Abstract
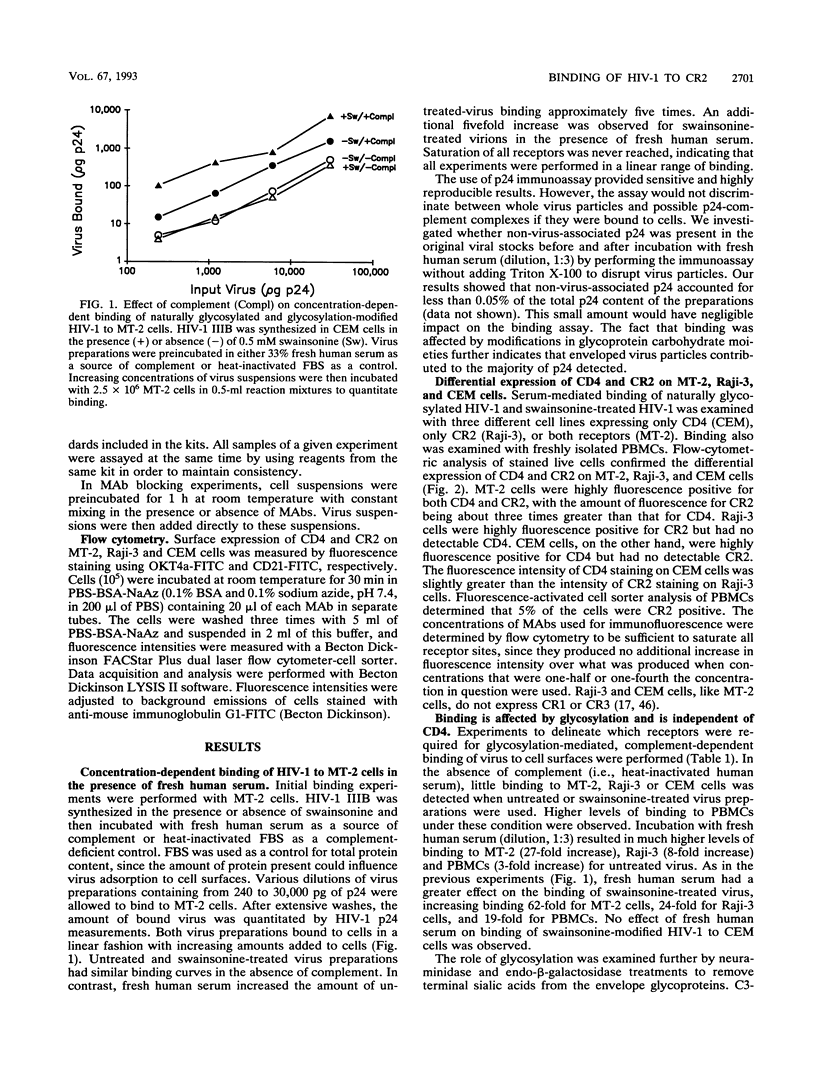
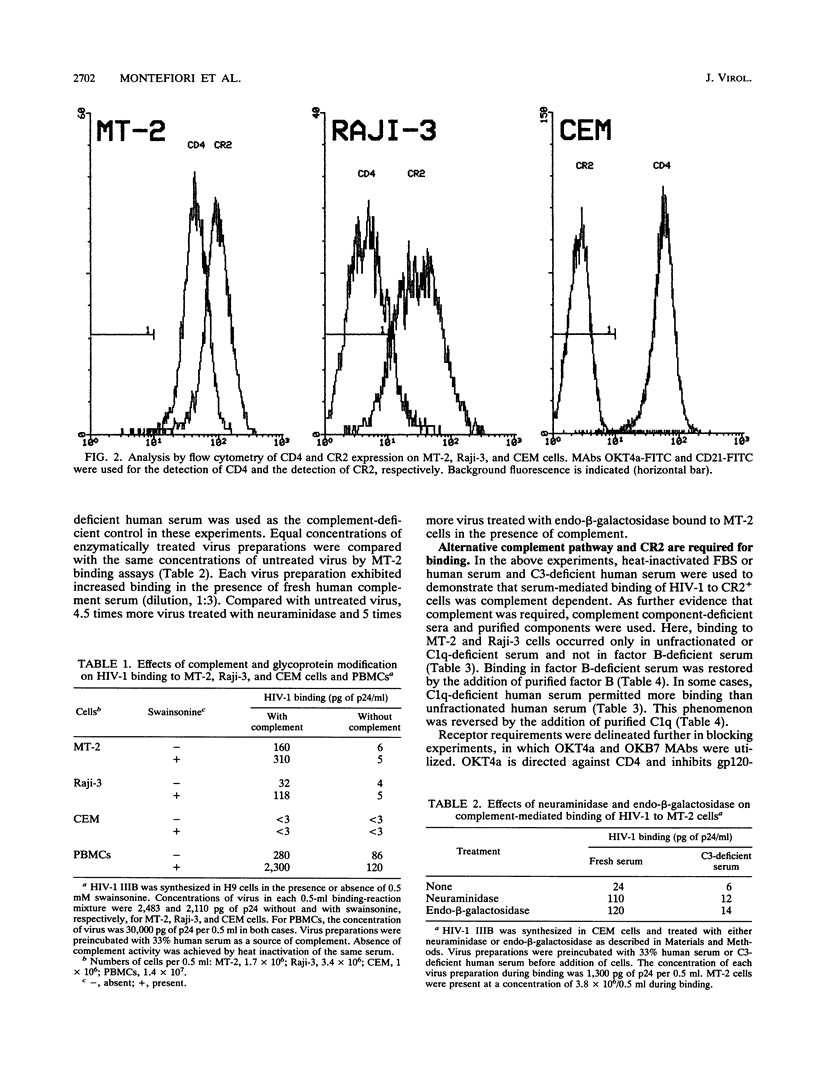
Particulate glycoproteins lacking sialic acid, such as desialylated enveloped viruses, readily activate complement through the alternative pathway. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) contains two heavily glycosylated and partially sialylated envelope glycoproteins: a surface gp120 and a transmembrane gp41. The abilities of naturally glycosylated HIV-1 and glycosylation-modified HIV-1 to interact with the complement system were examined with a biological assay which measured the binding of whole virus particles to cells expressing CR2 (CD21), the complement receptor found naturally in abundance on follicular dendritic cells and immature B cells. HIV-1 IIIB was synthesized in the presence or absence of the mannosidase II inhibitor, swainsonine, to give rise to high-mannose-type, nonsialylated, nonfucosylated carbohydrate moieties. The virus also was treated with neuraminidase or endo-beta-galactosidase to remove terminal sialic acids. An enzyme immunoassay specific for HIV-1 p24 core protein was used to quantitate the amount of virus bound to cell surfaces. Virus particles incubated with 1:3-diluted, fresh HIV-1-negative human serum as a source of complement readily bound to MT-2 (CD4+ CR2+) and Raji-3 (CD4- CR2+) cells but not to CEM (CD4+ CR2-) cells, suggesting that the virus bound to CR2 independently of CD4. Compared with heat-inactivated or C3-deficient sera, fresh complement increased binding by as much as 62 times for naturally glycosylated virus, and 5 times more than this for glycosylation-modified virus. Similar observations were made with freshly isolated, non-mitogen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Additional evidence that HIV-1 bound to CR2 independently of CD4 was provided by the fact that binding was blocked by monoclonal antibody OKB7 (anti-CR2) but not by OKT4a (anti-CD4). Also, the virus bound to transfected K562 cells (CD4-) which expressed recombinant human CR2 but did not bind to untransfected K562 cells. Results obtained with complement component-deficient sera indicated that binding required the alternative complement pathway. Raji-3 and transfected K562 cells could not be infected with HIV-1 in the presence of complement, suggesting that utilization of CR2 as a receptor in the absence of CD4 does not allow virus entry. The demonstration of CR2 as a receptor for HIV-1 in the presence of complement, together with the ability to enhance binding by desialylation, provides new insights into mechanisms of HIV-1-induced immunity and immunopathogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Fearon D. T. Structure and function of the complement receptors, CR1 (CD35) and CR2 (CD21). Adv Immunol. 1989;46:183–219. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J. S., Coligan J. E., Barin F., McLane M. F., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Lee T. H., Essex M. Major glycoprotein antigens that induce antibodies in AIDS patients are encoded by HTLV-III. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1091–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.2986290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banapour B., Sernatinger J., Levy J. A. The AIDS-associated retrovirus is not sensitive to lysis or inactivation by human serum. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):268–271. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90392-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjouad A., Gluckman J. C., Rochat H., Montagnier L., Bahraoui E. Influence of carbohydrate moieties on the immunogenicity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 recombinant gp160. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2473–2483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2473-2483.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohnsack J. F., Cooper N. R. CR2 ligands modulate human B cell activation. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2569–2576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer V., Desgranges C., Trabaud M. A., Fischer E., Kazatchkine M. D. Complement mediates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of a human T cell line in a CD4- and antibody-independent fashion. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1151–1158. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. H., Fearon D. T. CD19: lowering the threshold for antigen receptor stimulation of B lymphocytes. