Muñoz M., Freije J. M., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Amino acid sequence and structural properties of protein p12, an African swine fever virus attachment protein. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3860–3868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3860-3868.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcamí A., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Interaction of African swine fever virus with macrophages. Virus Res. 1990 Oct;17(2):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90071-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almazán F., Rodríguez J. M., Andrés G., Pérez R., Viñuela E., Rodriguez J. F. Transcriptional analysis of multigene family 110 of African swine fever virus. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6655–6667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6655-6667.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banham A. H., Smith G. L. Vaccinia virus gene B1R encodes a 34-kDa serine/threonine protein kinase that localizes in cytoplasmic factories and is packaged into virions. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):803–812. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90256-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco R., Agüero M., Almendral J. M., Viñuela E. Variable and constant regions in African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa A. L., Santarén J. F., Viñuela E. Production and titration of African swine fever virus in porcine alveolar macrophages. J Virol Methods. 1982 Jan;3(6):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa A. L., Sastre I., Viñuela E. African swine fever virus attachment protein. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2283–2289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2283-2289.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa A. L., del Val M., Santarén J. F., Viñuela E. Purification and properties of African swine fever virus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.337-344.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho Z. G., Rodrigues-Pousada C. African swine fever virus gene expression in infected Vero cells. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1343–1350. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer C. J. Studies to determine neutralizing antibody in sera from animals recovered from African swine fever and laboratory animals inoculated with African virus with adjuvants. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;20(2):164–179. doi: 10.1007/BF01241270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Barreno B., Sanz A., Nogal M. L., Viñuela E., Enjuanes L. Monoclonal antibodies of African swine fever virus: antigenic differences among field virus isolates and viruses passaged in cell culture. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):385–392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.385-392.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. M., Davison A. J., Lowe R. S., Bennett C. D., Ellis R. W. Identification and structure of the gene encoding gpII, a major glycoprotein of varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley V., Almendral J. M., Carbonero P., Beloso A., Viñuela E., Talavera A. Molecular cloning of African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Chen W., Broyles S. S. The vaccinia virus B1R gene product is a serine/threonine protein kinase. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2717–2723. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2717-2723.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Otín C., Simón-Mateo C., Martínez L., Viñuela E. Gly-Gly-X, a novel consensus sequence for the proteolytic processing of viral and cellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9107–9110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase phosphorylation site sequences and consensus specificity motifs: tabulations. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:62–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00127-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rempel R. E., Traktman P. Vaccinia virus B1 kinase: phenotypic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants and enzymatic characterization of recombinant proteins. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4413–4426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4413-4426.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revilla Y., Pena L., Viñuela E. A protein of molar mass 12 kDa incorporates into the membrane of ASF virus-infected cells. Virus Res. 1988 Sep;11(2):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome L. H., Garvin A. J., Allietta M. M., Neufeld E. F. Two species of lysosomal organelles in cultured human fibroblasts. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M. L., Rey-Campos J., Almendral J. M., Talavera A., Viñuela E. Transcription and translation maps of African swine fever virus. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):228–240. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M. L., Salas J., Viñuela E. Phosphorylation of African swine fever virus proteins in vitro and in vivo. Biochimie. 1988 May;70(5):627–635. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santarén J. F., Viñuela E. African swine fever virus-induced polypeptides in Vero cells. Virus Res. 1986 Sep;5(4):391–405. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz A., García-Barreno B., Nogal M. L., Viñuela E., Enjuanes L. Monoclonal antibodies specific for African swine fever virus proteins. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):199–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.199-206.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K. Solubilization and immune-detection of beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins carrying foreign antigenic determinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4077–4092. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarés E., Martinez J., Ruiz Gonzalvo F., Sánchez-Botija C. Proteins specified by African swine fever virus. II. Analysis of proteins in infected cells and antigenic properties. Arch Virol. 1980;66(2):119–132. doi: 10.1007/BF01314980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarés E., Martínez J., Martín E., Escribano J. M. Proteins specified by African Swine Fever virus. IV. Glycoproteins and phosphoproteins. Arch Virol. 1983;77(2-4):167–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01309265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano E., Maki M., Mori H., Hatanaka M., Marti T., Titani K., Kannagi R., Ooi T., Murachi T. Pig heart calpastatin: identification of repetitive domain structures and anomalous behavior in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1964–1972. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Val M., Carrascosa J. L., Viñuela E. Glycosylated components of African swine fever virus particles. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90369-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Val M., Viñuela E. Glycosylated components induced in African swine fever (ASF) virus-infected Vero cells. Virus Res. 1987 Jun;7(4):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]