Abstract
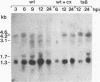
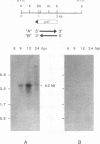
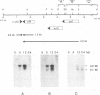
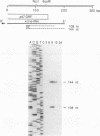
A 2.8-kb region of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome was sequenced and found to contain an open reading frame (p47) which was capable of rescuing a previously characterized temperature-sensitive mutant, ts317 (S. Partington, H. Yu, A. Lu, and E. B. Carstens, Virology 157:91-102, 1990). Transcriptional mapping demonstrated that an early 4.2-kb RNA encoded the p47 open reading frame and probably overlapped the 39K delayed-early gene. The p47 open reading frame was cloned behind the polyhedrin promoter in a baculovirus transfer plasmid, which was then used to prepare a recombinant baculovirus overexpressing the p47 polypeptide. The overexpressed polypeptide was used to prepare p47-specific monoclonal antibodies. These antibodies detected a polypeptide of 47 kDa in A. californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus-infected cells, demonstrating that p47 is expressed as an authentic viral product. The p47 gene product was localized to the nucleus of infected cells, supporting the hypothesis that it is involved in regulating viral transcription at late times postinfection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blissard G. W., Rohrmann G. F. Baculovirus diversity and molecular biology. Annu Rev Entomol. 1990;35:127–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.35.010190.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Crawford A. M., Faulkner P. Genetic Analysis of a Baculovirus, Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus I. Isolation of Temperature-Sensitive Mutants and Assortment into Complementation Groups. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):190–198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.190-198.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstens E. B., Tjia S. T., Doerfler W. Infectious DNA from Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran M. A., Carstens E. B., Eaton B. T., Faulkner P. Molecular Cloning and Physical Mapping of Restriction Endonuclease Fragments of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus DNA. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):940–946. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.940-946.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Faulkner P. Bromodeoxyuridine-induced mutants of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus defective in occlusion body formation. J Gen Virol. 1982 Oct;62(Pt 2):369–373. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-2-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandson M. A., Gordon J., Carstens E. B. Size and map locations of early transcription products on the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome. Virology. 1985 Apr 15;142(1):12–23. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. D., Carstens E. B. Phenotypic characterization and physical mapping of a temperature-sensitive mutant of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus defective in DNA synthesis. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Smith M. W. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the 39K gene region of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90266-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huh N. E., Weaver R. F. Identifying the RNA polymerases that synthesize specific transcripts of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):195–201. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Bohlmeyer D. A., Garcia A., Jr Requirements for nuclear localization and supramolecular assembly of a baculovirus polyhedrin protein. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):795–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90551-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. H., Miller L. K. Isolation, Complementation, and Initial Characterization of Temperature-Sensitive Mutants of the Baculovirus Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):240–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.240-252.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A., Carstens E. B. Nucleotide sequence of a gene essential for viral DNA replication in the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):336–347. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90500-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A., Carstens E. B. Transcription analysis of the EcoRI D region of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus identifies an early 4-kilobase RNA encoding the essential p143 gene. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):655–663. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.655-663.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K. Gene expression in insects. Biotechnical applications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991 Dec 27;646:231–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb18584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi B. G., Miller L. K. Regulation of host RNA levels during baculovirus infection. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):515–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partington S., Yu H., Lu A., Carstens E. B. Isolation of temperature sensitive mutants of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus: phenotype characterization of baculovirus mutants defective in very late gene expression. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90189-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjia S. T., Carstens E. B., Doerfler W. Infection of Spodoptera frugiperda cells with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus II. The viral DNA and the kinetics of its replication. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):399–409. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomalski M. D., Wu J. G., Miller L. K. The location, sequence, transcription, and regulation of a baculovirus DNA polymerase gene. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):591–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vialard J., Lalumière M., Vernet T., Briedis D., Alkhatib G., Henning D., Levin D., Richardson C. Synthesis of the membrane fusion and hemagglutinin proteins of measles virus, using a novel baculovirus vector containing the beta-galactosidase gene. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):37–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.37-50.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood H. A., Granados R. R. Genetically engineered baculoviruses as agents for pest control. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:69–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]