Abstract
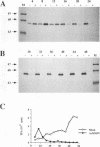
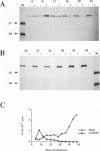
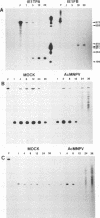
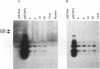
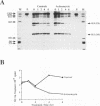
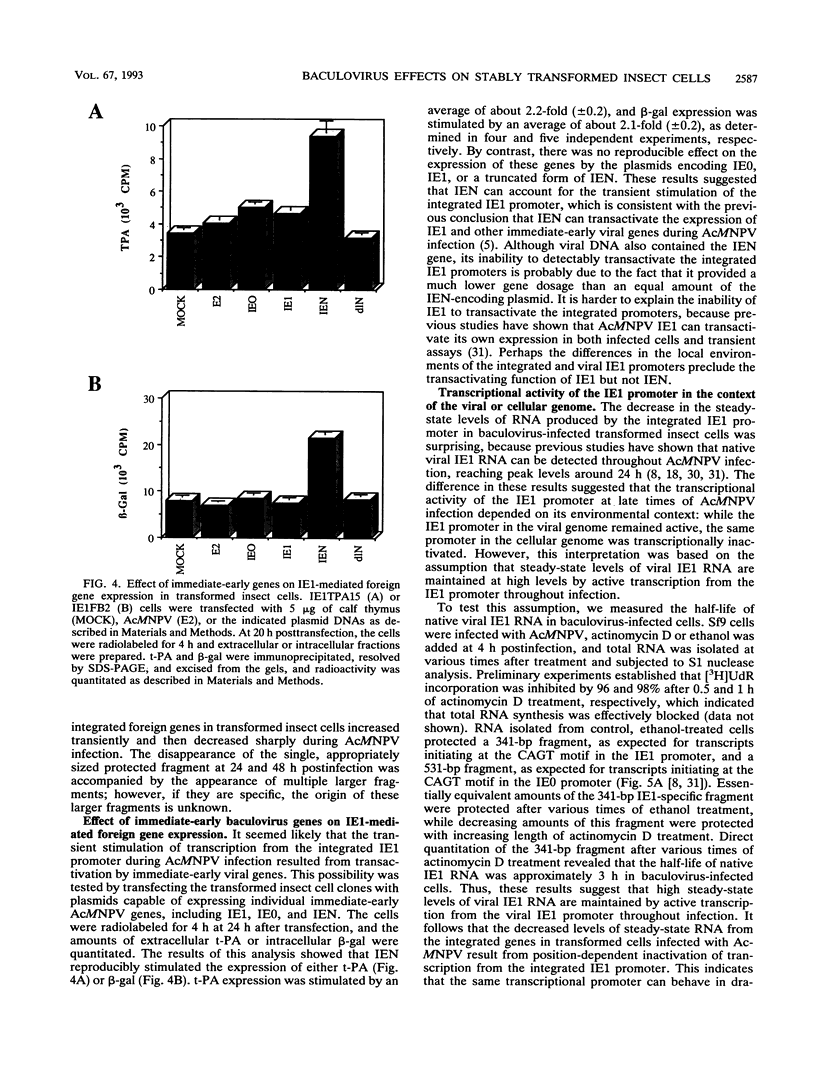
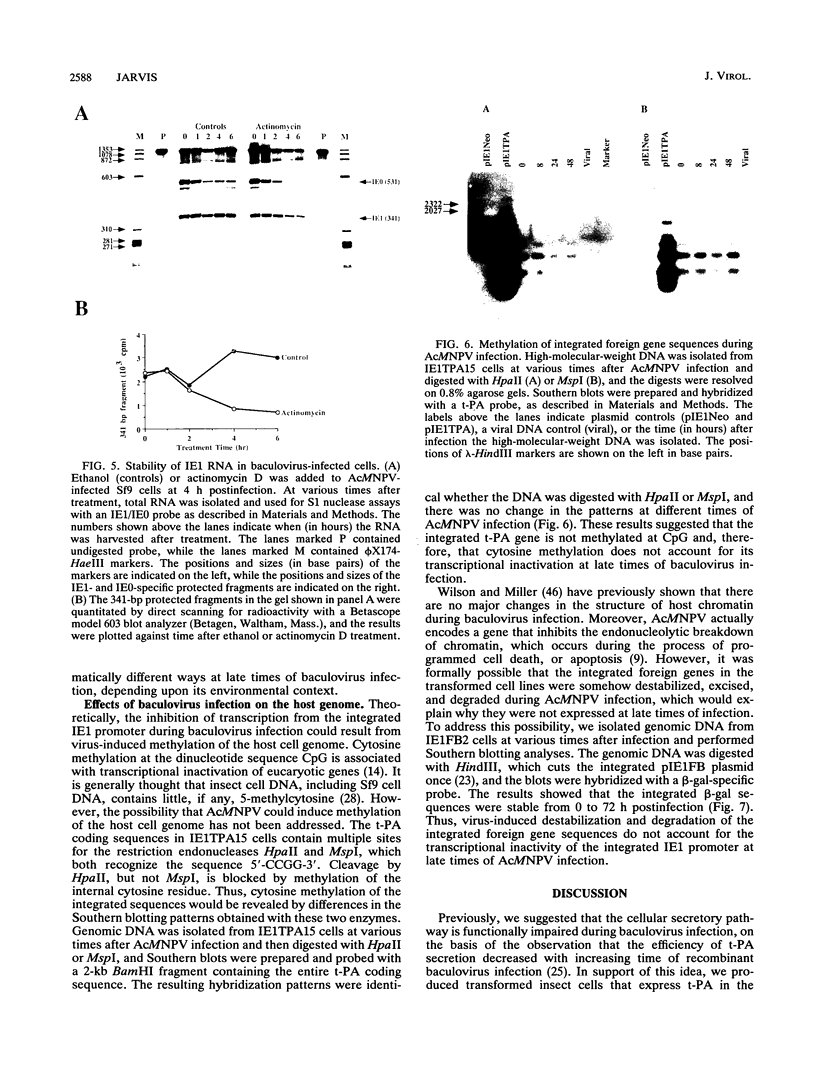
Previously, we produced transformed insect cell lines that can express a selected foreign protein constitutively, in the absence of baculovirus infection (D. L. Jarvis, J. G. W. Fleming, G. R. Kovacs, M. D. Summers, and L. A. Guarino, Bio/Technology 8:950-955, 1990). These cells contain stably integrated copies of chimeric genes consisting of the promoter from an immediate-early baculovirus gene, IE1, and the sequences encoding either human tissue plasminogen activator or Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase. Transcription of the integrated genes in these cells is specifically controlled by the IE1 promoter. The purpose of this study was to determine how baculovirus infection influences IE1-mediated foreign protein production by these stably transformed insect cell lines. The results showed that viral infection transiently stimulated and then strongly inhibited the production of both tissue plasminogen activator, a secreted protein, and beta-galactosidase, an intracellular protein. These effects reflected virus-induced changes in the steady-state levels of RNA produced by the integrated genes. Transient assays showed that expression of the viral IEN gene alone could account for the increased levels of RNA observed early in infection. The precise mechanism accounting for the decreased levels of RNA observed later in infection was not determined. However, we obtained evidence that the native IE1 promoter remains active throughout infection, which suggested indirectly that the integrated IE1 promoter is transcriptionally inactivated at late times of baculovirus infection. Thus, the same promoter behaved quite differently late in infection, depending on its local environment. Neither methylation nor degradation appeared to be responsible for inactivating IE1-mediated expression of the integrated genes. The significance of these results with respect to the baculovirus-host interaction and the practical applications of stably transformed insect cell lines are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butters T. D., Hughes R. C. Isolation and characterization of mosquito cell membrane glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters T. D., Hughes R. C., Vischer P. Steps in the biosynthesis of mosquito cell membrane glycoproteins and the effects of tunicamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):672–686. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. D., Summers M. D., Guarino L. A. Molecular analysis of a baculovirus regulatory gene. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):279–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90671-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstens E. B., Tjia S. T., Doerfler W. Infection of Spodoptera frugiperda cells with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus I. Synthesis of intracellular proteins after virus infection. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):386–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm G. E., Henner D. J. Multiple early transcripts and splicing of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus IE-1 gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3193–3200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3193-3200.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clem R. J., Fechheimer M., Miller L. K. Prevention of apoptosis by a baculovirus gene during infection of insect cells. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1388–1390. doi: 10.1126/science.1962198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D. J., Bretthauer R. K., Castellino F. J. alpha-Mannosidase-catalyzed trimming of high-mannose glycans in noninfected and baculovirus-infected Spodoptera frugiperda cells (IPLB-SF-21AE). A possible contributing regulatory mechanism for assembly of complex-type oligosaccharides in infected cells. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 15;30(41):9811–9815. doi: 10.1021/bi00105a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D. J., Castellino F. J. Asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing in lepidopteran insect cells. Temporal dependence of the nature of the oligosaccharides assembled on asparagine-289 of recombinant human plasminogen produced in baculovirus vector infected Spodoptera frugiperda (IPLB-SF-21AE) cells. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6165–6174. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D. J., Fraser M. J., Castellino F. J. Oligosaccharide processing in the expression of human plasminogen cDNA by lepidopteran insect (Spodoptera frugiperda) cells. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5584–5590. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and its functional significance: studies on the adenovirus system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;108:79–98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69370-0_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Nissen M. S. Gene organization and transcription of TED, a lepidopteran retrotransposon integrated within the baculovirus genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3067–3077. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of a trans-activating gene required for expression of a baculovirus delayed-early gene. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.563-571.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Nucleotide sequence and temporal expression of a baculovirus regulatory gene. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2091–2099. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2091-2099.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Robbins P. W. Regulation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing. Oligosaccharide processing in Aedes albopictus mosquito cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2375–2382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Bohlmeyer D. A., Garcia A., Jr Requirements for nuclear localization and supramolecular assembly of a baculovirus polyhedrin protein. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):795–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90551-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Fleming J. A., Kovacs G. R., Summers M. D., Guarino L. A. Use of early baculovirus promoters for continuous expression and efficient processing of foreign gene products in stably transformed lepidopteran cells. