Abstract
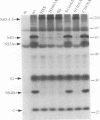
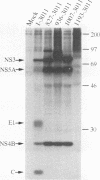
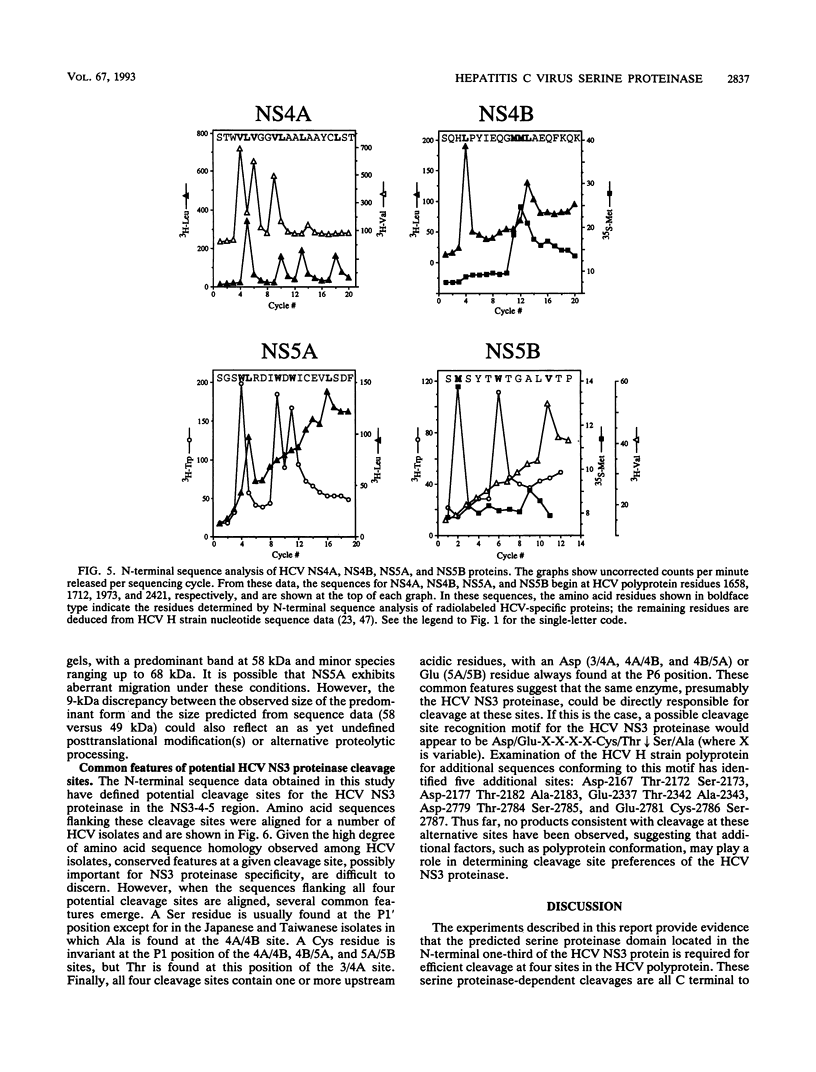
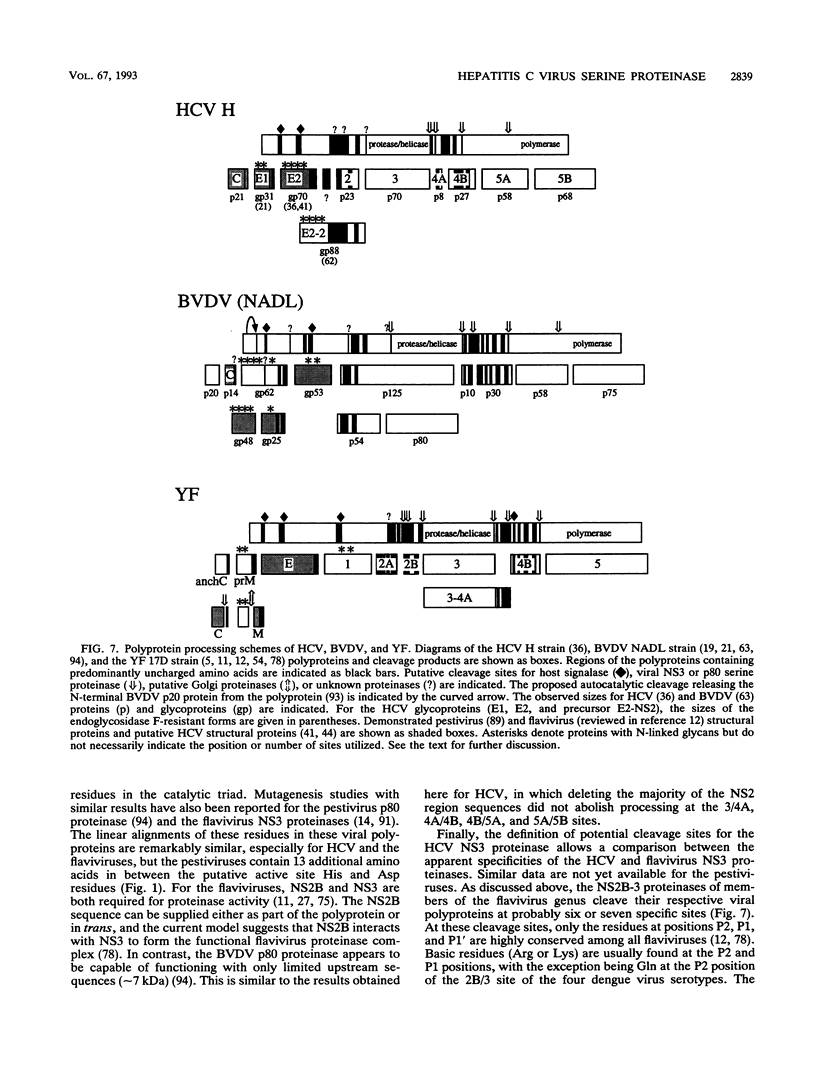
Processing of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) H strain polyprotein yields at least nine distinct cleavage products: NH2-C-E1-E2-NS2-NS3-NS4A-NS4B-NS5A-NS5B-CO OH. As described in this report, site-directed mutagenesis and transient expression analyses were used to study the role of a putative serine proteinase domain, located in the N-terminal one-third of the NS3 protein, in proteolytic processing of HCV polyproteins. All four cleavages which occur C terminal to the proteinase domain (3/4A, 4A/4B, 4B/5A, and 5A/5B) were abolished by substitution of alanine for either of two predicted residues (His-1083 and Ser-1165) in the proteinase catalytic triad. However, such substitutions have no observable effect on cleavages in the structural region or at the 2/3 site. Deletion analyses suggest that the structural and NS2 regions of the polyprotein are not required for the HCV NS3 proteinase activity. NS3 proteinase-dependent cleavage sites were localized by N-terminal sequence analysis of NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B. Sequence comparison of the residues flanking these cleavage sites for all sequenced HCV strains reveals conserved residues which may play a role in determining HCV NS3 proteinase substrate specificity. These features include an acidic residue (Asp or Glu) at the P6 position, a Cys or Thr residue at the P1 position, and a Ser or Ala residue at the P1' position.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter H. J., Purcell R. H., Holland P. V., Popper H. Transmissible agent in non-A, non-B hepatitis. Lancet. 1978 Mar 4;1(8062):459–463. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Purcell R. H., Shih J. W., Melpolder J. C., Houghton M., Choo Q. L., Kuo G. Detection of antibody to hepatitis C virus in prospectively followed transfusion recipients with acute and chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 30;321(22):1494–1500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911303212202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J., Hadler S. C., Judson F. N., Mares A., Alexander W. J., Hu P. Y., Miller J. K., Moyer L. A., Fields H. A., Bradley D. W. Risk factors for acute non-A, non-B hepatitis in the United States and association with hepatitis C virus infection. JAMA. 1990 Nov 7;264(17):2231–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Detection of a trypsin-like serine protease domain in flaviviruses and pestiviruses. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):637–639. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90639-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Maynard J. E., Popper H., Cook E. H., Ebert J. W., McCaustland K. A., Schable C. A., Fields H. A. Posttransfusion non-A, non-B hepatitis: physicochemical properties of two distinct agents. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):254–265. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruix J., Barrera J. M., Calvet X., Ercilla G., Costa J., Sanchez-Tapias J. M., Ventura M., Vall M., Bruguera M., Bru C. Prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis C virus in Spanish patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic cirrhosis. Lancet. 1989 Oct 28;2(8670):1004–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahour A., Falgout B., Lai C. J. Cleavage of the dengue virus polyprotein at the NS3/NS4A and NS4B/NS5 junctions is mediated by viral protease NS2B-NS3, whereas NS4A/NS4B may be processed by a cellular protease. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1535–1542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1535-1542.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Grakoui A., Rice C. M. Processing of the yellow fever virus nonstructural polyprotein: a catalytically active NS3 proteinase domain and NS2B are required for cleavages at dibasic sites. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6042–6050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6042-6050.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Hahn C. S., Galler R., Rice C. M. Flavivirus genome organization, expression, and replication. