Abstract
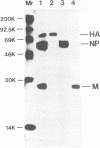
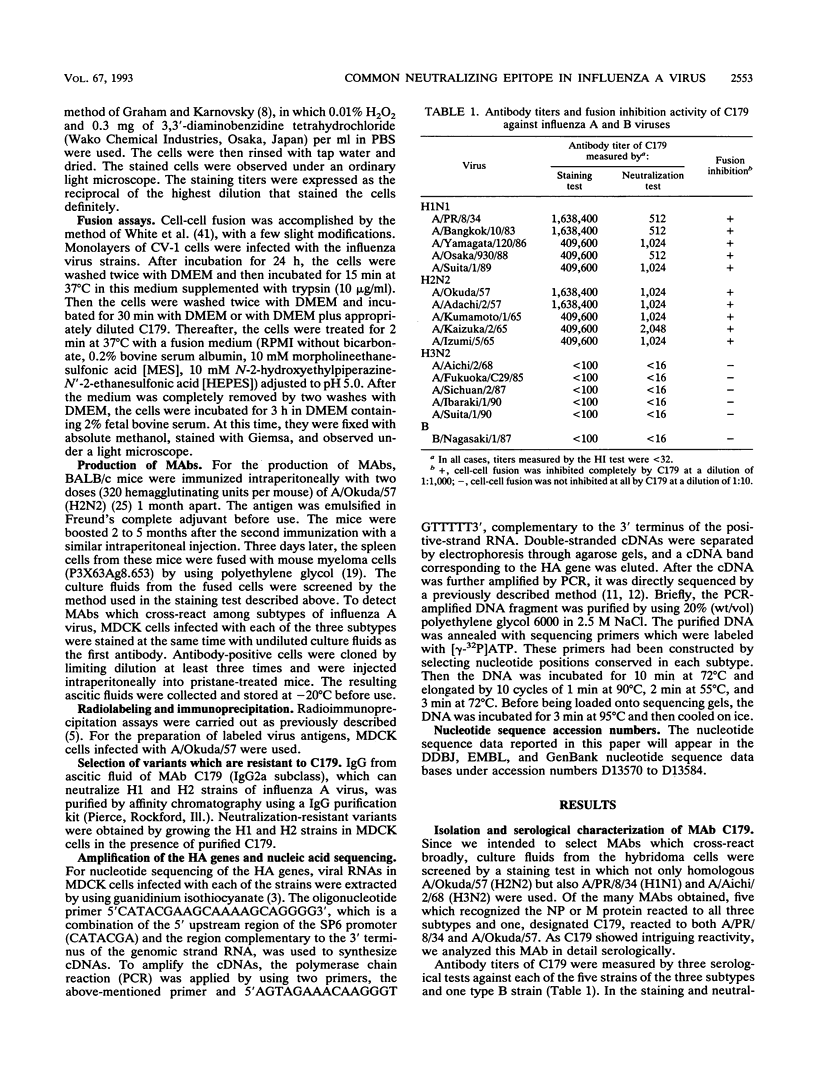
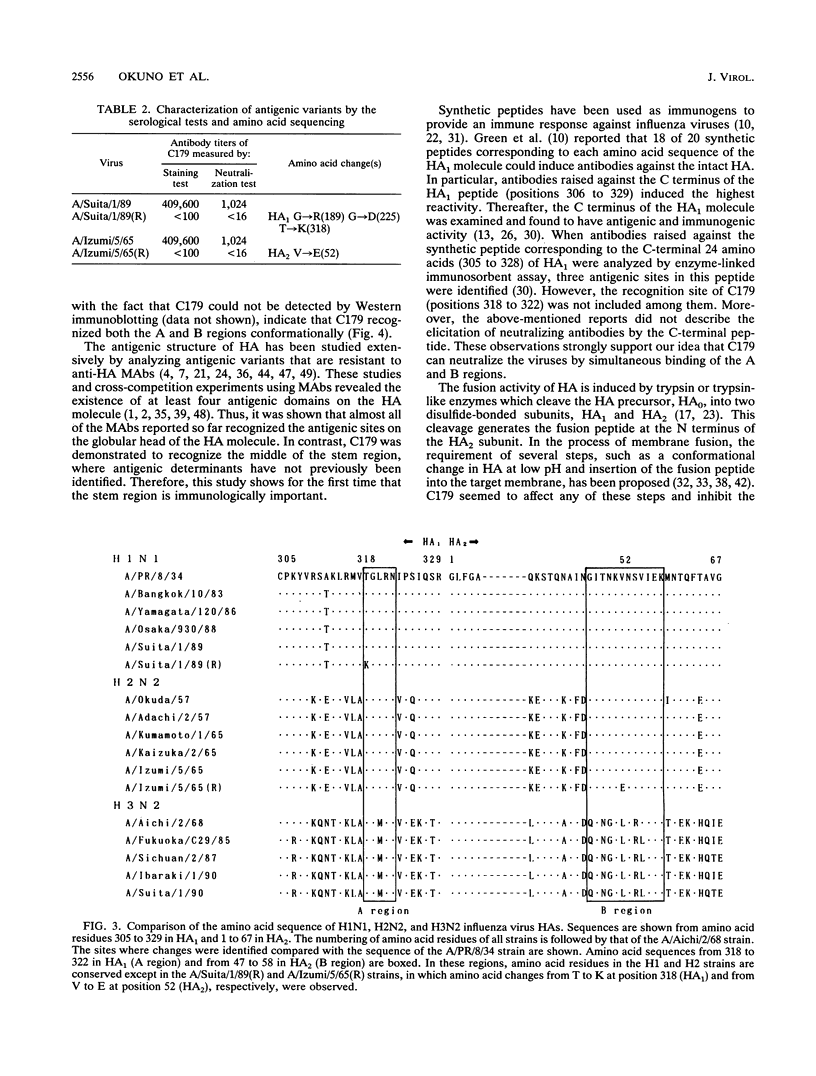
When mice were immunized with the A/Okuda/57 (H2N2) strain of influenza virus, a unique monoclonal antibody designated C179 was obtained. Although C179 was confirmed to recognize the hemagglutinin (HA) glycoprotein by immunoprecipitation assays, it did not show hemagglutination inhibition activity to any of the strains of the three subtypes of influenza A virus. However, it neutralized all of the H1 and H2 strains but not the H3 strains. Moreover, it inhibited polykaryon formation induced by the H1 and H2 strains but not by the H3 strains. Two antigenic variants against C179 were obtained, and nucleotide sequence analysis revealed that amino acid sequences, from 318 to 322 of HA1 and from 47 to 58 of HA2, conserved among H1 and H2 strains were responsible for the recognition of C179. Since the two sites were located close to each other at the middle of the stem region of the HA molecule, C179 seemed to recognize these sites conformationally. These data indicated that binding of C179 to the stem region of HA inhibits the fusion activity of HA and thus results in virus neutralization and inhibition of cell-cell fusion. This is the first report which describes the presence of conserved antigenic sites on HA not only in a specific subtype but also in two subtypes of influenza A virus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breschkin A. M., Ahern J., White D. O. Antigenic determinants of influenza virus hemagglutinin. VIII. Topography of the antigenic regions of influenza virus hemagglutinin determined by competitive radioimmunoassay with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):130–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caton A. J., Brownlee G. G., Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W. The antigenic structure of the influenza virus A/PR/8/34 hemagglutinin (H1 subtype). Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels P. S., Jeffries S., Yates P., Schild G. C., Rogers G. N., Paulson J. C., Wharton S. A., Douglas A. R., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. The receptor-binding and membrane-fusion properties of influenza virus variants selected using anti-haemagglutinin monoclonal antibodies. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantas J. R., Jr, Okuno Y., Asada H., Tamura M., Takahashi M., Tanishita O., Takahashi Y., Kurata T., Yamanishi K. Characterization of glycoproteins of viruses causing hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) using monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):379–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard W., Webster R. G. Antigenic drift in influenza A viruses. I. Selection and characterization of antigenic variants of A/PR/8/34 (HON1) influenza virus with monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):383–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves P. N., Schulman J. L., Young J. F., Palese P. Preparation of influenza virus subviral particles lacking the HA1 subunit of hemagglutinin: unmasking of cross-reactive HA2 determinants. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):106–116. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90465-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isegawa Y., Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Ueda S. A VP4 sequence highly conserved in human rotavirus strain AU-1 and feline rotavirus strain FRV-1. J Gen Virol. 1992 Aug;73(Pt 8):1939–1946. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-8-1939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isegawa Y., Sheng J., Sokawa Y., Yamanishi K., Nakagomi O., Ueda S. Selective amplification of cDNA sequence from total RNA by cassette-ligation mediated polymerase chain reaction (PCR): application to sequencing 6.5 kb genome segment of hantavirus strain B-1. Mol Cell Probes. 1992 Dec;6(6):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(92)90043-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. C., Tang X. L., Brown L. E., Murray J. M., White D. O., Tregear G. W. Antigenic determinants of influenza virus hemagglutinin. XII. the epitopes of a synthetic peptide representing the C-terminus of HA1. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):625–632. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kida H., Brown L. E., Webster R. G. Biological activity of monoclonal antibodies to operationally defined antigenic regions on the hemagglutinin molecule of A/Seal/Massachusetts/1/80 (H7N7) influenza virus. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):38–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90375-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kida H., Yoden S., Kuwabara M., Yanagawa R. Interference with a conformational change in the haemagglutinin molecule of influenza virus by antibodies as a possible neutralization mechanism. Vaccine. 1985 Sep;3(3 Suppl):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(85)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourne E. D. Comparative efficacy of neuraminidase-specific and conventional influenza virus vaccines in induction of antibody to neuraminidase in humans. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):384–394. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knossow M., Daniels R. S., Douglas A. R., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Three-dimensional structure of an antigenic mutant of the influenza virus haemagglutinin. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):678–680. doi: 10.1038/311678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Dopheide T. A., Ward C. W. Amino acid sequence changes in the haemagglutinin of A/Hong Kong (H3N2) influenza virus during the period 1968--77. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):454–457. doi: 10.1038/283454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Gerhard W., Ward C. W., Dopheide T. A. Antigenic drift in type A influenza virus: sequence differences in the hemagglutinin of Hong Kong (H3N2) variants selected with monoclonal hybridoma antibodies. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):226–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90540-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G. M., Shapira M., Arnon R. Anti-influenza response achieved by immunization with a synthetic conjugate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):569–573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Nakajima K., Kendal A. P. Identification of the binding sites to monoclonal antibodies on A/USSR/90/77 (H1N1) hemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic drift in H1N1 influenza viruses. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):116–127. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90538-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestorowicz A., Tregear G. W., Southwell C. N., Martyn J., Murray J. M., White D. O., Jackson D. C. Antibodies elicited by influenza virus hemagglutinin fail to bind to synthetic peptides representing putative antigenic sites. Mol Immunol. 1985 Feb;22(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(85)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno Y., Tanaka K., Baba K., Maeda A., Kunita N., Ueda S. Rapid focus reduction neutralization test of influenza A and B viruses in microtiter system. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1308–1313. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1308-1313.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R. R., Teillaud J. L., Scharff M. D. Monoclonal antibodies: a powerful tool for selecting and analyzing mutations in antigens and antibodies. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:389–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond F. L., Caton A. J., Cox N. J., Kendal A. P., Brownlee G. G. The antigenicity and evolution of influenza H1 haemagglutinin, from 1950-1957 and 1977-1983: two pathways from one gene. Virology. 1986 Jan 30;148(2):275–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoofs P. G., Geysen H. M., Jackson D. C., Brown L. E., Tang X. L., White D. O. Epitopes of an influenza viral peptide recognized by antibody at single amino acid resolution. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Jibson M., Muller G., Arnon R. Immunity and protection against influenza virus by synthetic peptide corresponding to antigenic sites of hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2461–2465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Delfino J. M., Richards F. M., Helenius A. The HA2 subunit of influenza hemagglutinin inserts into the target membrane prior to fusion. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18404–18410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., White J. M., Helenius A. Intermediates in influenza induced membrane fusion. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4231–4241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood P. A. Mapping of antigenic changes in the haemagglutinin of Hong Kong influenza (H3N2) strains using a large panel of monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):153–169. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood P. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Receptor-binding characteristics of monoclonal antibody-selected antigenic variants of influenza virus. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):206–208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.206-208.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeyen M., Fang R., Jou W. M., Devos R., Huylebroeck D., Saman E., Fiers W. Antigenic drift between the haemagglutinin of the Hong Kong influenza strains A/Aichi/2/68 and A/Victoria/3/75. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):771–776. doi: 10.1038/286771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Brown L. E., Jackson D. C. Changes in the antigenicity of the hemagglutinin molecule of H3 influenza virus at acidic pH. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):587–599. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G. Determination of the number of nonoverlapping antigenic areas on Hong Kong (H3N2) influenza virus hemagglutinin with monoclonal antibodies and the selection of variants with potential epidemiological significance. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90372-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M., Wilson I. A. Anti-peptide antibodies detect steps in a protein conformational change: low-pH activation of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):2887–2896. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A., Gething M. J. Haemagglutinin of influenza virus expressed from a cloned gene promotes membrane fusion. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):658–659. doi: 10.1038/300658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Skehel J. J. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):373–378. doi: 10.1038/289373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Fields S., Brownlee G. G. Nucleotide sequence of the haemagglutinin gene of a human influenza virus H1 subtype. Nature. 1981 Jul 2;292(5818):72–75. doi: 10.1038/292072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Caton A. J., Gerhard W. Selection of influenza A virus adsorptive mutants by growth in the presence of a mixture of monoclonal antihemagglutinin antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):623–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.623-628.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W. Antigenic characterization of viruses by monoclonal antibodies. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:185–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Webster R. G., Gerhard W. U. Antigenic variation in three distinct determinants of an influenza type A haemagglutinin molecule. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):246–248. doi: 10.1038/279246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoden S., Kida H., Yanagawa R. An avian influenza virus of which infectivity is neutralized by antisera lacking hemagglutination-inhibition activity. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1982;74(2-3):205–210. doi: 10.1007/BF01314713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]