Abstract
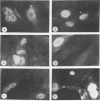
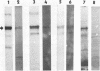
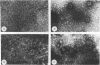
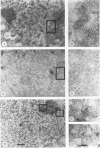
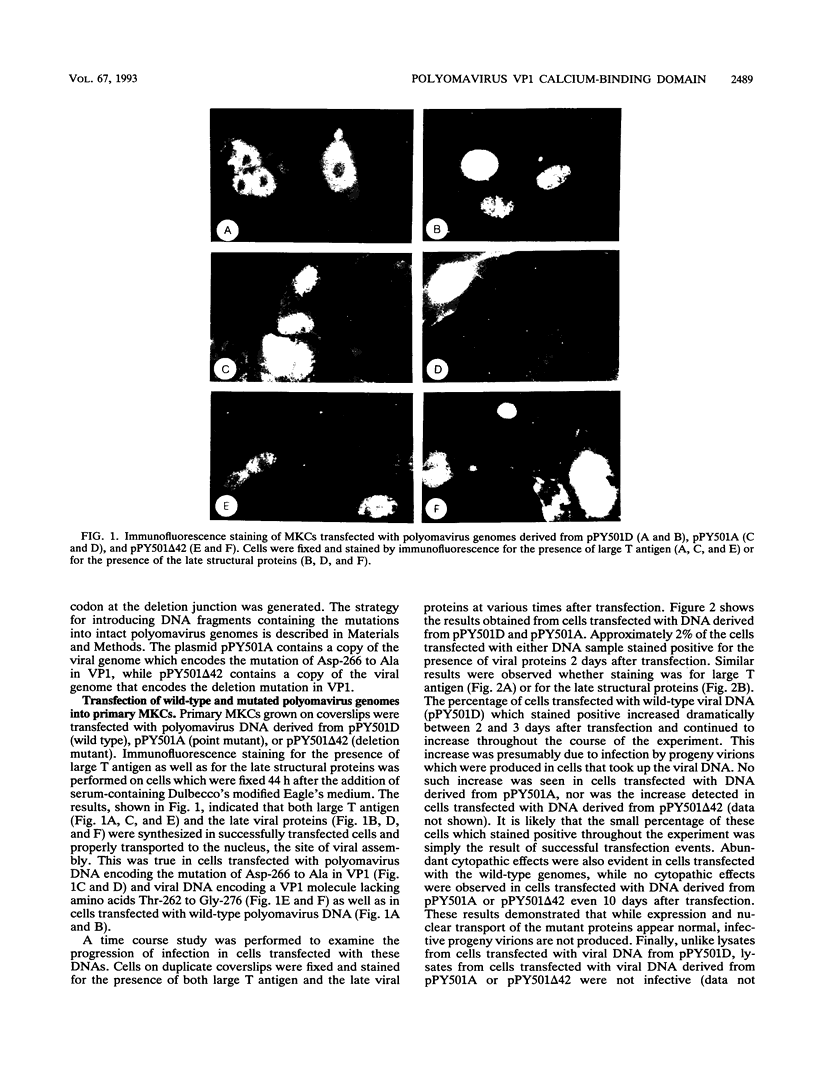
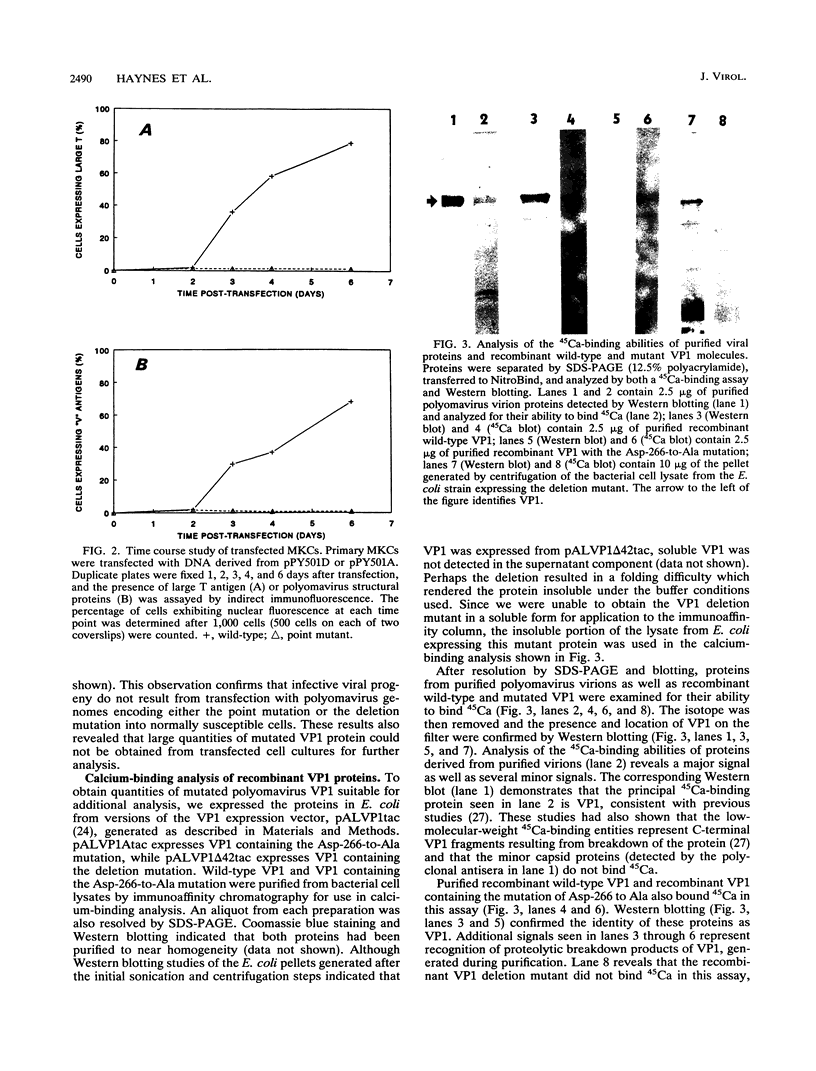
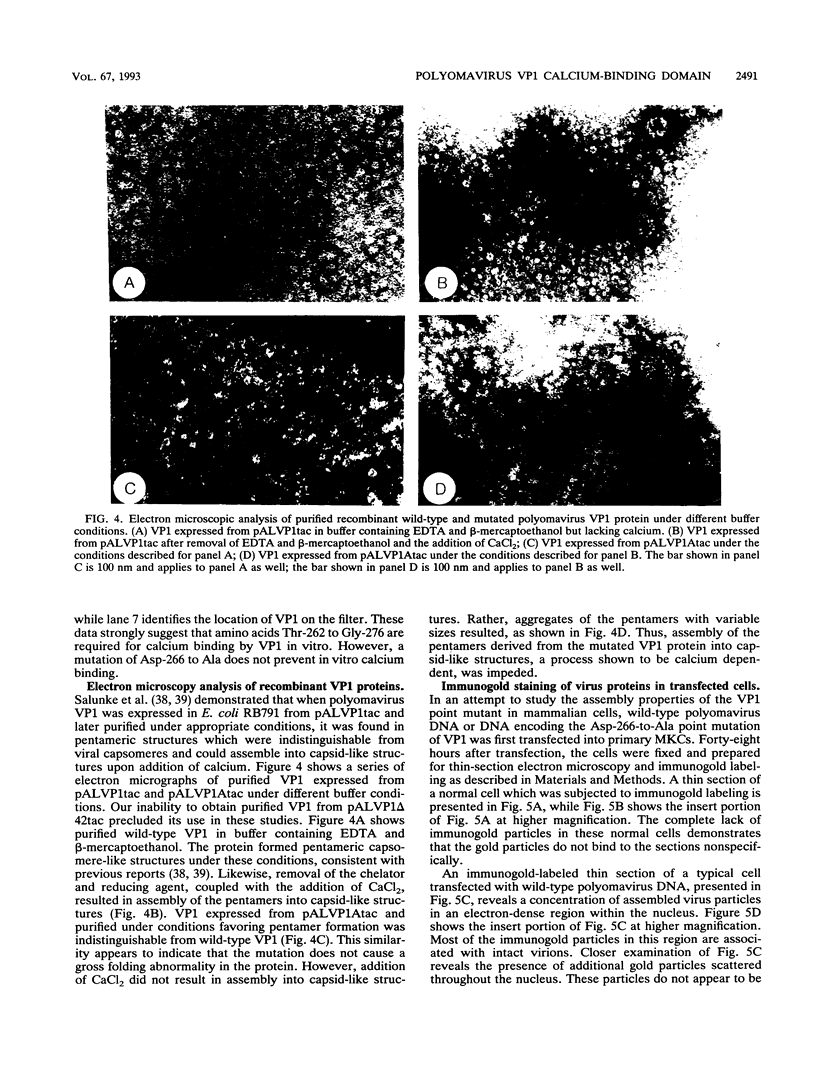
Calcium ions appear to play a major role in maintaining the structural integrity of the polyomavirus and are likely involved in the processes of viral uncoating and assembly. Previous studies demonstrated that a VP1 fragment extending from Pro-232 to Asp-364 has calcium-binding capabilities. This fragment contains an amino acid stretch from Asp-266 to Glu-277 which is quite similar in sequence to the amino acids that make up the calcium-binding EF hand structures found in many proteins. To assess the contribution of this domain to polyomavirus structural integrity, the effects of mutations in this region were examined by transfecting mutated viral DNA into susceptible cells. Immunofluorescence studies indicated that although viral protein synthesis occurred normally, infective viral progeny were not produced in cells transfected with polyomavirus genomes encoding either a VP1 molecule lacking amino acids Thr-262 through Gly-276 or a VP1 molecule containing a mutation of Asp-266 to Ala. VP1 molecules containing the deletion mutation were unable to bind 45Ca in an in vitro assay. Upon expression in Escherichia coli and purification by immunoaffinity chromatography, wild-type VP1 was isolated as pentameric, capsomere-like structures which could be induced to form capsid-like structures upon addition of CaCl2, consistent with previous studies. However, although VP1 containing the point mutation was isolated as pentamers which were indistinguishable from wild-type VP1 pentamers, addition of CaCl2 did not result in their assembly into capsid-like structures. Immunogold labeling and electron microscopy studies of transfected mammalian cells provided in vivo evidence that a mutation in this region affects the process of viral assembly.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders D. G., Consigli R. A. Chemical cleavage of polyomavirus major structural protein VP1: identification of cleavage products and evidence that the receptor moiety resides in the carboxy-terminal region. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):197–205. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.197-205.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders D. G., Consigli R. A. Comparison of nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated species of polyomavirus major capsid protein VP1 and identification of the major phosphorylation region. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):206–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.206-217.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Anders D. G., Trempy J., Consigli R. A. Differences in the subpopulations of the structural proteins of polyoma virions and capsids: biological functions of the multiple VP1 species. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):80–91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.80-91.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Consigli R. A. Differential adsorption of polyoma virions and capsids to mouse kidney cells and guinea pig erythrocytes. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):679–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.679-683.