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:649–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., McCourt D. W., Rice C. M. Yellow fever virus proteins NS2A, NS2B, and NS4B: identification and partial N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):100–109. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Weir R. C., Grakoui A., McCourt D. W., Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J., Rice C. M. Evidence that the N-terminal domain of nonstructural protein NS3 from yellow fever virus is a serine protease responsible for site-specific cleavages in the viral polyprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8898–8902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. J., Lin M. H., Tai K. F., Liu P. C., Lin C. J., Chen D. S. The Taiwanese hepatitis C virus genome: sequence determination and mapping the 5' termini of viral genomic and antigenomic RNA. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):102–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90739-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba J., Ohba H., Matsuura Y., Watanabe Y., Katayama T., Kikuchi S., Saito I., Miyamura T. Serodiagnosis of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection with an HCV core protein molecularly expressed by a recombinant baculovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4641–4645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Richman K. H., Han J. H., Berger K., Lee C., Dong C., Gallegos C., Coit D., Medina-Selby R., Barr P. J. Genetic organization and diversity of the hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2451–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colett M. S., Larson R., Gold C., Strick D., Anderson D. K., Purchio A. F. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the pestivirus bovine viral diarrhea virus. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90672-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S. Molecular genetics of pestiviruses. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;15(3):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(92)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Wiskerchen M., Welniak E., Belzer S. K. Bovine viral diarrhea virus genomic organization. Arch Virol Suppl. 1991;3:19–27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9153-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M., Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Donato M. F., Del Ninno E., Tommasini M. A., Dioguardi N., Houghton M. Prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis C virus in Italian patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 1989 Oct 28;2(8670):1006–1008. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. L., Balart L. A., Schiff E. R., Lindsay K., Bodenheimer H. C., Jr, Perrillo R. P., Carey W., Jacobson I. M., Payne J., Dienstag J. L. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C with recombinant interferon alfa. A multicenter randomized, controlled trial. Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 30;321(22):1501–1506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911303212203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Bisceglie A. M., Martin P., Kassianides C., Lisker-Melman M., Murray L., Waggoner J., Goodman Z., Banks S. M., Hoofnagle J. H. Recombinant interferon alfa therapy for chronic hepatitis C. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 30;321(22):1506–1510. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911303212204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elroy-Stein O., Fuerst T. R., Moss B. Cap-independent translation of mRNA conferred by encephalomyocarditis virus 5' sequence improves the performance of the vaccinia virus/bacteriophage T7 hybrid expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6126–6130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falgout B., Pethel M., Zhang Y. M., Lai C. J. Both nonstructural proteins NS2B and NS3 are required for the proteolytic processing of dengue virus nonstructural proteins. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2467–2475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2467-2475.