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Oct;8(10):950–955. doi: 10.1038/nbt1090-950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Summers M. D. Glycosylation and secretion of human tissue plasminogen activator in recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):214–223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knebel D., Lübbert H., Doerfler W. The promoter of the late p10 gene in the insect nuclear polyhedrosis virus Autographa californica: activation by viral gene products and sensitivity to DNA methylation. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1301–1306. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs G. R., Guarino L. A., Graham B. L., Summers M. D. Identification of spliced baculovirus RNAs expressed late in infection. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90534-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs G. R., Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Novel regulatory properties of the IE1 and IE0 transactivators encoded by the baculovirus Autographa californica multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5281–5288. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5281-5288.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda K., Geyer H., Geyer R., Doerfler W., Klenk H. D. The oligosaccharides of influenza virus hemagglutinin expressed in insect cells by a baculovirus vector. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):418–429. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda K., Veit M., Klenk H. D. Retarded processing of influenza virus hemagglutinin in insect cells. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K. Baculoviruses as gene expression vectors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:177–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi B. G., Miller L. K. Regulation of host RNA levels during baculovirus infection. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):515–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberge C., Bastin M. Site-directed mutagenesis of the polyomavirus genome: replication-defective large T mutants with increased immortalization potential. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):144–150. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Fraser M. J., Summers M. D. Molecular Engineering of the Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Genome: Deletion Mutations Within the Polyhedrin Gene. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):584–593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.584-593.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. D., Smith G. E. Baculovirus structural polypeptides. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):390–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90257-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. L., Goodwin R. H., Tompkins G. J., McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro. 1977 Apr;13(4):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02615077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Miller L. K. Changes in the nucleoprotein complexes of a baculovirus DNA during infection. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]