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):105–107. doi: 10.1126/science.1373518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy J. T., Jourdian G. W., Roseman S. The sialic acids. VI. Purification and properties of sialidase from Clostridium perfringens. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3501–3506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R., Moore M. D., Nemerow G. R. Immunobiology of CR2, the B lymphocyte receptor for Epstein-Barr virus and the C3d complement fragment. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:85–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolin R., Graham B. S., Greenberg S. B., Tacket C. O., Belshe R. B., Midthun K., Clements M. L., Gorse G. J., Horgan B. W., Atmar R. L. The safety and immunogenicity of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) recombinant gp160 candidate vaccine in humans. NIAID AIDS Vaccine Clinical Trials Network. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Jan 15;114(2):119–127. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-2-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebenbichler C. F., Thielens N. M., Vornhagen R., Marschang P., Arlaud G. J., Dierich M. P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activates the classical pathway of complement by direct C1 binding through specific sites in the transmembrane glycoprotein gp41. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1417–1424. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Inhibitors of the biosynthesis and processing of N-linked oligosaccharide chains. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:497–534. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The human immunodeficiency virus: infectivity and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):617–622. doi: 10.1126/science.3277274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation by membrane sialic acid of beta1H-dependent decay-dissociation of amplification C3 convertase of the alternative complement pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1971–1975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingeroth J. D., Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Strominger J. L., Biro P. A., Fearon D. T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer H., Holschbach C., Hunsmann G., Schneider J. Carbohydrates of human immunodeficiency virus. Structures of oligosaccharides linked to the envelope glycoprotein 120. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11760–11767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gras G. S., Dormont D. Antibody-dependent and antibody-independent complement-mediated enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in a human, Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B-lymphocytic cell line. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):541–545. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.541-545.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Koyanagi Y., Yamamoto N. Infection of human T-lymphotropic virus type-I (HTLV-I)-bearing MT-4 cells with HTLV-III (AIDS virus): chronological studies of early events. Virology. 1985 Oct 30;146(2):272–281. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Yoshiyama H., Yamamoto N. Effect of heat and fresh human serum on the infectivity of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III evaluated with new bioassay systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):908–911. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.908-911.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbison M. A., Kim S. Y., Gillis J. M., Hammer S. M. Effect of the calcium channel blocker verapamil on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in lymphoid cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):53–60. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebell T., Ahearn J. M., Fearon D. T. Suppression of the immune response by a soluble complement receptor of B lymphocytes. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):102–105. doi: 10.1126/science.1718035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman B., Wiersma E. J., Kinoshita T. In vivo inhibition of the antibody response by a complement receptor-specific monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):665–668. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. L., Griffin D. E., Winkelstein J. A. Host modification of Sindbis virus sialic acid content influences alternative complement pathway activation and virus clearance. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1740–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. L., Wolinsky J. S., Winkelstein J. A. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by mumps infected cells: relationship to viral neuraminidase activity. Arch Virol. 1986;87(3-4):181–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01315298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., Humphrey J. H. The generation of memory cells. I. The role of C3 in the generation of B memory cells. Immunology. 1977 Jul;33(1):31–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Ganu V. S., Hirani S., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mapping of the C3d receptor (CR2)-binding site and a neoantigenic site in the C3d domain of the third component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4235–4239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. M. AIDS--the second decade: a global perspective. J Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;165(2):245–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. R., Yuryev A., Kalli K. R., Fearon D. T., Ahearn J. M. Determination of the structural basis for selective binding of Epstein-Barr virus to human complement receptor type 2. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1299–1311. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Maza O., Crabb E., Mitsuyasu R. T., Fahey J. L., Giorgi J. V. Infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is associated with an in vivo increase in B lymphocyte activation and immaturity. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3720–3724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto A. K., Kopicky-Burd J., Carter R. H., Tuveson D. A., Tedder T. F., Fearon D. T. Intersection of the complement and immune systems: a signal transduction complex of the B lymphocyte-containing complement receptor type 2 and CD19. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):55–64. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Pickering R. J., Caliguiri L. A. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by enveloped viruses containing limited amounts of sialic acid. Virology. 1981 Oct 30;114(2):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuochi T., Spellman M. W., Larkin M., Solomon J., Basa L. J., Feizi T. Carbohydrate structures of the human-immunodeficiency-virus (HIV) recombinant envelope glycoprotein gp120 produced in Chinese-hamster ovary cells. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 1;254(2):599–603. doi: 10.1042/bj2540599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montefiori D. C., Robinson W. E., Jr, Mitchell W. M. Antibody-independent, complement-mediated enhancement of HIV-1 infection by mannosidase I and II inhibitors. Antiviral Res. 1989 Apr;11(3):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(89)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montefiori D. C., Robinson W. E., Jr, Mitchell W. M. Role of protein N-glycosylation in pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9248–9252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Butini L., Pizzo P. A., Schnittman S. M., Kotler D. P., Fauci A. S. Lymphoid organs function as major reservoirs for human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9838–9842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisinger E. C., Vogetseder W., Berzow D., Köfler D., Bitterlich G., Lehr H. A., Wachter H., Dierich M. P. Complement-mediated enhancement of HIV-1 infection of the monoblastoid cell line U937. AIDS. 1990 Oct;4(10):961–965. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199010000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynes M., Aubert J. P., Cohen J. H., Audouin J., Tricottet V., Diebold J., Kazatchkine M. D. Human follicular dendritic cells express CR1, CR2, and CR3 complement receptor antigens. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2687–2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Gillespie D. H., Mitchell W. M. Complement-mediated, antibody-dependent enhancement of HIV-1 infection in vitro is characterized by increased protein and RNA syntheses and infectious virus release. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(1):33–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M. Complement-mediated antibody-dependent enhancement of HIV-1 infection requires CD4 and complement receptors. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):600–604. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90449-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J. The role of the CD4 antigen in HIV infection and immune pathogenesis. AIDS. 1988;2 (Suppl 1):S11–S16. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198800001-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Ng Y. C., Peters D. K. The role of complement and its receptor in the elimination of immune complexes. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 21;315(8):488–495. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608213150805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scudder P., Hanfland P., Uemura K., Feizi T. Endo-beta-D-galactosidases of Bacteroides fragilis and Escherichia freundii hydrolyze linear but not branched oligosaccharide domains of glycolipids of the neolacto series. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6586–6592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senaldi G., Peakman M., McManus T., Davies E. T., Tee D. E., Vergani D. Activation of the complement system in human immunodeficiency virus infection: relevance of the classical pathway to pathogenesis and disease severity. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1227–1232. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Cosentino M., Leitman-Klinman S. F., Klinman D. M. Human immunodeficiency virus infection induces both polyclonal and virus-specific B cell activation. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):561–566. doi: 10.1172/JCI115621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel H., Herbst H., Niedobitek G., Foss H. D., Stein H. Follicular dendritic cells are a major reservoir for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in lymphoid tissues facilitating infection of CD4+ T-helper cells. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jan;140(1):15–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tausk F. A., McCutchan A., Spechko P., Schreiber R. D., Gigli I. Altered erythrocyte C3b receptor expression, immune complexes, and complement activation in homosexual men in varying risk groups for acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):977–982. doi: 10.1172/JCI112688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner-Racz K., Racz P., Bofill M., Schulz-Meyer A., Dietrich M., Kern P., Weber J., Pinching A. J., Veronese-Dimarzo F., Popovic M. HTLV-III/LAV viral antigens in lymph nodes of homosexual men with persistent generalized lymphadenopathy and AIDS. Am J Pathol. 1986 Apr;123(1):9–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese F. D., DeVico A. L., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Characterization of gp41 as the transmembrane protein coded by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope gene. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1402–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.2994223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R., Ellerbeck E., Garrison L., Midthun K., Clements M. L., Clayman B., Fernie B., Smith G. Characterization of serum antibody responses to recombinant HIV-1 gp160 vaccine by enzyme immunoassay. NIAID AIDS Vaccine Clinical Trials Network. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Nov;6(11):1251–1256. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins B. A., Dorn H. H., Kelly W. B., Armstrong R. C., Potts B. J., Michaels F., Kufta C. V., Dubois-Dalcq M. Specific tropism of HIV-1 for microglial cells in primary human brain cultures. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2200125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Fearon D. T. Identification of a 145,000 Mr membrane protein as the C3d receptor (CR2) of human B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):881–885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Toothaker L. E., Smith J. A., Weis J. H., Fearon D. T. Structure of the human B lymphocyte receptor for C3d and the Epstein-Barr virus and relatedness to other members of the family of C3/C4 binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1047–1066. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Platt J. L., Kay N. E. Monoclonal antibodies to the 140,000 mol wt glycoprotein of B lymphocyte membranes (CR2 receptor) initiates proliferation of B cells in vitro. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):824–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintsch J., Chaignat C. L., Braun D. G., Jeannet M., Stalder H., Abrignani S., Montagna D., Clavijo F., Moret P., Dayer J. M. Safety and immunogenicity of a genetically engineered human immunodeficiency virus vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):219–225. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