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Moss B. Escherichia coli gpt gene provides dominant selection for vaccinia virus open reading frame expression vectors. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1849–1854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1849-1854.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farci P., Alter H. J., Govindarajan S., Wong D. C., Engle R., Lesniewski R. R., Mushahwar I. K., Desai S. M., Miller R. H., Ogata N. Lack of protective immunity against reinfection with hepatitis C virus. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):135–140. doi: 10.1126/science.1279801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Mihalik K. B., Kamimura T., Alter H. J., London W. T., Purcell R. H. Inactivation of hepatitis B virus and non-A, non-B hepatitis by chloroform. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):816–821. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.816-821.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J., Tan B. H., Yap E. H., Chan Y. C., Tan Y. H. Full-length cDNA sequence of dengue type 1 virus (Singapore strain S275/90). Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):953–958. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90560-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Donchenko A. P., Koonin E. V., Blinov V. M. N-terminal domains of putative helicases of flavi- and pestiviruses may be serine proteases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3889–3897. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4713–4730. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grakoui A., Wychowski C., Lin C., Feinstone S. M., Rice C. M. Expression and identification of hepatitis C virus polyprotein cleavage products. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1385–1395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1385-1395.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Hahn Y. S., Braciale T. J., Rice C. M. Infectious Sindbis virus transient expression vectors for studying antigen processing and presentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn Y. S., Galler R., Hunkapiller T., Dalrymple J. M., Strauss J. H., Strauss E. G. Nucleotide sequence of dengue 2 RNA and comparison of the encoded proteins with those of other flaviviruses. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90406-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Watanabe Y., Takeuchi K., Suzuki T., Katayama T., Takebe Y., Saito I., Miyamura T. Expression of processed core protein of hepatitis C virus in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3015–3021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3015-3021.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He L. F., Alling D., Popkin T., Shapiro M., Alter H. J., Purcell R. H. Determining the size of non-A, non-B hepatitis virus by filtration. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):636–640. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijikata M., Kato N., Ootsuyama Y., Nakagawa M., Shimotohno K. Gene mapping of the putative structural region of the hepatitis C virus genome by in vitro processing analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger F. B., Gitnick G. L., Aach R. D., Szmuness W., Mosley J. W., Stevens C. E., Peters R. L., Weiner J. M., Werch J. B., Lander J. J. Non-A, non-B hepatitis transmission in chimpanzees: a project of the transfusion-transmitted viruses study group. Intervirology. 1978;10(1):60–68. doi: 10.1159/000148969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton M., Weiner A., Han J., Kuo G., Choo Q. L. Molecular biology of the hepatitis C viruses: implications for diagnosis, development and control of viral disease. Hepatology. 1991 Aug;14(2):381–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Guarino L. A., Kates J. R. Vaccinia virus replication. I. Requirement for the host-cell nucleus. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):705–715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.705-715.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacono-Connors L. C., Schmaljohn C. S. Cloning and sequence analysis of the genes encoding the nonstructural proteins of Langat virus and comparative analysis with other flaviviruses. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):875–880. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90545-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Zebedee S., Lee D. H., Sugitani M., Nasoff M., Prince A. M. Genomic structure of the human prototype strain H of hepatitis C virus: comparison with American and Japanese isolates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10292–10296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob J. R., Burk K. H., Eichberg J. W., Dreesman G. R., Lanford R. E. Expression of infectious viral particles by primary chimpanzee hepatocytes isolated during the acute phase of non-A, non-B hepatitis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1121–1127. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Hijikata M., Ootsuyama Y., Nakagawa M., Ohkoshi S., Sugimura T., Shimotohno K. Molecular cloning of the human hepatitis C virus genome from Japanese patients with non-A, non-B hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9524–9528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara M., Tsukiyama-Kohara K., Maki N., Asano K., Yamaguchi K., Miki K., Tanaka S., Hattori N., Matsuura Y., Saito I. Expression and characterization of glycoprotein gp35 of hepatitis C virus using recombinant vaccinia virus. J Gen Virol. 1992 Sep;73(Pt 9):2313–2318. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-9-2313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar U., Cheng D., Thomas H., Monjardino J. Cloning and sequencing of the structural region and expression of putative core gene of hepatitis C virus from a British case of chronic sporadic hepatitis. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jun;73(Pt 6):1521–1525. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-6-1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Alter H. J., Gitnick G. L., Redeker A. G., Purcell R. H., Miyamura T., Dienstag J. L., Alter M. J., Stevens C. E. An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):362–364. doi: 10.1126/science.2496467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C., Amberg S. M., Chambers T. J., Rice C. M. Cleavage at a novel site in the NS4A region by the yellow fever virus NS2B-3 proteinase is a prerequisite for processing at the downstream 4A/4B signalase site. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2327–2335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2327-2335.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C., Chambers T. J., Rice C. M. Mutagenesis of conserved residues at the yellow fever virus 3/4A and 4B/5 dibasic cleavage sites: effects on cleavage efficiency and polyprotein processing. Virology. 1993 Feb;192(2):596–604. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L. Vaccinia virus expression vectors. J Gen Virol. 1986 Oct;67(Pt 10):2067–2082. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-10-2067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackow E., Makino Y., Zhao B. T., Zhang Y. M., Markoff L., Buckler-White A., Guiler M., Chanock R., Lai C. J. The nucleotide sequence of dengue type 4 virus: analysis of genes coding for nonstructural proteins. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl C. W., Heinz F. X., Stöckl E., Kunz C. Genome sequence of tick-borne encephalitis virus (Western subtype) and comparative analysis of nonstructural proteins with other flaviviruses. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Harada S., Suzuki R., Watanabe Y., Inoue Y., Saito I., Miyamura T. Expression of processed envelope protein of hepatitis C virus in mammalian and insect cells. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1425–1431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1425-1431.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Rümenapf T., Thiel H. J. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the genome of hog cholera virus. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):555–567. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90625-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Tautz N., Dubovi E. J., Thiel H. J. Viral cytopathogenicity correlated with integration of ubiquitin-coding sequences. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):602–616. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90074-L. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Tautz N., Stark R., Brownlie J., Dubovi E. J., Collett M. S., Thiel H. J. Rearrangement of viral sequences in cytopathogenic pestiviruses. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):368–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90199-Y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis C virus shares amino acid sequence similarity with pestiviruses and flaviviruses as well as members of two plant virus supergroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2057–2061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Elroy-Stein O., Mizukami T., Alexander W. A., Fuerst T. R. Product review. New mammalian expression vectors. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):91–92. doi: 10.1038/348091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak T., Färber P. M., Wengler G., Wengler G. Analyses of the terminal sequences of West Nile virus structural proteins and of the in vitro translation of these proteins allow the proposal of a complete scheme of the proteolytic cleavages involved in their synthesis. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Kurai K., Okada S., Yamamoto K., Lizuka H., Tanaka T., Fukuda S., Tsuda F., Mishiro S. Full-length sequence of a hepatitis C virus genome having poor homology to reported isolates: comparative study of four distinct genotypes. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90762-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Okada S., Sugiyama Y., Kurai K., Iizuka H., Machida A., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of hepatitis C virus isolated from a human carrier: comparison with reported isolates for conserved and divergent regions. J Gen Virol. 1991 Nov;72(Pt 11):2697–2704. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-11-2697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osatomi K., Sumiyoshi H. Complete nucleotide sequence of dengue type 3 virus genome RNA. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):643–647. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90037-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petric M., Yolken R. H., Dubovi E. J., Wiskerchen M., Collett M. S. Baculovirus expression of pestivirus non-structural proteins. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jul;73(Pt 7):1867–1871. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-7-1867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Sauvaget I., Delarue M., Tordo N. Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Lenches E. M., Strauss J. H. Flavivirus enzyme-substrate interactions studied with chimeric proteinases: identification of an intragenic locus important for substrate recognition. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4749–4758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4749-4758.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Strauss J. H. Processing of nonstructural proteins NS4A and NS4B of dengue 2 virus in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):689–697. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90540-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Yao C. W., Strauss J. H. In vitro processing of dengue virus type 2 nonstructural proteins NS2A, NS2B, and NS3. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4364–4374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4364-4374.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Brotman B., Huima T., Pascual D., Jaffery M., Inchauspé G. Immunity in hepatitis C infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):438–443. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Lenches E. M., Eddy S. R., Shin S. J., Sheets R. L., Strauss J. H. Nucleotide sequence of yellow fever virus: implications for flavivirus gene expression and evolution. Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):726–733. doi: 10.1126/science.4023707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Miyamura T., Ohbayashi A., Harada H., Katayama T., Kikuchi S., Watanabe Y., Koi S., Onji M., Ohta Y. Hepatitis C virus infection is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6547–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y. K., Iwamoto A., Hijikata M., Purcell R. H., Yoshikura H. Evidence for in vitro replication of hepatitis C virus genome in a human T-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5477–5481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Alexander D., Rugroden M. E., Choo Q. L., Berger K., Crawford K., Kuo C., Leng S., Lee C., Ralston R. Characterization of the hepatitis C virus E2/NS1 gene product expressed in mammalian cells. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):819–830. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90537-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speight G., Coia G., Parker M. D., Westaway E. G. Gene mapping and positive identification of the non-structural proteins NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4B and NS5 of the flavivirus Kunjin and their cleavage sites. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):23–34. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumiyoshi H., Mori C., Fuke I., Morita K., Kuhara S., Kondou J., Kikuchi Y., Nagamatu H., Igarashi A. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Japanese encephalitis virus genome RNA. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor E., Gerety R. J., Drucker J. A., Seeff L. B., Hoofnagle J. H., Jackson D. R., April M., Barker L. F., Pineda-Tamondong G. Transmission of non-A, non-B hepatitis from man to chimpanzee. Lancet. 1978 Mar 4;1(8062):463–466. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamizawa A., Mori C., Fuke I., Manabe S., Murakami S., Fujita J., Onishi E., Andoh T., Yoshida I., Okayama H. Structure and organization of the hepatitis C virus genome isolated from human carriers. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1105–1113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1105-1113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Kato N., Nakagawa M., Ootsuyama Y., Cho M. J., Nakazawa T., Hijikata M., Ishimura Y., Shimotohno K. Molecular cloning of hepatitis C virus genome from a single Japanese carrier: sequence variation within the same individual and among infected individuals. Virus Res. 1992 Apr;23(1-2):39–53. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90066-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel H. J., Stark R., Weiland E., Rümenapf T., Meyers G. Hog cholera virus: molecular composition of virions from a pestivirus. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4705–4712. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4705-4712.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. J., Kuo G., Bradley D. W., Bonino F., Saracco G., Lee C., Rosenblatt J., Choo Q. L., Houghton M. Detection of hepatitis C viral sequences in non-A, non-B hepatitis. Lancet. 1990 Jan 6;335(8680):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90134-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Czaya G., Färber P. M., Hegemann J. H. In vitro synthesis of West Nile virus proteins indicates that the amino-terminal segment of the NS3 protein contains the active centre of the protease which cleaves the viral polyprotein after multiple basic amino acids. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):851–858. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. The carboxy-terminal part of the NS 3 protein of the West Nile flavivirus can be isolated as a soluble protein after proteolytic cleavage and represents an RNA-stimulated NTPase. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):707–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90440-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskerchen M., Belzer S. K., Collett M. S. Pestivirus gene expression: the first protein product of the bovine viral diarrhea virus large open reading frame, p20, possesses proteolytic activity. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4508–4514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4508-4514.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskerchen M., Collett M. S. Pestivirus gene expression: protein p80 of bovine viral diarrhea virus is a proteinase involved in polyprotein processing. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90850-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]