Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection is associated with elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of infected persons, but the sources of these proteins as well as the specific stimuli which trigger their production and release have not been fully defined. In this study, we evaluated the ability of HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) clones derived from seropositive persons to release gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and TNF-beta upon contact with target cells presenting viral antigen. Peripheral blood- and cerebrospinal fluid-derived HIV-1-specific CD3+ CD4- CD8+ CTL clones as well as freshly isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from infected persons were tested in parallel for HIV-1-specific cytotoxicity and cytokine release. Target cells consisted of autologous and allogeneic B-lymphoblastoid cell lines sensitized with synthetic HIV-1 peptides containing the epitopes recognized by these CTL. Cytokine production was measured by specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of culture supernatant fluid. HIV-1-specific CTL clones directed at envelope, Gag, reverse transcriptase, and Nef epitopes specifically released IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, and TNF-beta upon contact with their relevant target epitopes but not following contact with irrelevant epitopes. These cytokines were released in an HLA class I-restricted fashion, and release was detectable as early as 4 to 6 h of incubation and remained elevated at 48 h. Fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells from a seropositive person likewise released IFN-gamma in an antigen-specific and HLA class I-restricted manner when incubated with target cells presenting a peptide containing a CTL epitope, paralleling the HIV-specific cytolytic activity of these cells. These studies indicate that in addition to mediating direct cytotoxicity, HIV-1-specific CTL may affect other immune responses by releasing IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, and TNF-beta. Elevated levels of these cytokines which have been detected in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of infected persons may be due at least in part to the persistent HIV-1-specific CTL response.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolf G. R., Lamche H. R. Highly sensitive enzyme immunoassay for human lymphotoxin (tumor necrosis factor beta) in serum. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Jul 3;130(2):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson U., Adolf G., Dohlsten M., Möller G., Sjögren H. O. Characterization of individual tumor necrosis factor alpha-and beta-producing cells after polyclonal T cell activation. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Oct 24;123(2):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas P., Poli G., Kinter A. L., Justement J. S., Stanley S. K., Maury W. J., Bressler P., Orenstein J. M., Fauci A. S. Interferon gamma induces the expression of human immunodeficiency virus in persistently infected promonocytic cells (U1) and redirects the production of virions to intracytoplasmic vacuoles in phorbol myristate acetate-differentiated U1 cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):739–750. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew B. J., Bhalla R. B., Paul M., Gallardo H., McArthur J. C., Schwartz M. K., Price R. W. Cerebrospinal fluid neopterin in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Ann Neurol. 1990 Oct;28(4):556–560. