Abstract
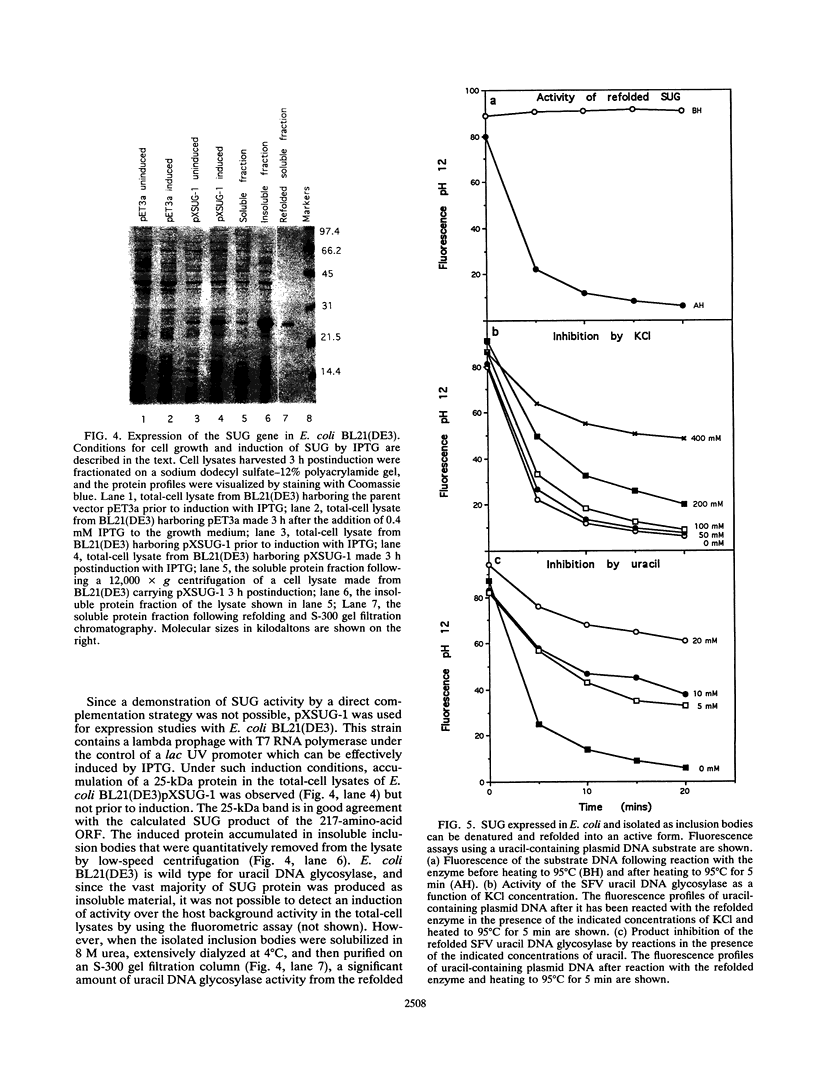
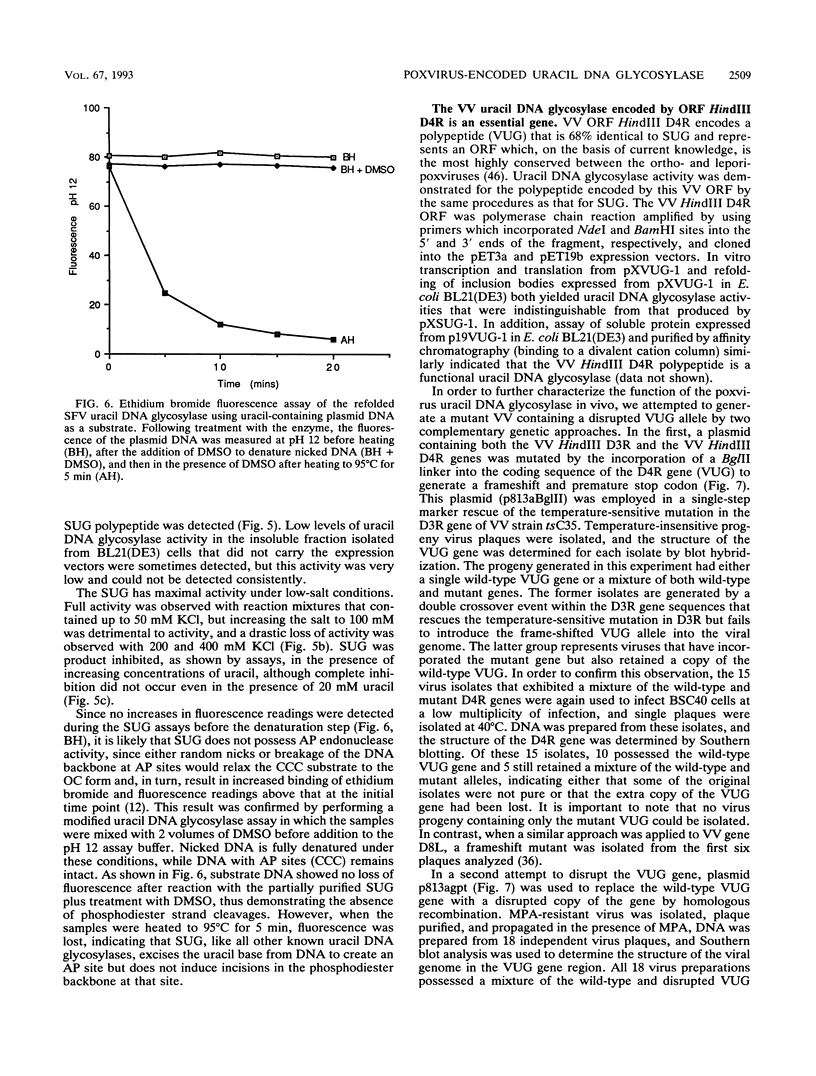
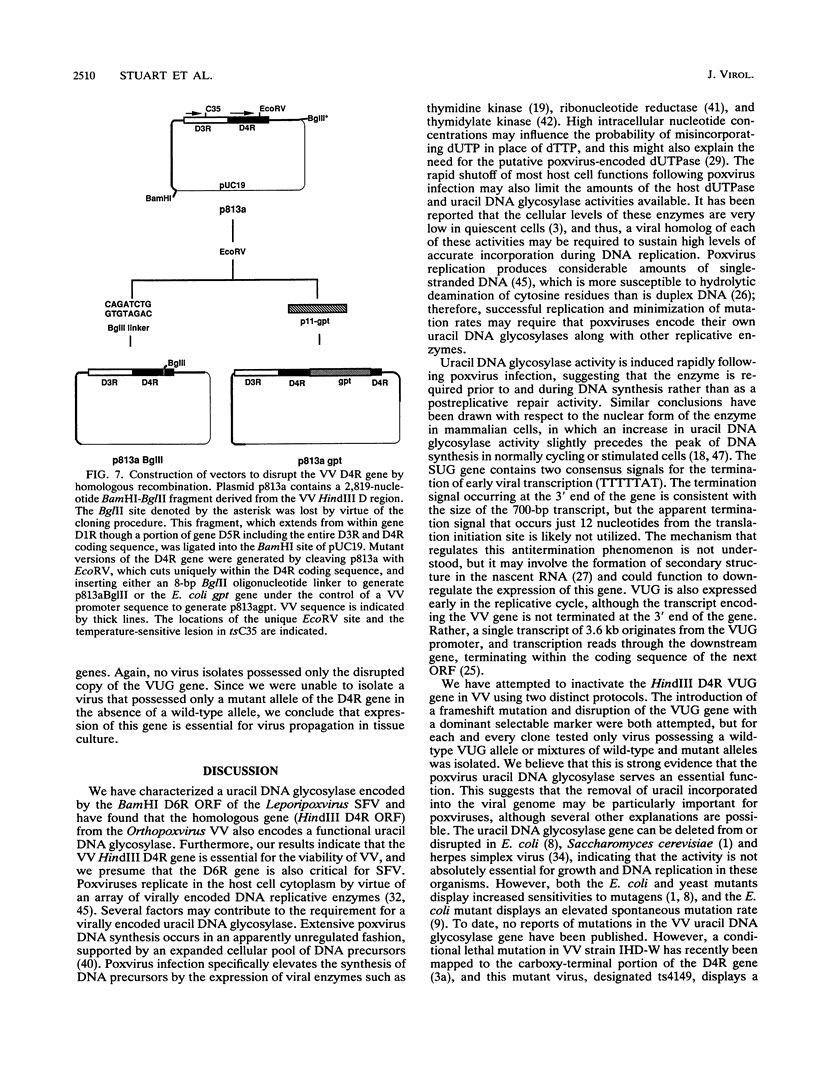
Infection of cultured mammalian cells with the Leporipoxvirus Shope fibroma virus (SFV) causes the induction of a novel uracil DNA glycosylase activity in the cytoplasms of the infected cells. The induction of this activity, early in infection, correlates with the early expression of the SFV BamHI D6R open reading frame which possesses significant protein sequence similarity to eukaryotic and prokaryotic uracil DNA glycosylases. The SFV BamHI D6R open reading frame and the homologous HindIII D4R open reading frame from the Orthopoxvirus vaccinia virus were cloned under the regulation of a phage T7 promoter and expressed in Escherichia coli as insoluble high-molecular-weight aggregates. During electrophoresis on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, the E. coli-expressed proteins migrate with an apparent molecular mass of 25 kDa. The insoluble protein aggregate generated by expression in E. coli was solubilized in urea and, following a subsequent refolding step, displayed the ability to excise uracil residues from double-stranded plasmid DNA substrates, with the subsequent formation of apyrimidinic sites. The viral enzyme, like all other characterized uracil DNA glycosylases, is active in the presence of high concentrations of EDTA, is substrate inhibited by uracil, and does not display any endonuclease activity. Attempts to inactivate the HindIII D4R gene of vaccinia virus by targeted insertion of a dominant xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase selection marker or direct insertion of a frame-shifted oligonucleotide were uniformly unsuccessful demonstrating that, unlike the uracil DNA glycosylase described for herpesviruses, the poxvirus enzyme is essential for virus viability.
Full text
PDF




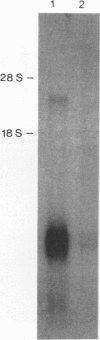
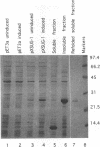
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgers P. M., Klein M. B. Selection by genetic transformation of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant defective for the nuclear uracil-DNA-glycosylase. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):905–913. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.905-913.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caradonna S. J., Cheng Y. C. Uracil DNA-glycosylase. Purification and properties of this enzyme isolated from blast cells of acute myelocytic leukemia patients. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2293–2300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool B. L., Sirover M. A. Immunocytochemical localization of the base excision repair enzyme uracil DNA glycosylase in quiescent and proliferating normal human cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):3029–3036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M., McFadden G. The role of telomeres in poxvirus DNA replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;163:71–92. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75605-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domena J. D., Mosbaugh D. W. Purification of nuclear and mitochondrial uracil-DNA glycosylase from rat liver. Identification of two distinct subcellular forms. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7320–7328. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley B., Hammond A., Deutsch W. A. The presence of uracil-DNA glycosylase in insects is dependent upon developmental complexity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11964–11967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B. K. Isolation of insertion, deletion, and nonsense mutations of the uracil-DNA glycosylase (ung) gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):689–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.689-695.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B. K., Weiss B. Specific mutator effects of ung (uracil-DNA glycosylase) mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):750–755. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.750-755.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyster L. M., Niles E. G. Genetic and biochemical characterization of vaccinia virus genes D2L and D3R which encode virion structural proteins. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):455–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90586-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito J., Condit R., Obijeski J. The preparation of orthopoxvirus DNA. J Virol Methods. 1981 Feb;2(3):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. H., Bugeja F. X., Yacyshyn B. J., Morgan A. R. Rapid sensitive fluorescence assays for DNA endonucleases and DNA glycosylases. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;62(12):1275–1282. doi: 10.1139/o84-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Moss B. Escherichia coli gpt gene provides dominant selection for vaccinia virus open reading frame expression vectors. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1849–1854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1849-1854.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C., Parks R. J., Lauzon M. L., Evans D. H. Heteroduplex DNA formation is associated with replication and recombination in poxvirus-infected cells. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):7–18. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulian M., Bleile B., Tseng B. Y. Methotrexate-induced misincorporation of uracil into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1956–1960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P. K., Sirover M. A. Stimulation of the nuclear uracil DNA glycosylase in proliferating human fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1981 Aug;41(8):3133–3136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Ball L. A. Mapping and identification of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):403–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.403-409.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Guarino L. A., Kates J. R. Vaccinia virus replication. I. Requirement for the host-cell nucleus. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):705–715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.705-715.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. T., Bjursell G. Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pools in herpes simplex type 1 infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Apr;31(1):101–113. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-1-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge J., Langridge P., Bergquist P. L. Extraction of nucleic acids from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Apr;103(2):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Chen G. J., Bourgeois N., Davidson K., Condit R. C., Niles E. G. Structure of the transcription initiation and termination sequences of seven early genes in the vaccinia virus HindIII D fragment. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):64–79. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Sirover M. A. Physical association of base excision repair enzymes with parental and replicating DNA in BHK-21 cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):3037–3044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Heat-induced deamination of cytosine residues in deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3405–3410. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden G., Dales S. Biogenesis of poxviruses: preliminary characterization of conditional lethal mutants of vaccinia virus defective in DNA synthesis. Virology. 1980 May;103(1):68–79. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J. Protein sequence comparisons show that the 'pseudoproteases' encoded by poxviruses and certain retroviruses belong to the deoxyuridine triphosphatase family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4105–4110. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Siegler K., Mauro D. J., Seal G., Wurzer J., deRiel J. K., Sirover M. A. A human nuclear uracil DNA glycosylase is the 37-kDa subunit of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8460–8464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Chlebek J. Uracil-DNA glycosylase in insects. Drosophila and the locust. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9911–9914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W. The role of the host cell nucleus in vaccinia virus morphogenesis. Virus Res. 1987 Sep;8(3):173–191. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullaney J., Moss H. W., McGeoch D. J. Gene UL2 of herpes simplex virus type 1 encodes a uracil-DNA glycosylase. J Gen Virol. 1989 Feb;70(Pt 2):449–454. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-2-449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G., Condit R. C., Caro P., Davidson K., Matusick L., Seto J. Nucleotide sequence and genetic map of the 16-kb vaccinia virus HindIII D fragment. Virology. 1986 Aug;153(1):96–112. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G., Seto J. Vaccinia virus gene D8 encodes a virion transmembrane protein. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3772–3778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3772-3778.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakumi K., Sekiguchi M. Structures and functions of DNA glycosylases. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90003-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomai J., Kornberg A. Deoxyuridine triphosphatase of Escherichia coli. Purification, properties, and use as a reagent to reduce uracil incorporation into DNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3305–3312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slabaugh M. B., Howell M. L., Wang Y., Mathews C. K. Deoxyadenosine reverses hydroxyurea inhibition of vaccinia virus growth. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2290–2298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2290-2298.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slabaugh M. B., Johnson T. L., Mathews C. K. Vaccinia virus induces ribonucleotide reductase in primate cells. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.507-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., de Carlos A., Chan Y. S. Vaccinia virus encodes a thymidylate kinase gene: sequence and transcriptional mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7581–7590. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traktman P. The enzymology of poxvirus DNA replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;163:93–123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75605-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollberg T. M., Siegler K. M., Cool B. L., Sirover M. A. Isolation and characterization of the human uracil DNA glycosylase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8693–8697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worrad D. M., Caradonna S. Identification of the coding sequence for herpes simplex virus uracil-DNA glycosylase. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4774–4777. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4774-4777.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]