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Consigli R. A. Chromatographic separation of the polyoma virus proteins and renaturation of the isolated VP1 major capsid protein. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):436–442. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.436-442.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Kendall J. D., Consigli R. A. In vitro reassembly of infectious polyoma virions. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):640–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.640-647.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Winston V. D., Consigli R. A. Characterization of a DNA-protein complex and capsomere subunits derived from polyoma virus by treatment with ethyleneglycol-bis-N,N'-tetraacetic acid and dithiothreitol. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):193–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.193-204.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Winston V. D., Consigli R. A. Dissociation of polyoma virus by the chelation of calcium ions found associated with purified virions. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):717–724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.717-724.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D., Haynes J. I., 2nd, Brady J. N., Consigli R. A. The use of additive and subtractive approaches to examine the nuclear localization sequence of the polyomavirus major capsid protein VP1. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):821–827. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90615-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consigli R. A., Zabielski J., Weil R. Plaque assay for polyoma virus on primary mouse kidney cell cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):627–628. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.627-628.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham A. C., Haidar M. A. Cation binding by tobacco rattle virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):520–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90477-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham A. C., Hendry D. A. Cation binding by tobacco mosaic virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):510–519. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90476-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham A. C., Hendry D. A., Von Wechmar M. B. Does calcium ion binding control plant virus disassembly? Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):524–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90478-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattaey A. R., Consigli R. A. Synthesis, posttranslational modifications, and nuclear transport of polyomavirus major capsid protein VP1. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3168–3175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3168-3175.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Ballmer-Hofer K., Benjamin T. L. Virion assembly defect of polyomavirus hr-t mutants: underphosphorylation of major capsid protein VP1 before viral DNA encapsidation. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):311–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.311-316.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Salunke D. M., Caspar D. L. Site-directed mutation affecting polyomavirus capsid self-assembly in vitro. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):86–87. doi: 10.1038/329086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith G. R., Consigli R. A. Isolation and characterization of monopinocytotic vesicles containing polyomavirus from the cytoplasm of infected mouse kidney cells. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):77–85. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.77-85.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J., Kirchhausen T., Harrison S. C. Divalent cation sites in tomato bushy stunt virus. Difference maps at 2-9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 25;171(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80315-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Hynes R. O. The structure of human thrombospondin, an adhesive glycoprotein with multiple calcium-binding sites and homologies with several different proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1635–1648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt A. D., Roberts T. M., Garcea R. L. Polyoma virus major capsid protein, VP1. Purification after high level expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12803–12809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddington R. C., Yan Y., Moulai J., Sahli R., Benjamin T. L., Harrison S. C. Structure of simian virus 40 at 3.8-A resolution. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):278–284. doi: 10.1038/354278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., Consigli R. A. Differences in biological activity and structural protein VP1 phosphorylation of polyomavirus progeny resulting from infection of primary mouse kidney and primary mouse embryo cell cultures. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):509–515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.509-515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., Consigli R. A. Hydroxyproline in the major capsid protein VP1 of polyomavirus. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2881–2884. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2881-2884.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., Consigli R. A. Localization of calcium on the polyomavirus VP1 capsid protein. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2934–2937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2934-2937.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., Consigli R. A. Polyomavirus major capsid protein VP1 is modified by tyrosine sulfuration. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1708–1711. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1708-1711.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. L., Consigli R. A. Early events in polyoma virus infection: attachment, penetration, and nuclear entry. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):620–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.620-636.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillen J., Consigli R. A. Immunological reactivity of antisera to sodium dodecyl sulfate-derived polypeptides of polyoma virions. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1113–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1113-1120.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montross L., Watkins S., Moreland R. B., Mamon H., Caspar D. L., Garcea R. L. Nuclear assembly of polyomavirus capsids in insect cells expressing the major capsid protein VP1. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4991–4998. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4991-4998.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman G. R., Hobot J. A. Modern acrylics for post-embedding immunostaining techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Sep;35(9):971–981. doi: 10.1177/35.9.3302021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson A. J., Bricogne G., Harrison S. C. Structure of tomato busy stunt virus IV. The virus particle at 2.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 25;171(1):61–93. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder B. A., Robbins A. K., Crawford L. V. Phophorylation of polyoma and SV40 virus proteins. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):75–83. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salunke D. M., Caspar D. L., Garcea R. L. Polymorphism in the assembly of polyomavirus capsid protein VP1. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):887–900. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82735-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salunke D. M., Caspar D. L., Garcea R. L. Self-assembly of purified polyomavirus capsid protein VP1. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Consigli R. A. Transient inhibition of polyoma virus synthesis by Sendai virus (parainfluenza I). I. Demonstration and nature of the inhibition by inactivated virus. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1091-1097.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Griffin B. E. Polyoma virus DNA: complete nucleotide sequence of the gene which codes for polyoma virus capsid protein VP1 and overlaps the VP2/VP3 genes. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):619–630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.619-630.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strynadka N. C., James M. N. Crystal structures of the helix-loop-helix calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:951–998. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Sharief F., Vanaman T. C. The complete amino acid sequence of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein (calmodulin) of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):962–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. The amino acid sequence of troponin C from chicken skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):254–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80769-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston V. D., Bolen J. B., Consigli R. A. Isolation and characterization of polyoma uncoating intermediates from the nuclei of infected mouse cells. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1173–1181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1173-1181.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen L. K., Consigli R. A. Identification and protein analysis of polyomavirus assembly intermediates from infected primary mouse embryo cells. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90311-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen L. K., Consigli R. A. Improved infectivity of reassembled polyoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):337–341. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.337-341.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]