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew B. J., Bhalla R. B., Paul M., Sidtis J. J., Keilp J. J., Sadler A. E., Gallardo H., McArthur J. C., Schwartz M. K., Price R. W. Cerebrospinal fluid beta 2-microglobulin in patients with AIDS dementia complex: an expanded series including response to zidovudine treatment. AIDS. 1992 May;6(5):461–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emilie D., Peuchmaur M., Maillot M. C., Crevon M. C., Brousse N., Delfraissy J. F., Dormont J., Galanaud P. Production of interleukins in human immunodeficiency virus-1-replicating lymph nodes. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):148–159. doi: 10.1172/JCI114678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. A., Mosmann T. R. Alloreactive murine CD8+ T cell clones secrete the Th1 pattern of cytokines. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1744–1752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Siepl C., Groscurth P., Bodmer S., Schwerdel C., Fontana A. Antigen presentation and tumor cytotoxicity by interferon-gamma-treated microglial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1271–1278. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs D., Chiodi F., Albert J., Asjö B., Hagberg L., Hausen A., Norkrans G., Reibnegger G., Werner E. R., Wachter H. Neopterin concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of individuals infected with HIV-1. AIDS. 1989 May;3(5):285–288. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198905000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs D., Hausen A., Reibnegger G., Werner E. R., Dierich M. P., Wachter H. Neopterin as a marker for activated cell-mediated immunity: application in HIV infection. Immunol Today. 1988 May;9(5):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., McArthur J. C., Cornblath D. R. Neopterin and interferon-gamma in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HIV-associated neurologic disease. Neurology. 1991 Jan;41(1):69–74. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulevich S. J., Wiley C. A. HIV infection and the brain. AIDS. 1991;5 (Suppl 2):S49–S54. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199101001-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadida F., Parrot A., Kieny M. P., Sadat-Sowti B., Mayaud C., Debre P., Autran B. Carboxyl-terminal and central regions of human immunodeficiency virus-1 NEF recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes from lymphoid organs. An in vitro limiting dilution analysis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):53–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI115585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrer T., Messing K., Bienzle U., Meyer E., Giedl J., Kalden J. R. Verlaufsbeobachtungen bei HIV-infizierten homosexuellen Männern mit Lymphadenopathiesyndrom. Klin Wochenschr. 1987 Sep 15;65(18):864–872. doi: 10.1007/BF01737007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorn K. L., Neumeyer D., Vogt M. W., Schooley R. T., Hirsch M. S. Activity of interferons alpha, beta, and gamma against human immunodeficiency virus replication in vitro. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Summer;3(2):125–133. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyes M. P., Brew B. J., Martin A., Price R. W., Salazar A. M., Sidtis J. J., Yergey J. A., Mouradian M. M., Sadler A. E., Keilp J. Quinolinic acid in cerebrospinal fluid and serum in HIV-1 infection: relationship to clinical and neurological status. Ann Neurol. 1991 Feb;29(2):202–209. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
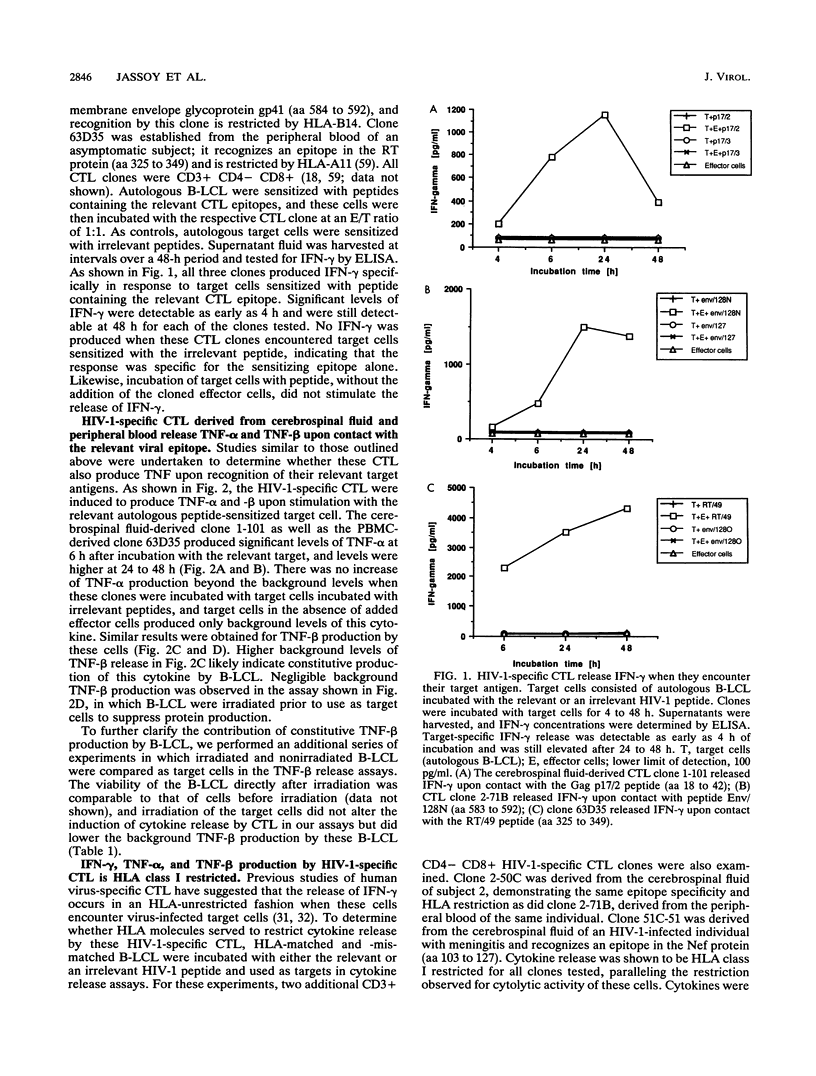
- Jassoy C., Johnson R. P., Navia B. A., Worth J., Walker B. D. Detection of a vigorous HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte response in cerebrospinal fluid from infected persons with AIDS dementia complex. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):3113–3119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochems G. J., Klein M. R., Jordens R., Pascual-Salcedo D., van Boxtel-Oosterhof F., van Lier R. A., Zeijlemaker W. P. Heterogeneity in both cytokine production and responsiveness of a panel of monoclonal human Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B-cell lines. Hum Antibodies Hybridomas. 1991 Apr;2(2):57–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. P., Trocha A., Buchanan T. M., Walker B. D. Identification of overlapping HLA class I-restricted cytotoxic T cell epitopes in a conserved region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein: definition of minimum epitopes and analysis of the effects of sequence variation. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):961–971. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. P., Trocha A., Yang L., Mazzara G. P., Panicali D. L., Buchanan T. M., Walker B. D. HIV-1 gag-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize multiple highly conserved epitopes. Fine specificity of the gag-specific response defined by using unstimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells and cloned effector cells. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1512–1521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly E., Mucke L., Oldstone M. B. Viral persistence in neurons explained by lack of major histocompatibility class I expression. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1283–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.1891717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. R., Pasternack M. S., Bevan M. J. Activation requirements for antigen- and mitogen-induced interferon-gamma release from cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2456–2461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
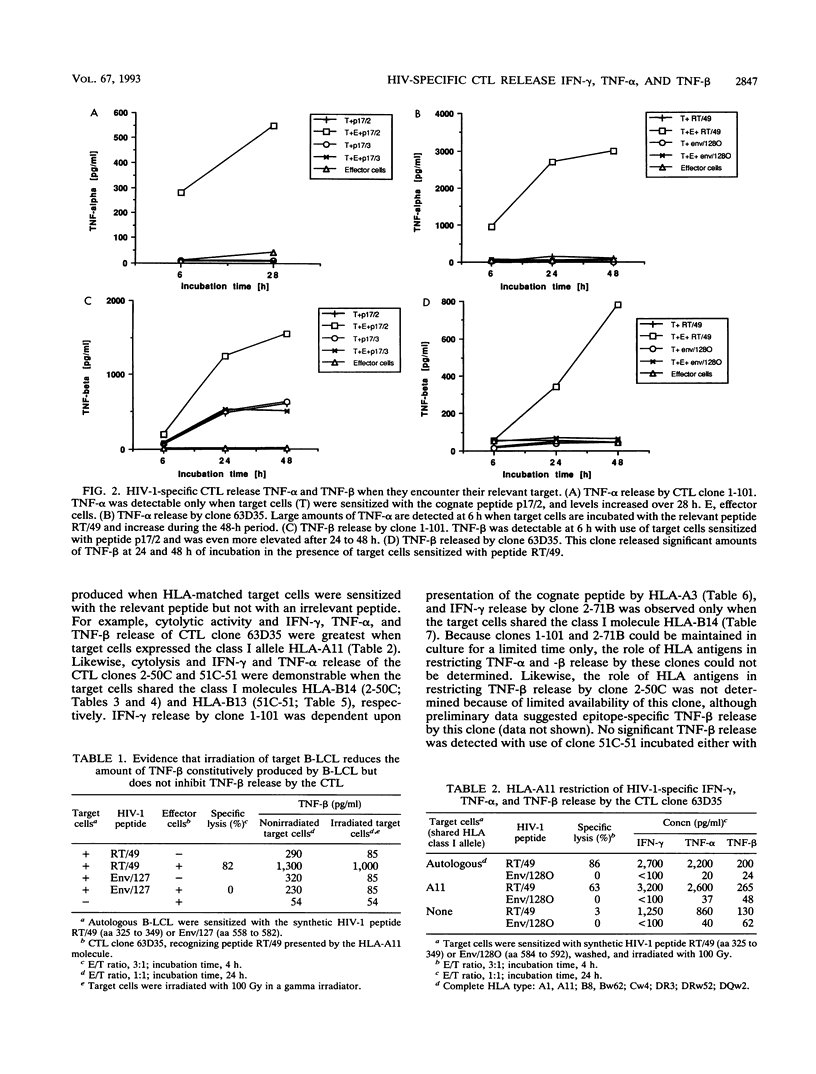
- Klein J. R., Raulet D. H., Pasternack M. S., Bevan M. J. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes produce immune interferon in response to antigen or mitogen. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1198–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Hamamoto Y., Kobayashi N., Yamamoto N. Serum level of TNF alpha in HIV-infected individuals. AIDS. 1990 Feb;4(2):169–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koup R. A., Sullivan J. L., Levine P. H., Brettler D., Mahr A., Mazzara G., McKenzie S., Panicali D. Detection of major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted, HIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the blood of infected hemophiliacs. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1909–1914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littaua R. A., Oldstone M. B., Takeda A., Ennis F. A. A CD4+ cytotoxic T-lymphocyte clone to a conserved epitope on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 p24: cytotoxic activity and secretion of interleukin-2 and interleukin-6. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):608–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.608-611.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Miskovsky E. P., Stanhope P. E., Siliciano R. F. Production of transmembrane and secreted forms of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha by HIV-1-specific CD4+ cytolytic T lymphocyte clones. Evidence for a TNF-alpha-independent cytolytic mechanism. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3789–3798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
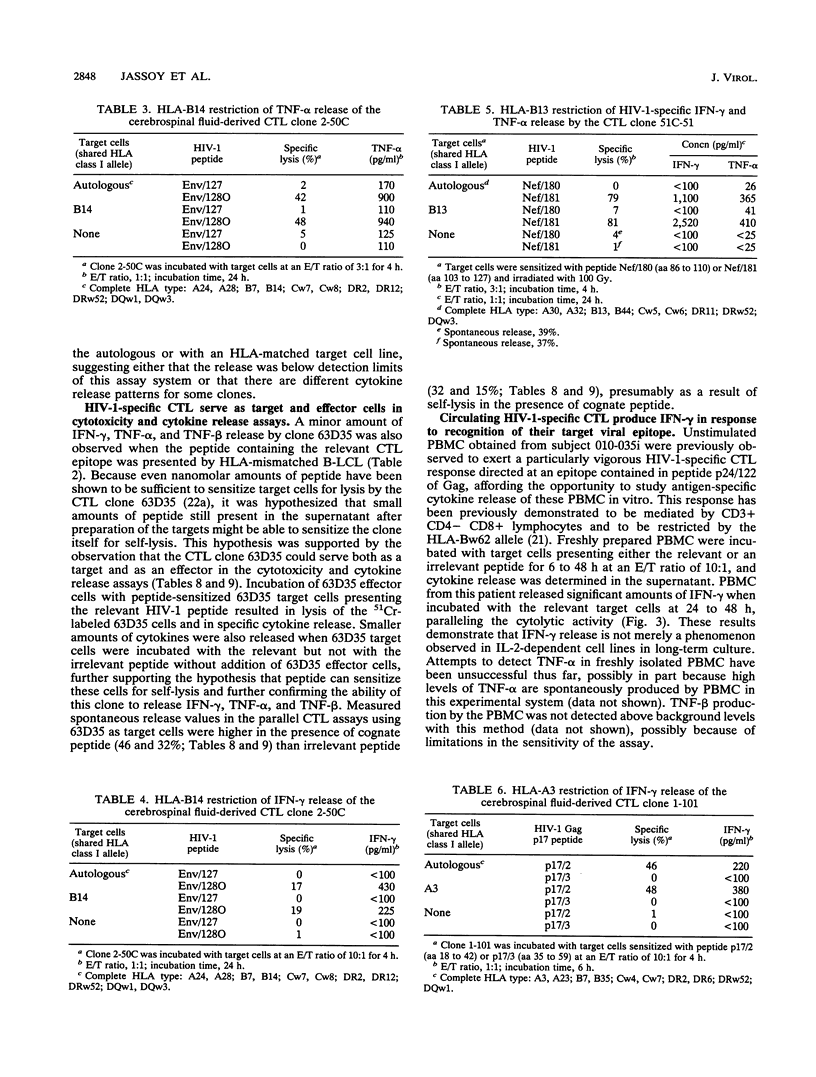
- Lucey D. R., Nunley M., Boswell R. N., Koopman T. L., Hensley R. E., Ward W. W. HLA-DR+ CD8+ T cells in the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with AIDS dementia complex and 355-494/mm3 CD4+ peripheral blood T cells. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(6):638–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier K., Gabriel P., Koscielniak E., Stierhof Y. D., Wiedmann K. H., Flehmig B., Vallbracht A. Human gamma interferon production by cytotoxic T lymphocytes sensitized during hepatitis A virus infection. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3756–3763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3756-3763.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Vallbracht A., Kreth H. W. Interferon-gamma secretion by in vivo activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes from the blood and cerebrospinal fluid during mumps meningitis. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Sep;33(3):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90106-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Kobayashi N., Yamamoto N. Cytokines and HIV infection: is AIDS a tumor necrosis factor disease? AIDS. 1991 Dec;5(12):1405–1417. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199112000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Mottram P. L., Thomas W. R., Miller J. F. Antigen-specific production of immune interferon by T Cells lines. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1204–1209. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. G., Lin Y. L., Askonas B. A. Immune interferon release when a cloned cytotoxic T-cell line meets its correct influenza-infected target cell. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):150–152. doi: 10.1038/295150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Burrows S. R., Baxter G. D., Lavin M. F. T cell-T cell killing is induced by specific epitopes: evidence for an apoptotic mechanism. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):681–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Petito C. K., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):525–535. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon D. F., McMichael A. J. Cytotoxic T-cell recognition of HIV proteins and peptides. AIDS. 1991 Sep;5(9):1049–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon D. F., Townsend A. R., Elvin J. G., Rizza C. R., Gallwey J., McMichael A. J. HIV-1 gag-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes defined with recombinant vaccinia virus and synthetic peptides. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):484–487. doi: 10.1038/336484a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Bevan M. J., Klein J. R. Release of discrete interferons by cytotoxic T lymphocytes in response to immune and nonimmune stimuli. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):277–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata F., Autran B., Martins L. P., Wain-Hobson S., Raphaël M., Mayaud C., Denis M., Guillon J. M., Debré P. AIDS virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in lung disorders. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):348–351. doi: 10.1038/328348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Armstrong J. A., Kingsley L. A., Zhou S., Ho M. Relation of alpha and gamma interferon levels to development of AIDS in homosexual men. J Exp Pathol. 1990;5(3):127–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salgame P., Abrams J. S., Clayberger C., Goldstein H., Convit J., Modlin R. L., Bloom B. R. Differing lymphokine profiles of functional subsets of human CD4 and CD8 T cell clones. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K. W., Farooq M., Norton W. T., Raine C. S., Brosnan C. F. Proliferation of astrocytes in vitro in response to cytokines. A primary role for tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K. W., Raine C. S. Tumor necrosis factor mediates myelin and oligodendrocyte damage in vitro. Ann Neurol. 1988 Apr;23(4):339–346. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethna M. P., Lampson L. A. Immune modulation within the brain: recruitment of inflammatory cells and increased major histocompatibility antigen expression following intracerebral injection of interferon-gamma. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Nov;34(2-3):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90121-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Street N. E., Mosmann T. R. Functional diversity of T lymphocytes due to secretion of different cytokine patterns. FASEB J. 1991 Feb;5(2):171–177. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.2.1825981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönnerborg A. B., von Stedingk L. V., Hansson L. O., Strannegård O. O. Elevated neopterin and beta 2-microglobulin levels in blood and cerebrospinal fluid occur early in HIV-1 infection. AIDS. 1989 May;3(5):277–283. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198905000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyor W. R., Glass J. D., Griffin J. W., Becker P. S., McArthur J. C., Bezman L., Griffin D. E. Cytokine expression in the brain during the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1992 Apr;31(4):349–360. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidovic M., Sparacio S. M., Elovitz M., Benveniste E. N. Induction and regulation of class II major histocompatibility complex mRNA expression in astrocytes by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Dec;30(2-3):189–200. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90103-T. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden P. R., Eisen H. N. Cognate peptides induce self-destruction of CD8+ cytolytic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9015–9019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. D., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Paradis T. J., Flynn T., Durno A. G., Blumberg R. S., Kaplan J. C., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T. HIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in seropositive individuals. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):345–348. doi: 10.1038/328345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. D., Flexner C., Birch-Limberger K., Fisher L., Paradis T. J., Aldovini A., Young R., Moss B., Schooley R. T. Long-term culture and fine specificity of human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte clones reactive with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9514–9518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. D., Flexner C., Paradis T. J., Fuller T. C., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Moss B. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase is a target for cytotoxic T lymphocytes in infected individuals. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.2451288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. D., Plata F. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes against HIV. AIDS. 1990 Mar;4(3):177–184. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199003000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner E. R., Bitterlich G., Fuchs D., Hausen A., Reibnegger G., Szabo G., Dierich M. P., Wachter H. Human macrophages degrade tryptophan upon induction by interferon-gamma. Life Sci. 1987 Jul 20;41(3):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte S. M., Ho D. D., Schooley R. T., Hirsch M. S., Richardson E. P., Jr Subacute encephalomyelitis of AIDS and its relation to HTLV-III infection. Neurology. 1987 Apr;37(4):562–569. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



